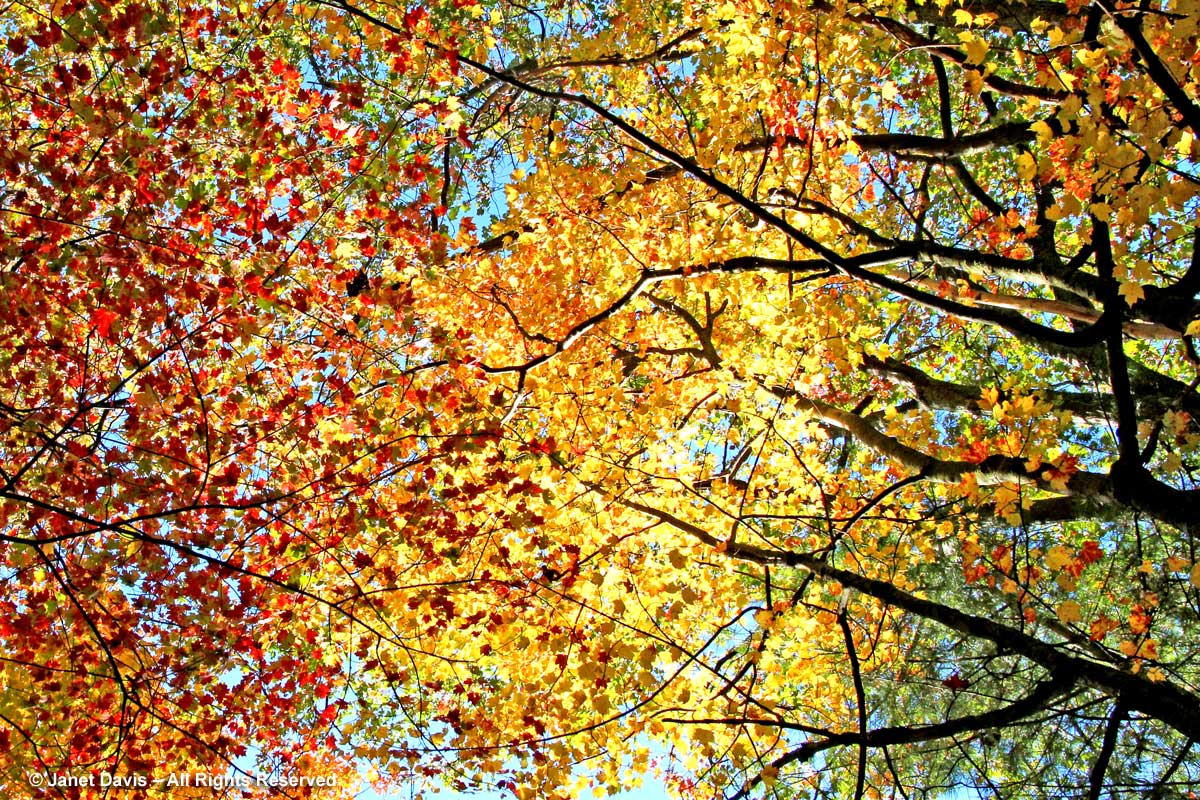
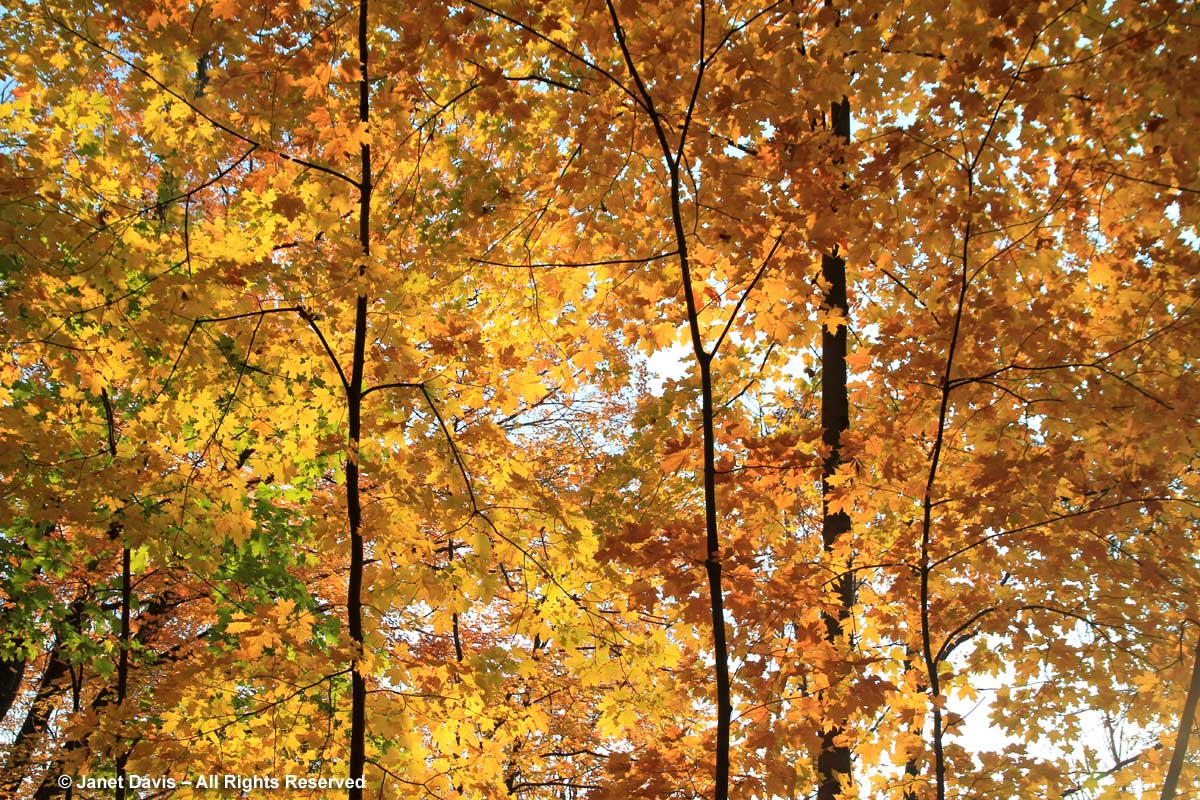
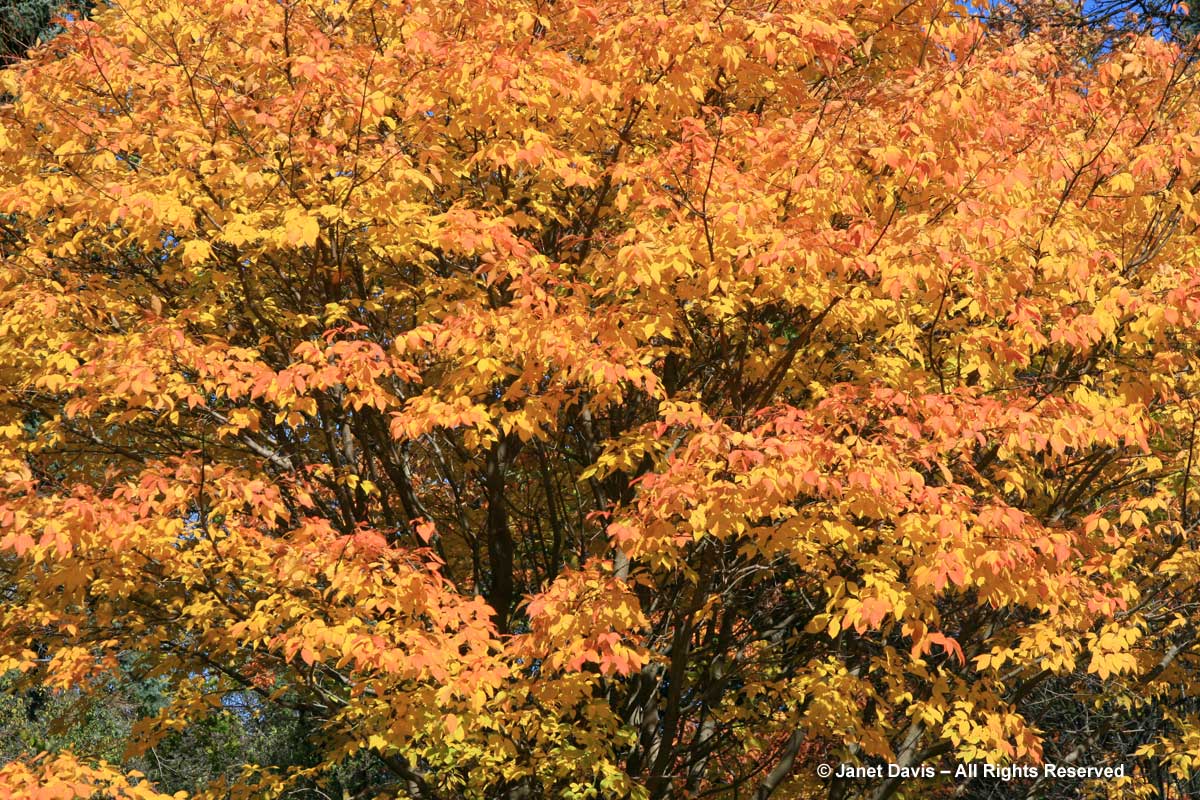
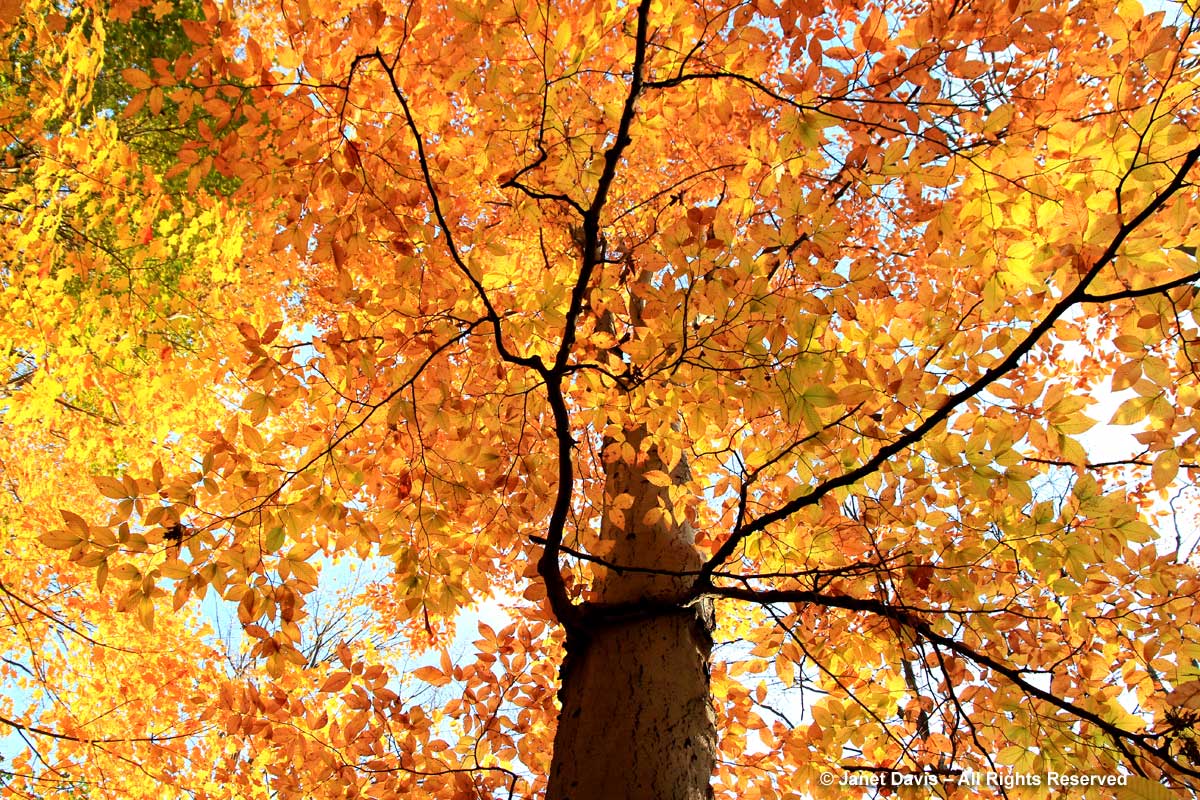
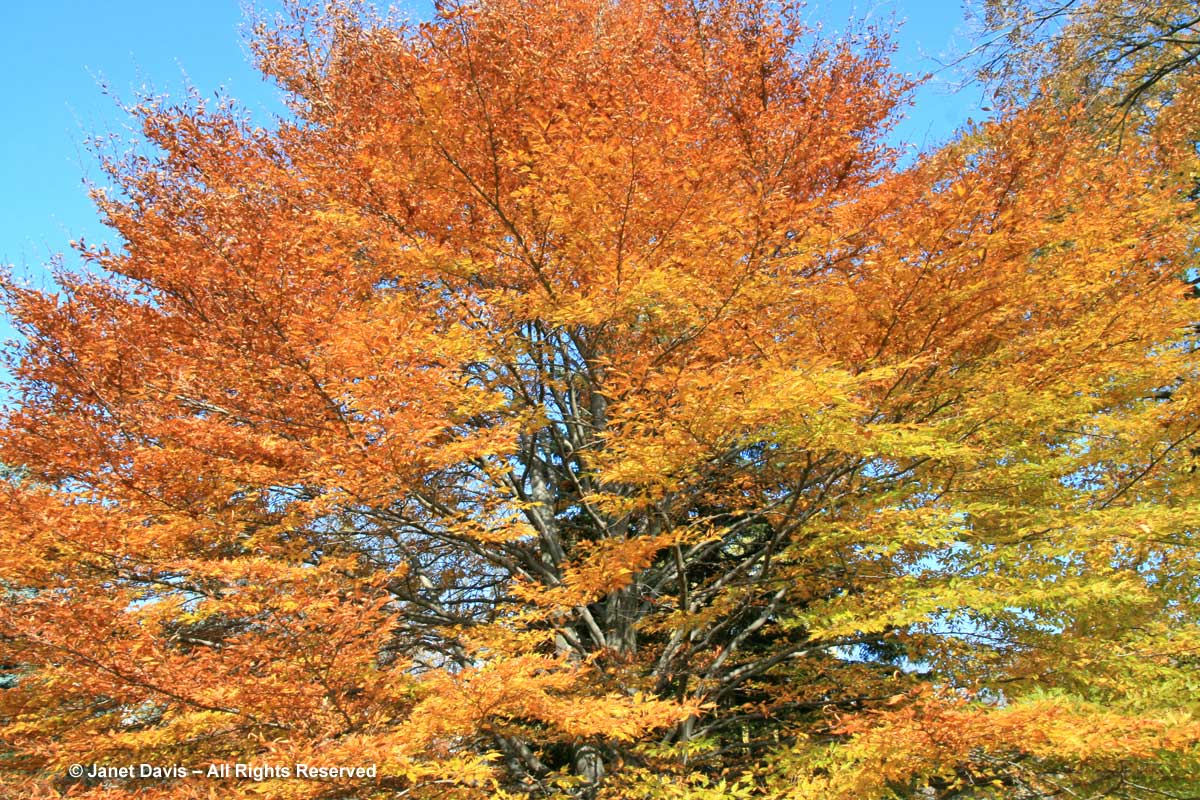
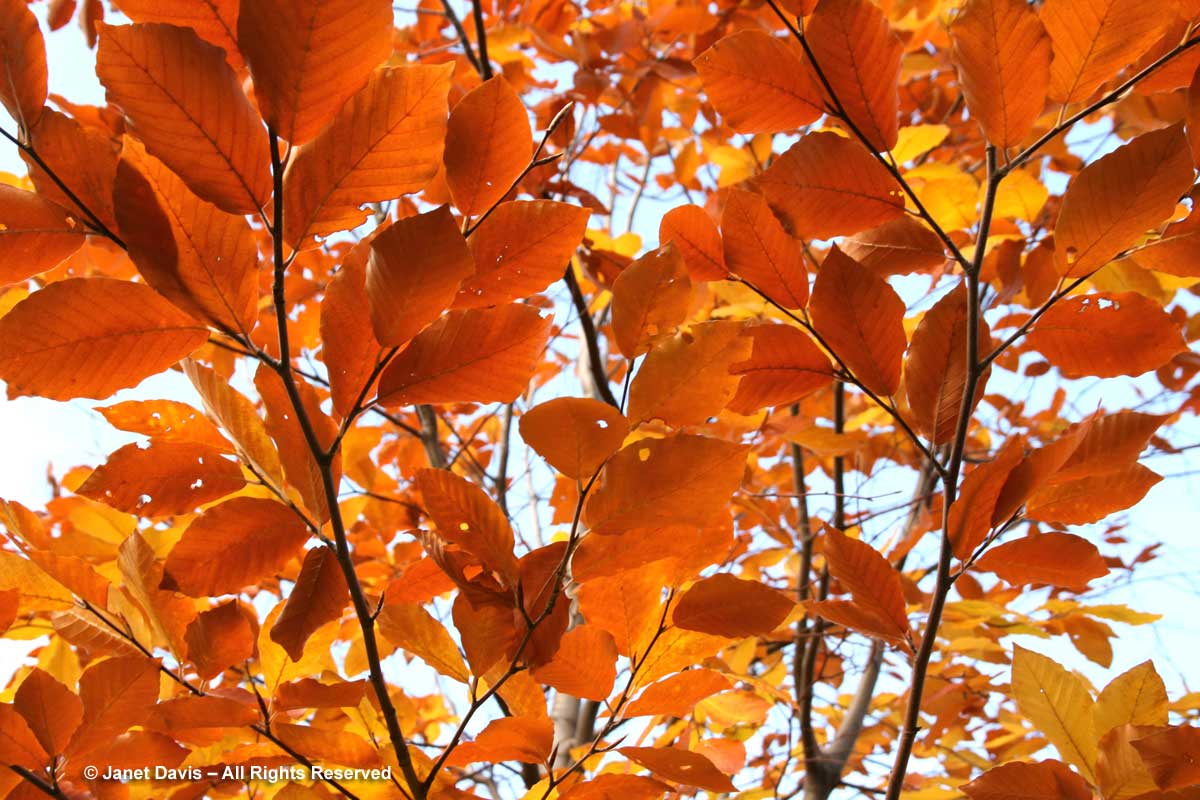
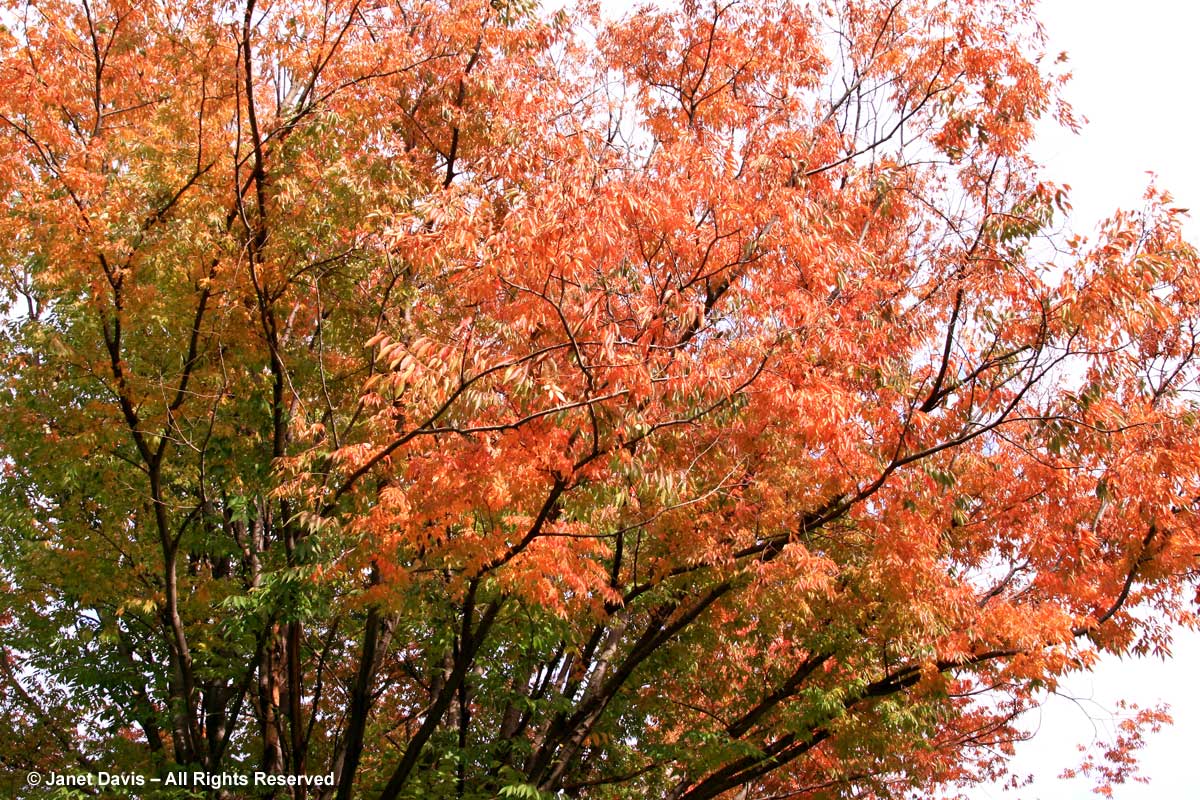
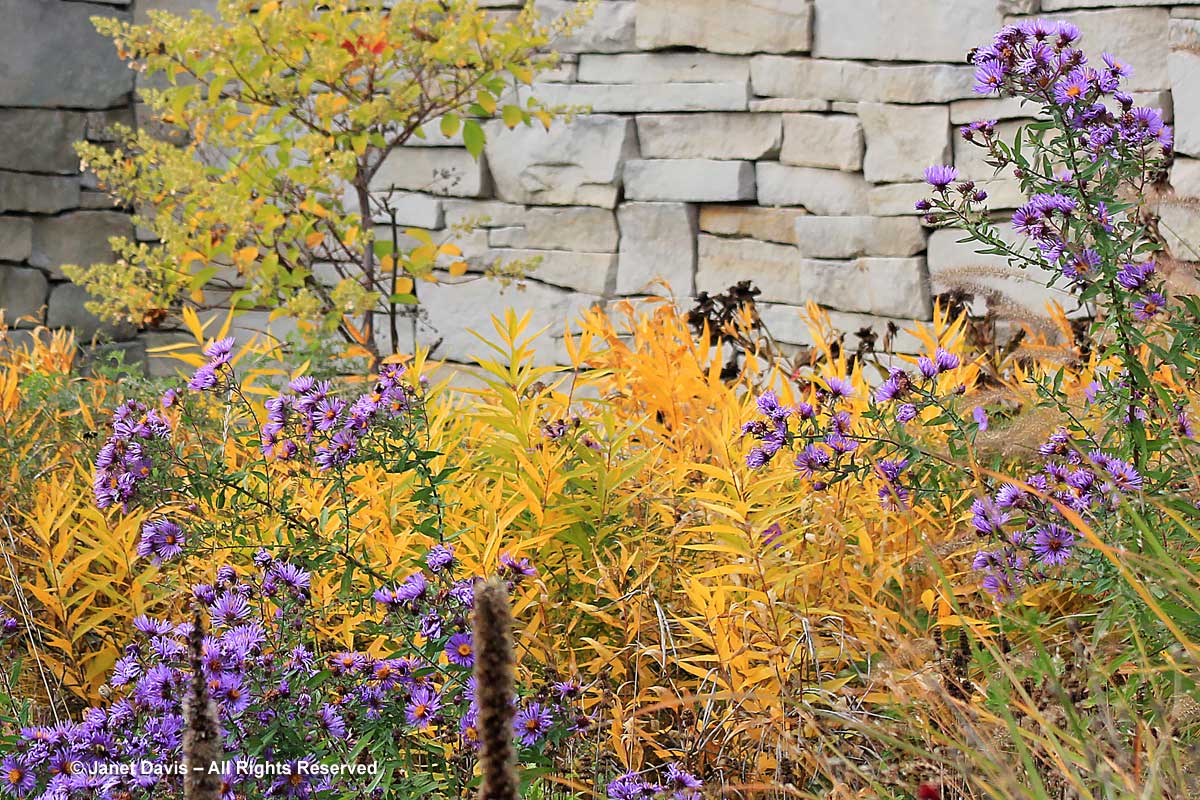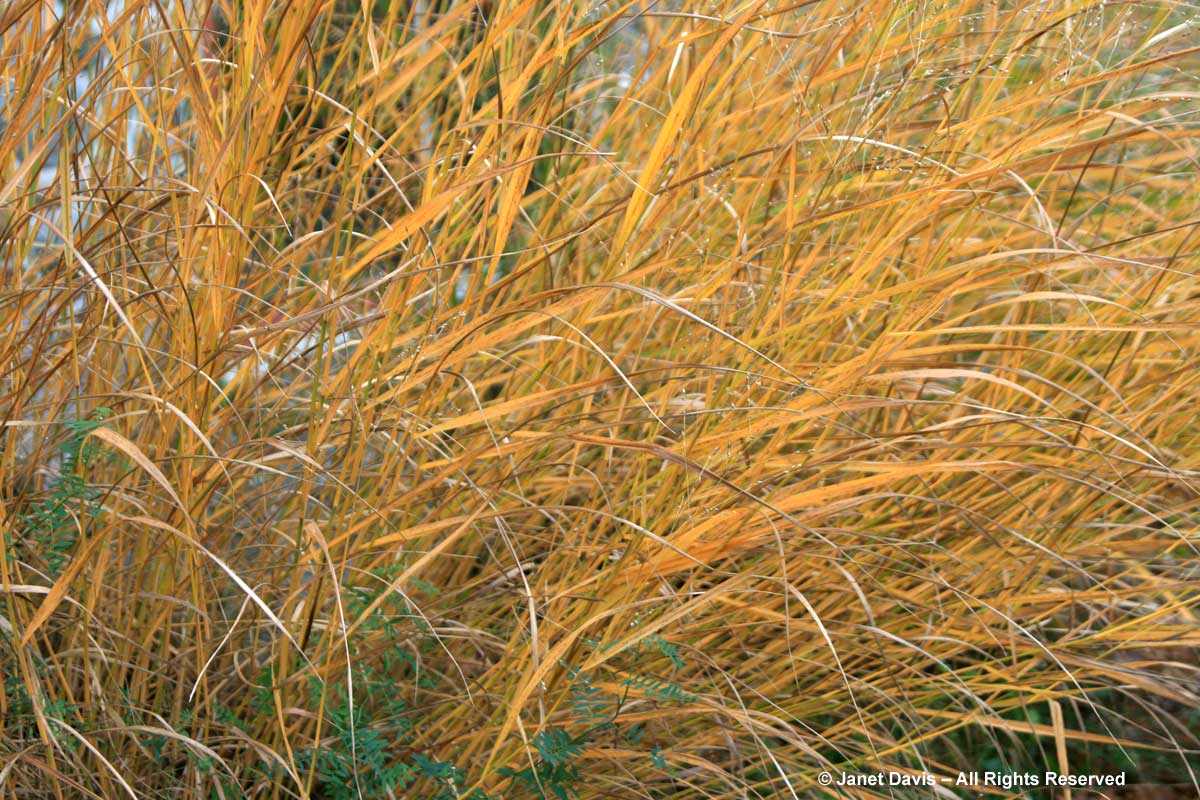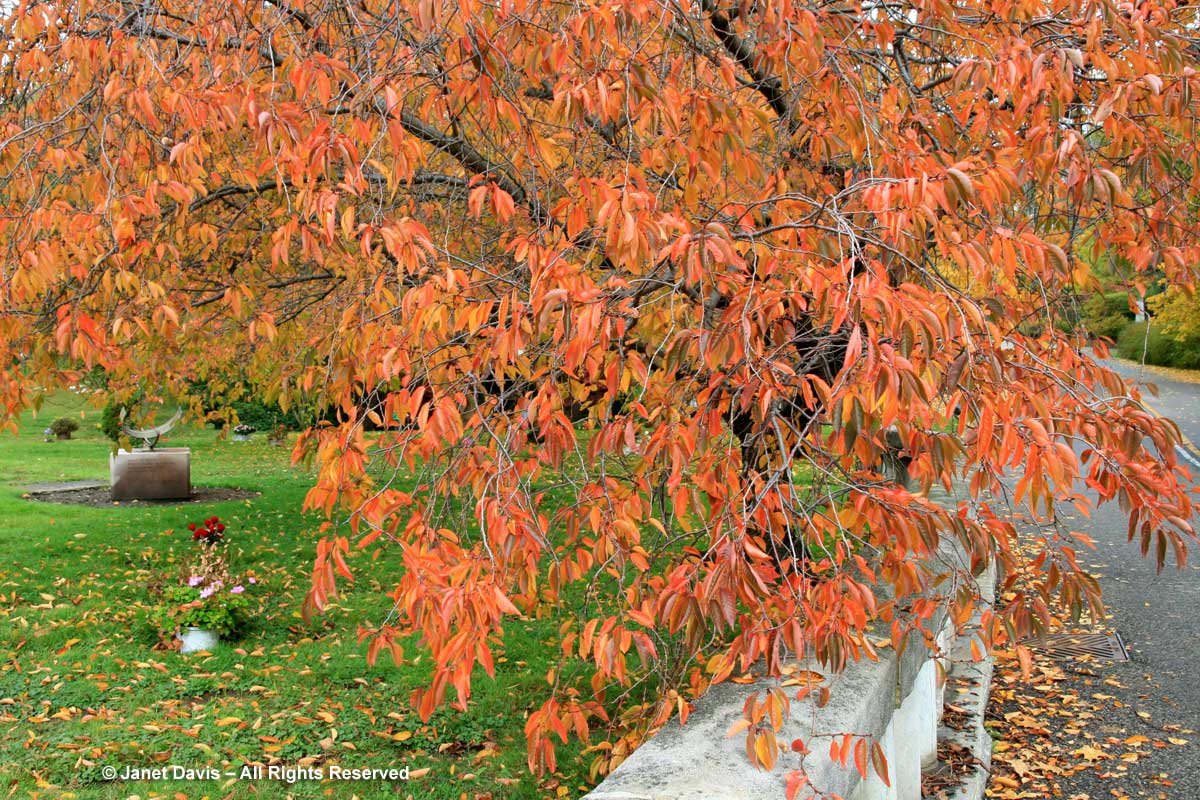This is a fact: red & orange fall colours would not be nearly so thrilling without the beautiful contrast of neighbouring yellows and golds.
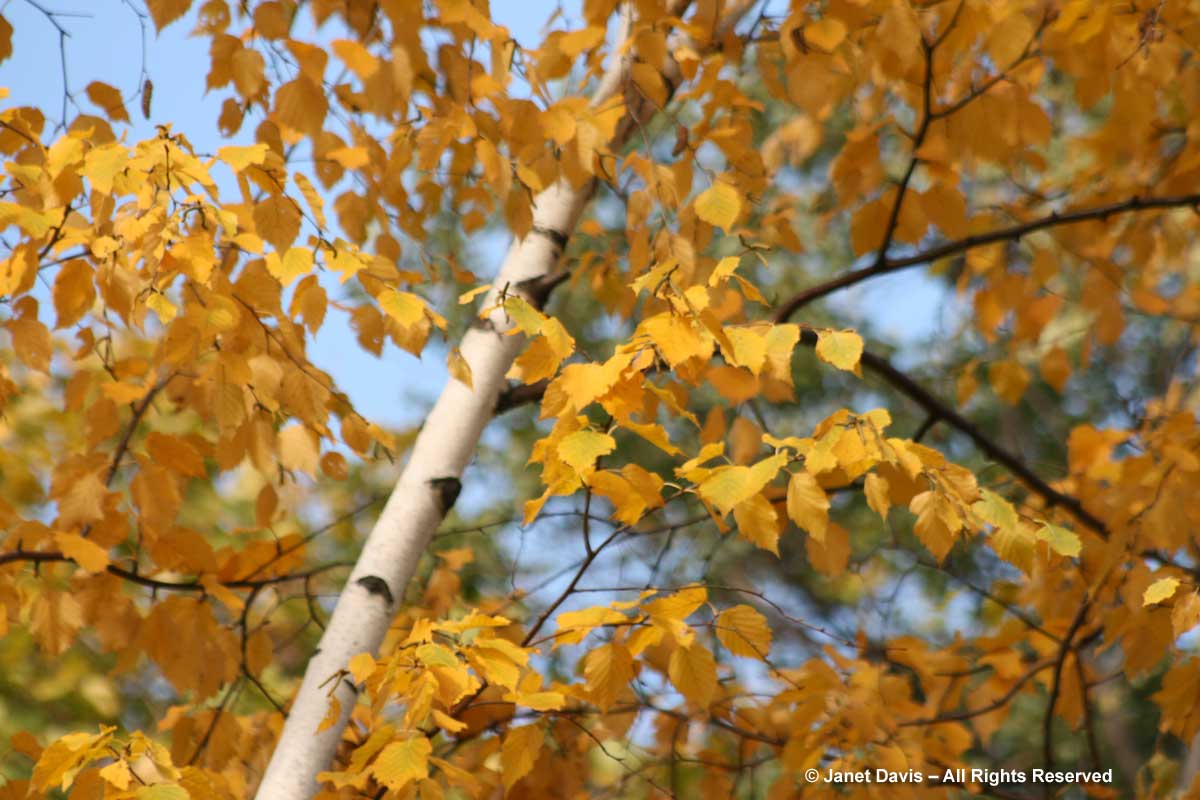
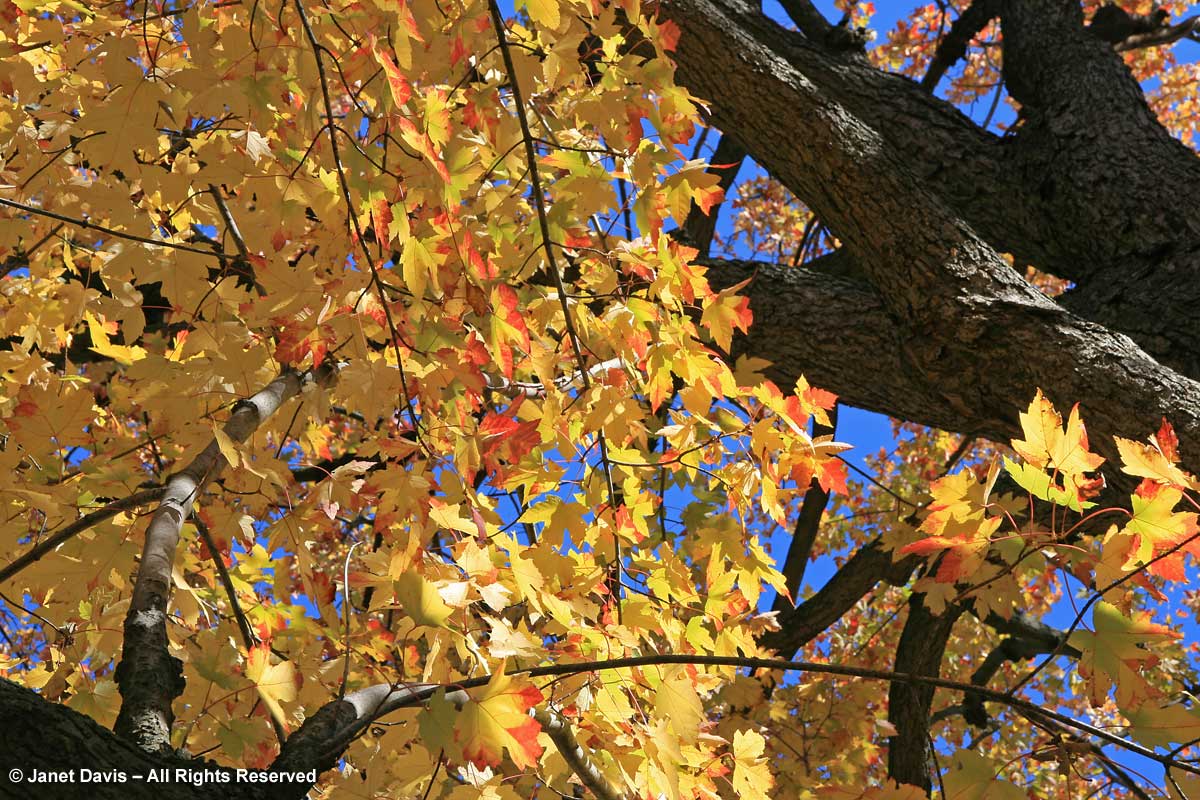
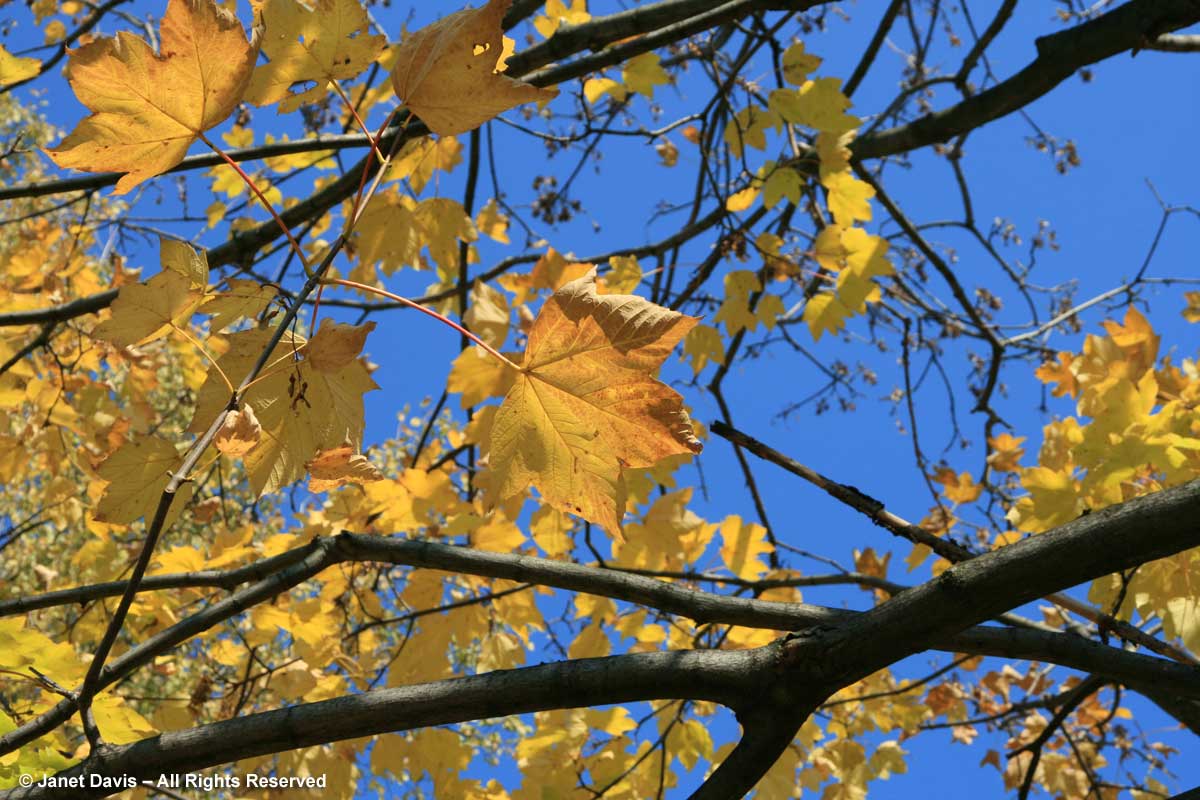
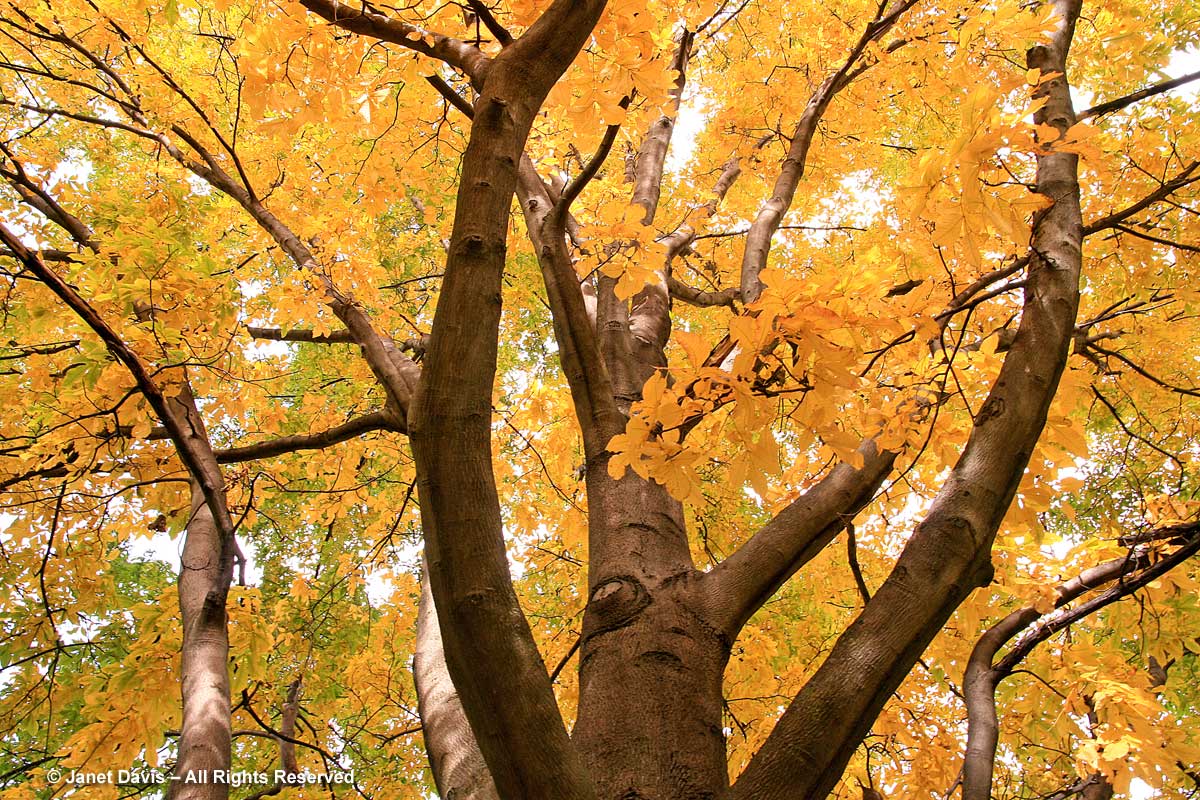
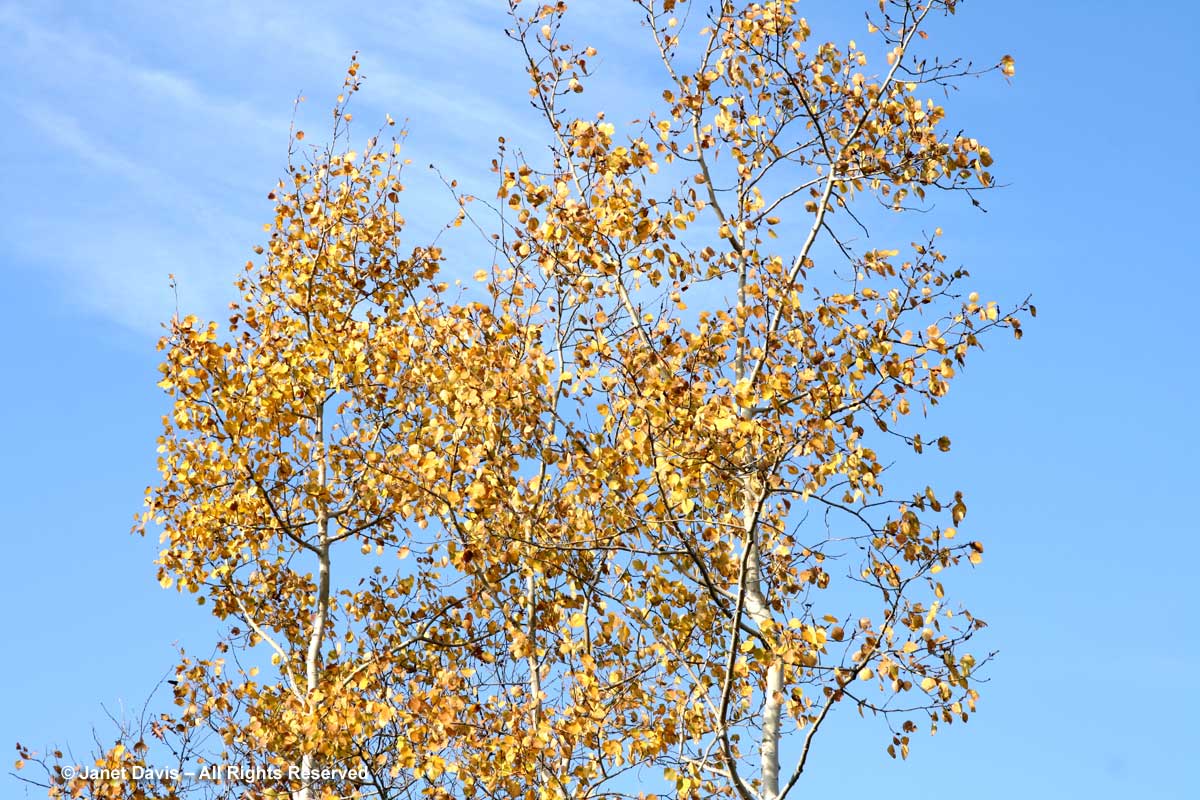
If you’ve followed along as I offered up some lovely trees, shrubs and perennials whose leaves turn red in autumn, and a second group whose foliage turns glorious shades of orange, apricot and bronze, I’m sure you’re waiting with bated breath for the final installment. No? Well, anyway, those would be the many species that turn yellow and gold. As we know, autumn colours result from the breakdown of chlorophyll (the ‘green’ pigment) as temperatures cool and days shorten in late summer and early fall. Yellow leaves owe their brilliance to the presence of a group of orange-yellow pigments called the carotenoids, and within that group, the yellow xanthophylls (the other group being the orange carotenes on display in my last post). Not only are xanthophylls found underlying the chlorophyll in leaves, where they absorb sunlight in a specific spectral range, they are also responsible for the petal colour of yellow flowers – all those “damned yellow composites” (DYCs), i.e. daisies like coreopis, heliopsis and silphium, among hundreds of others. Even the yellow in egg yolks comes from a xanthophyll called lutein in the hen’s diet. And, of course, xanthophylls give us the brilliant autumn yellow of trees like our beloved North American paper birch (Betula papyrifera), its pure-white bark and golden leaves resplendent against a bright-blue October sky.
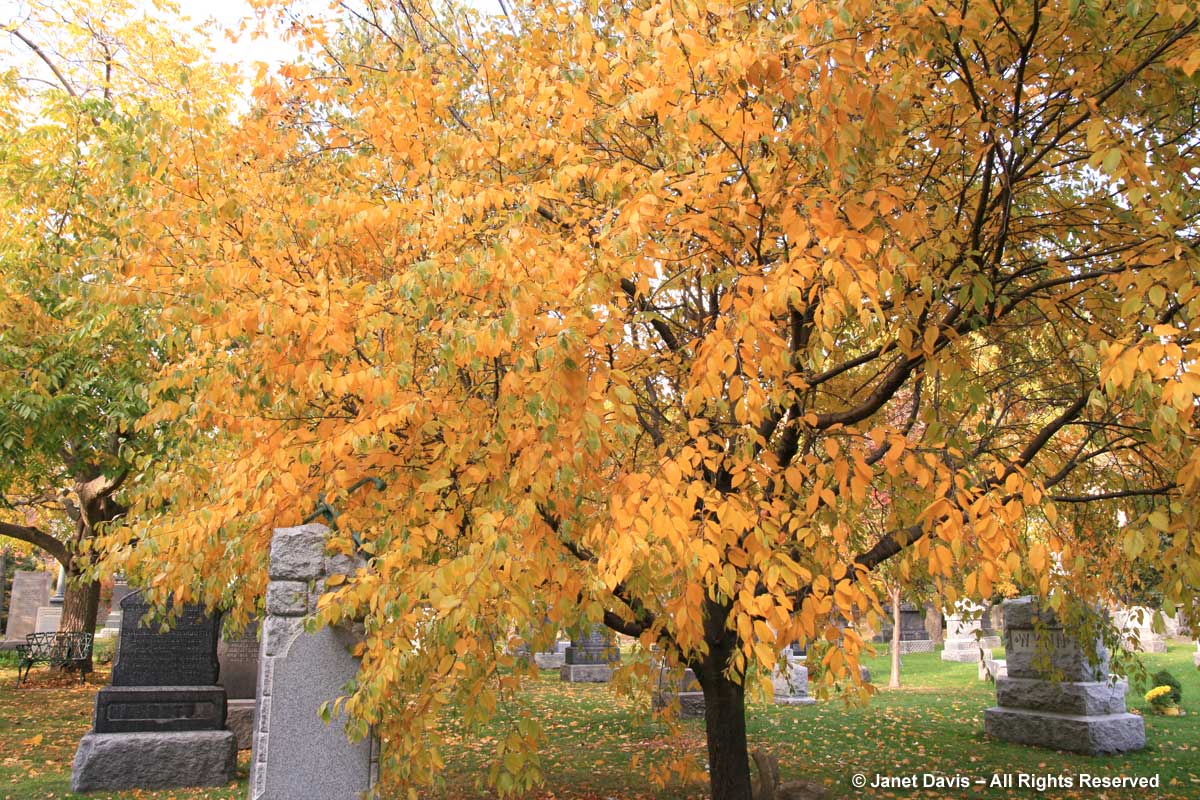
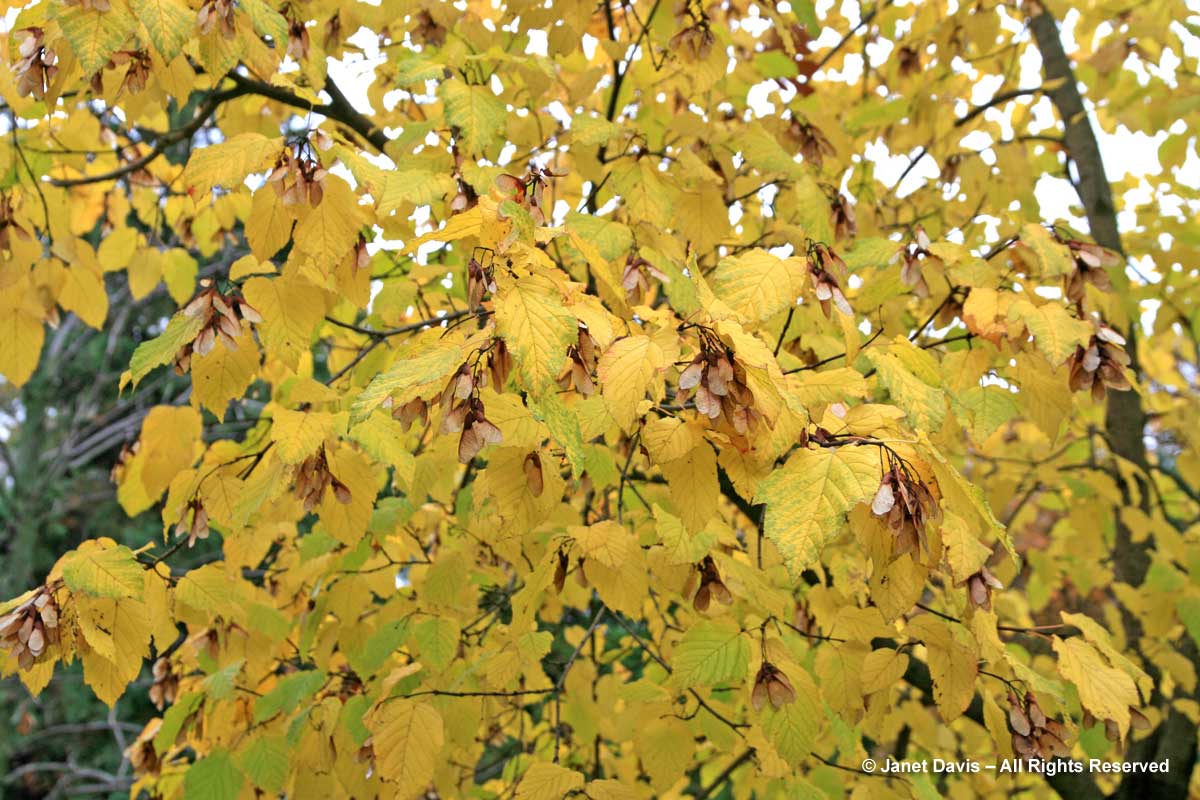
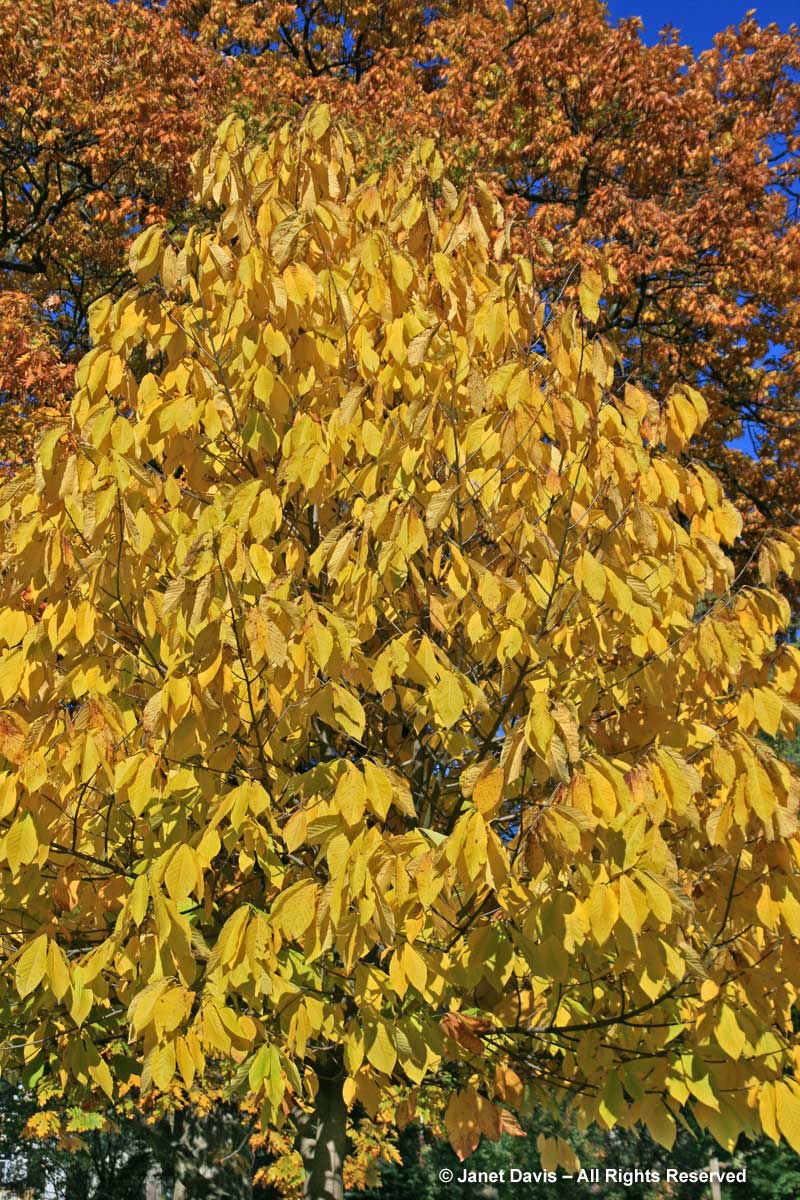
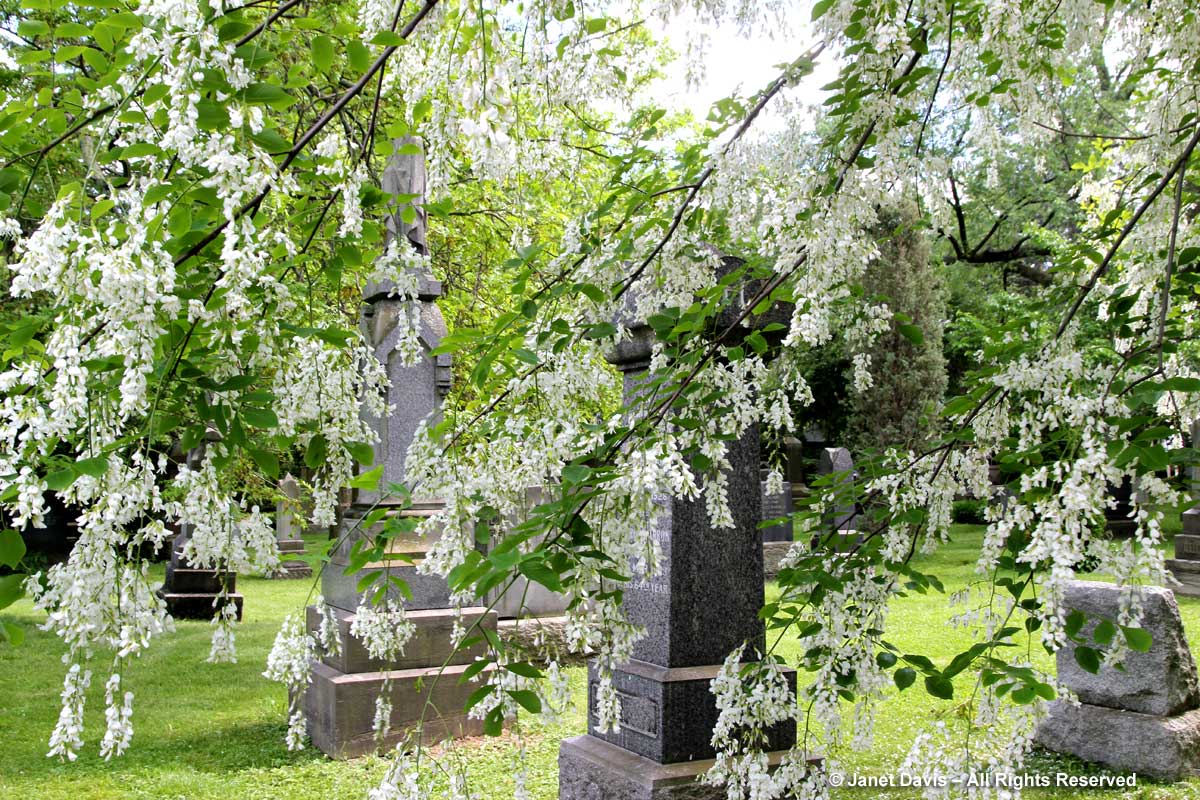
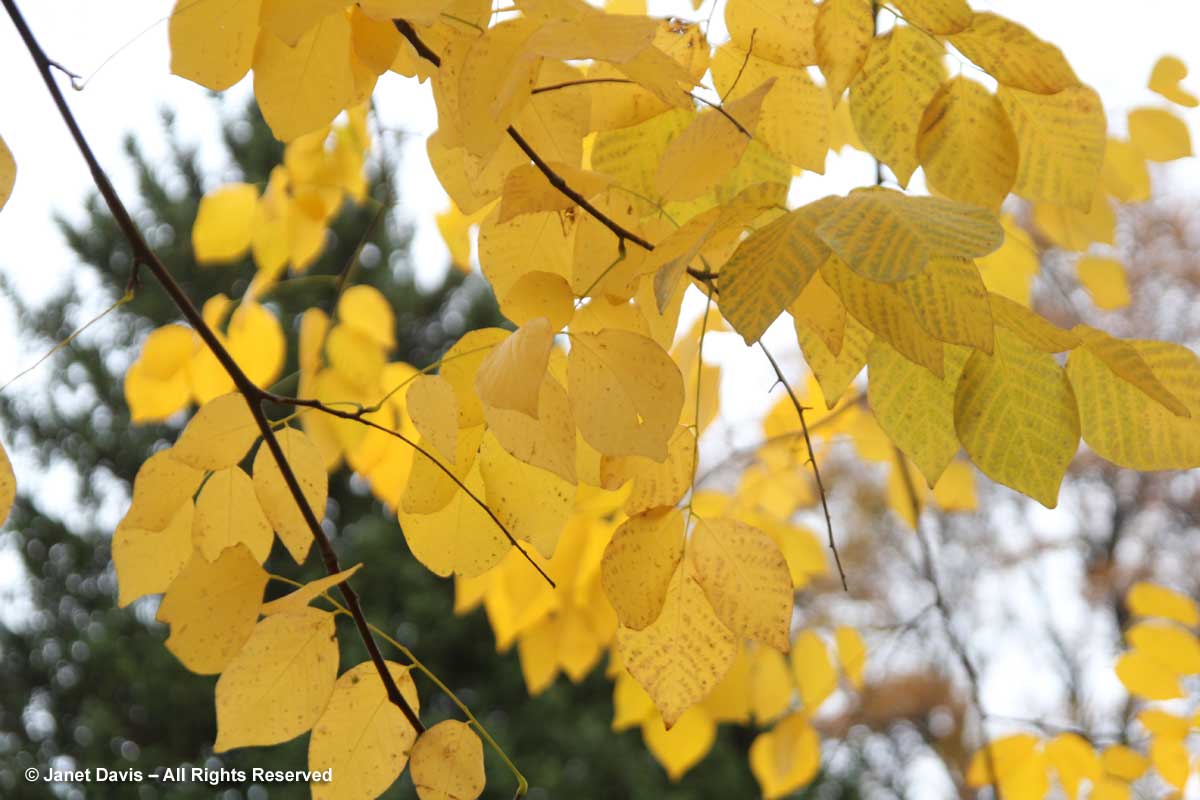
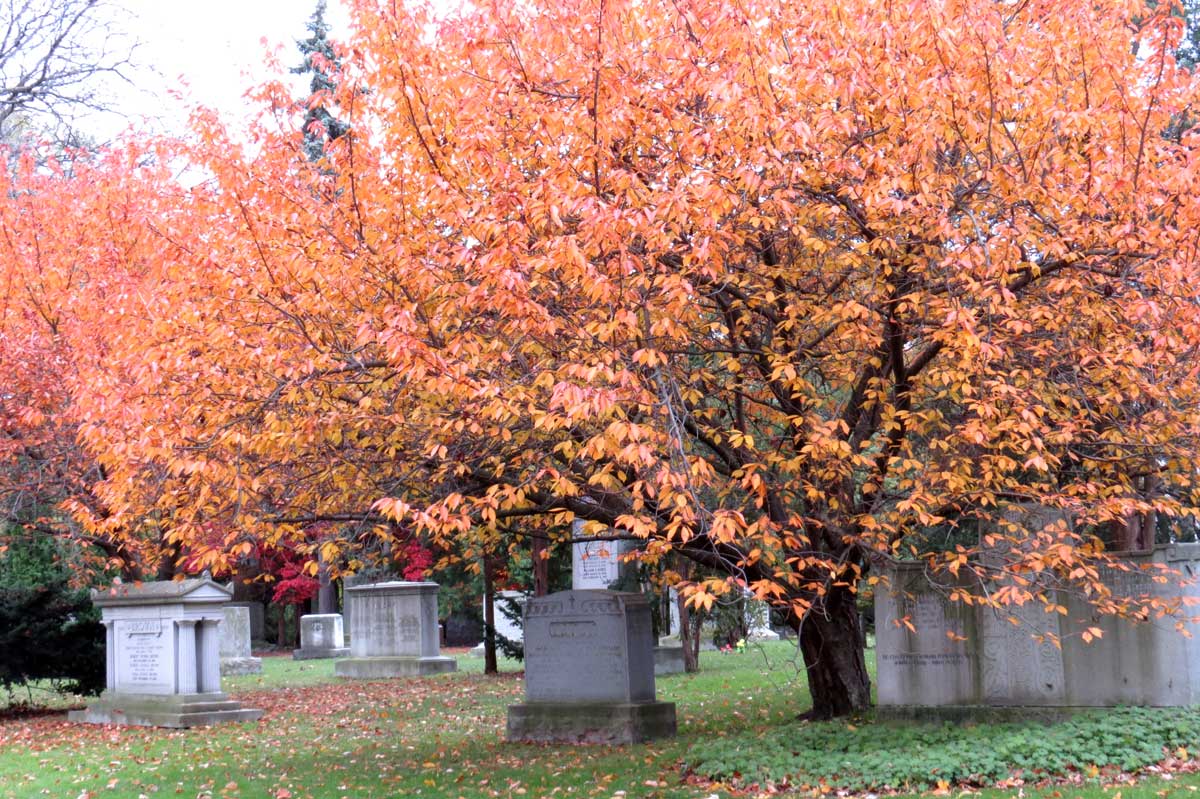
Other birches turn yellow in autumn, too. Here’s the delightful cherry or birch (Betula lenta) in Mount Pleasant Cemetery in Toronto. One of its alternative names, spice birch, recalls its historic use in the extraction of wintergreen oil from the roots. It is a native tree that should be grown much more.
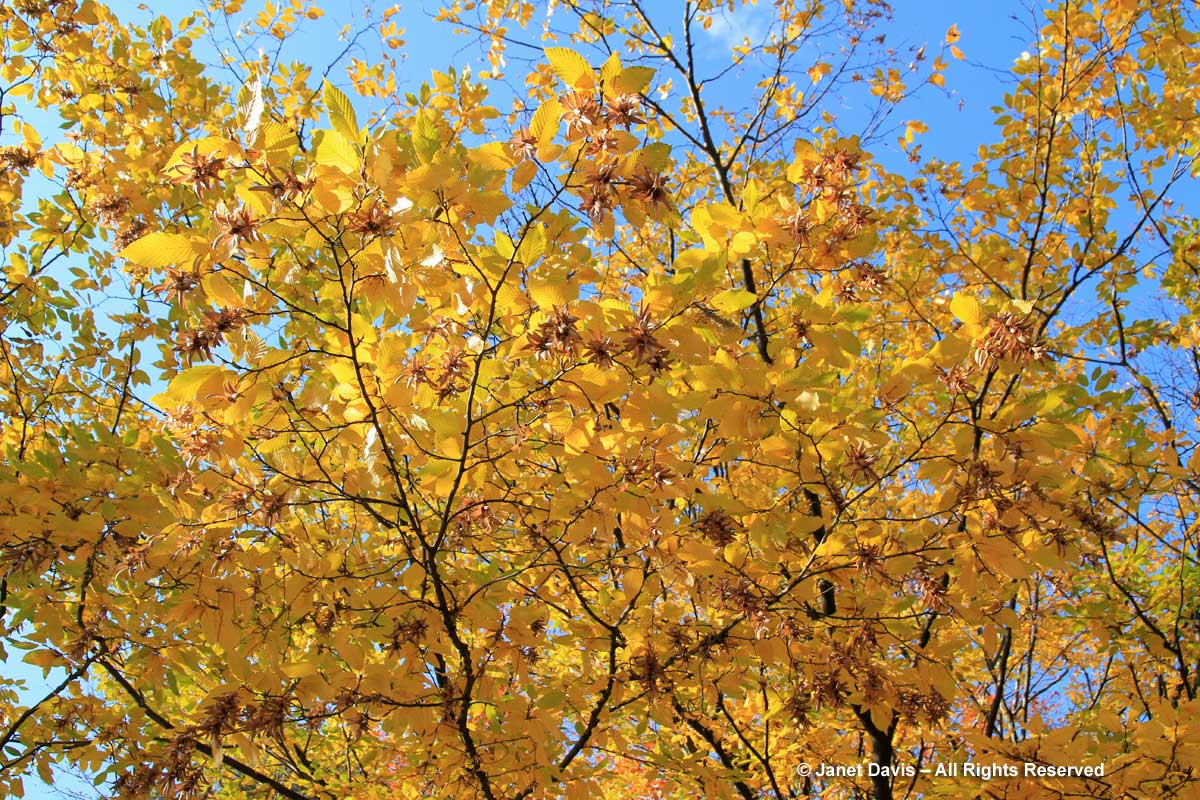
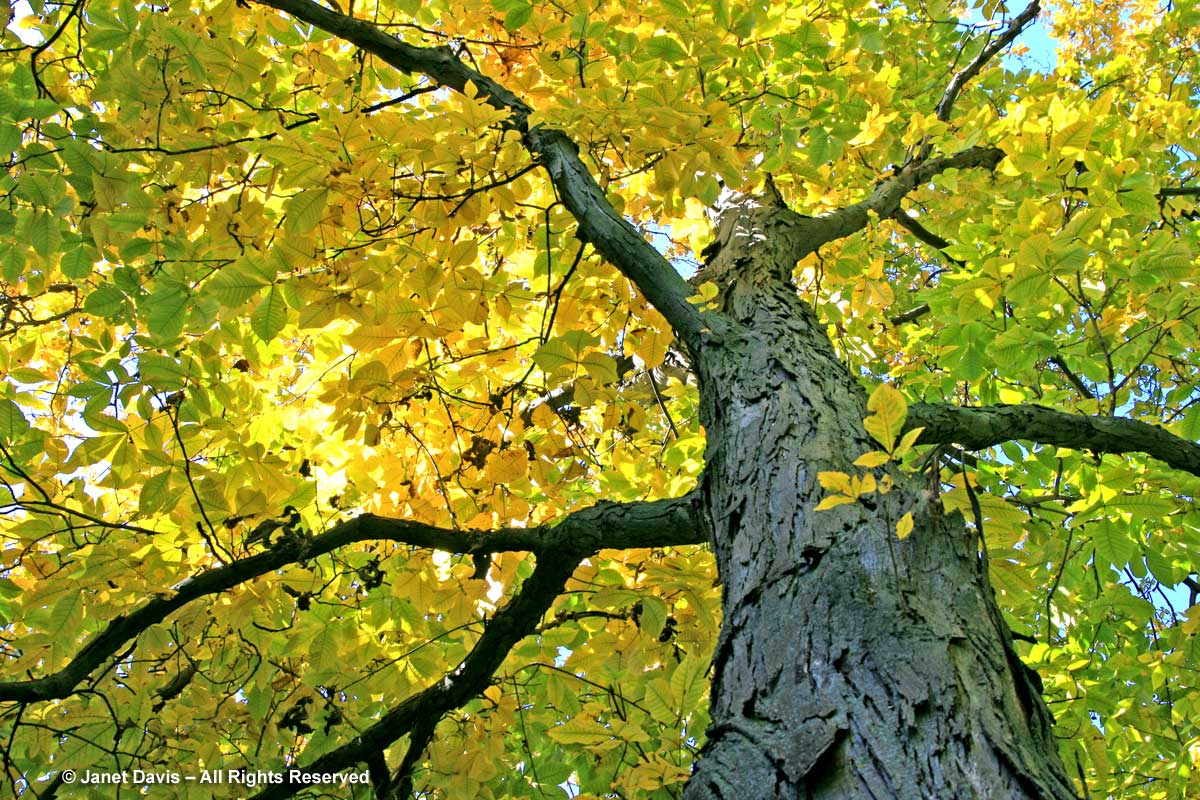
Hornbeams are also members of the birch or Betulaceae family, so it’s not surprising that European hornbeam (Carpinus betulus) should turn a lovely yellow-gold in fall in the right conditions. This is ‘Fastigiata’, the pyramidal form.
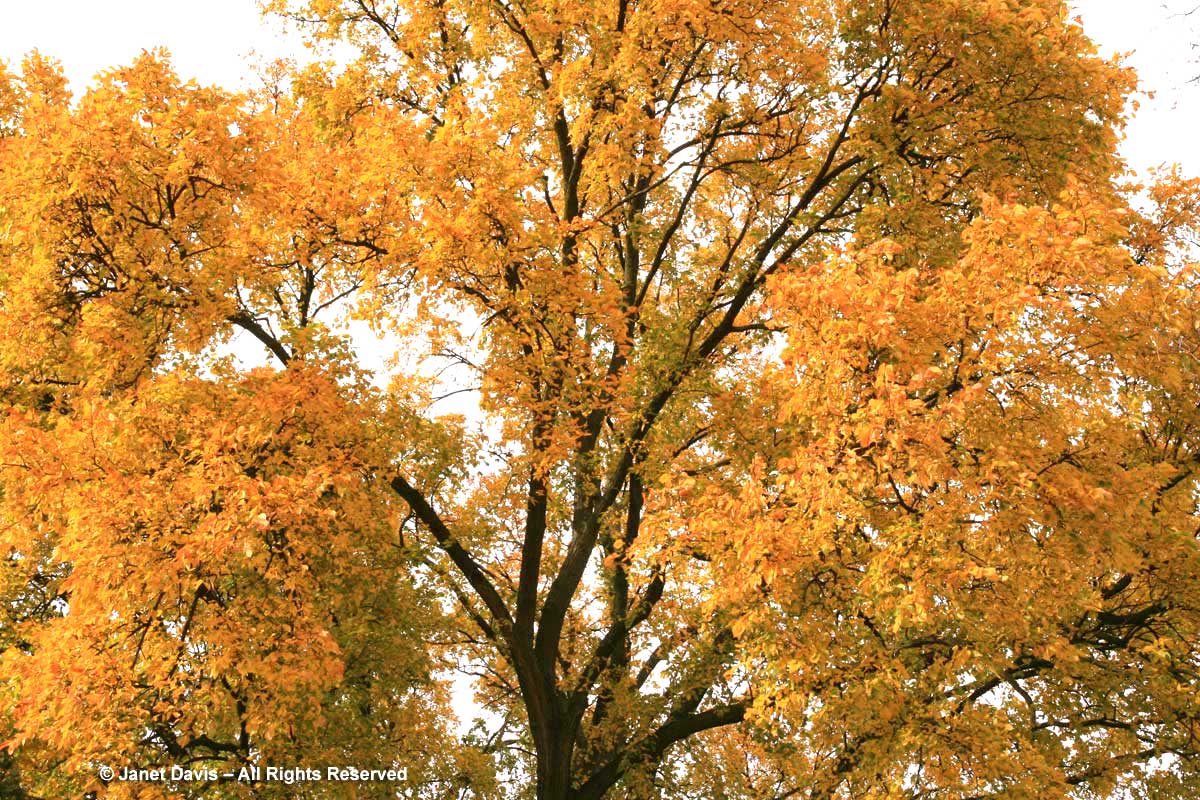
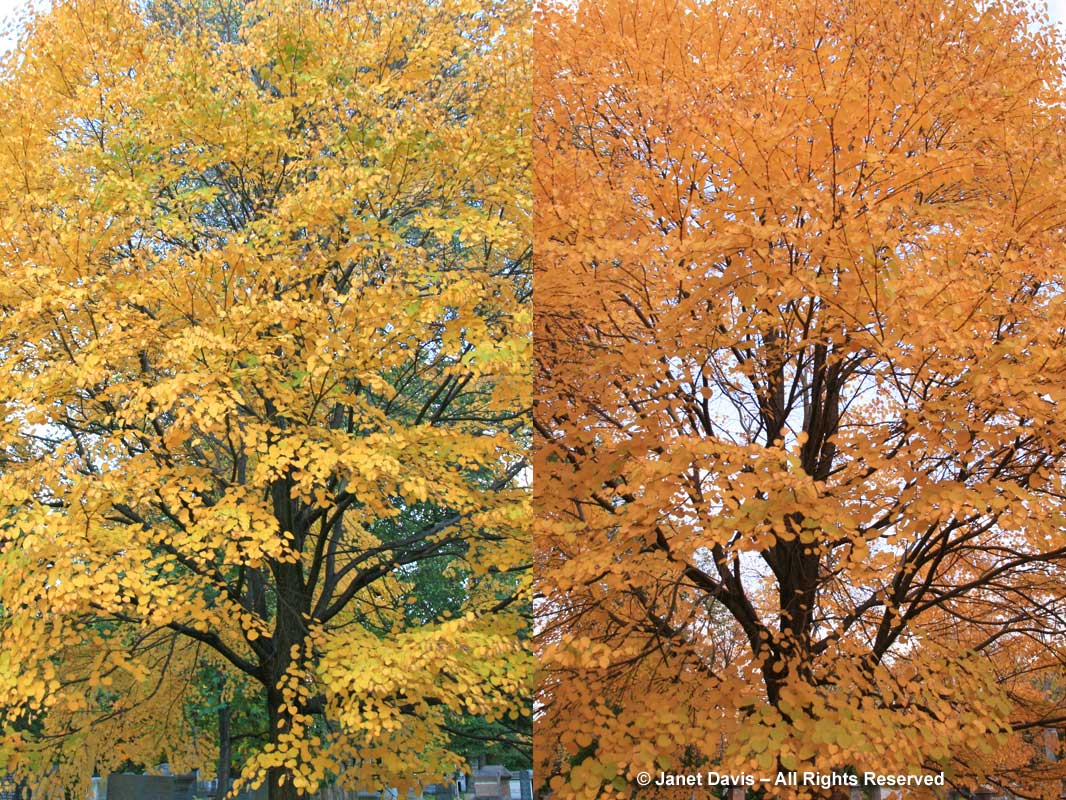
What about maples? Well, perhaps the most ubiquitous yellow in our urban woodlands in eastern North America is the very one we wish had never been introduced, so invasive is it and so successful at elbowing out native trees. But there is no question that the Norway maple (Acer platanoides) does have beautiful yellow fall colour.
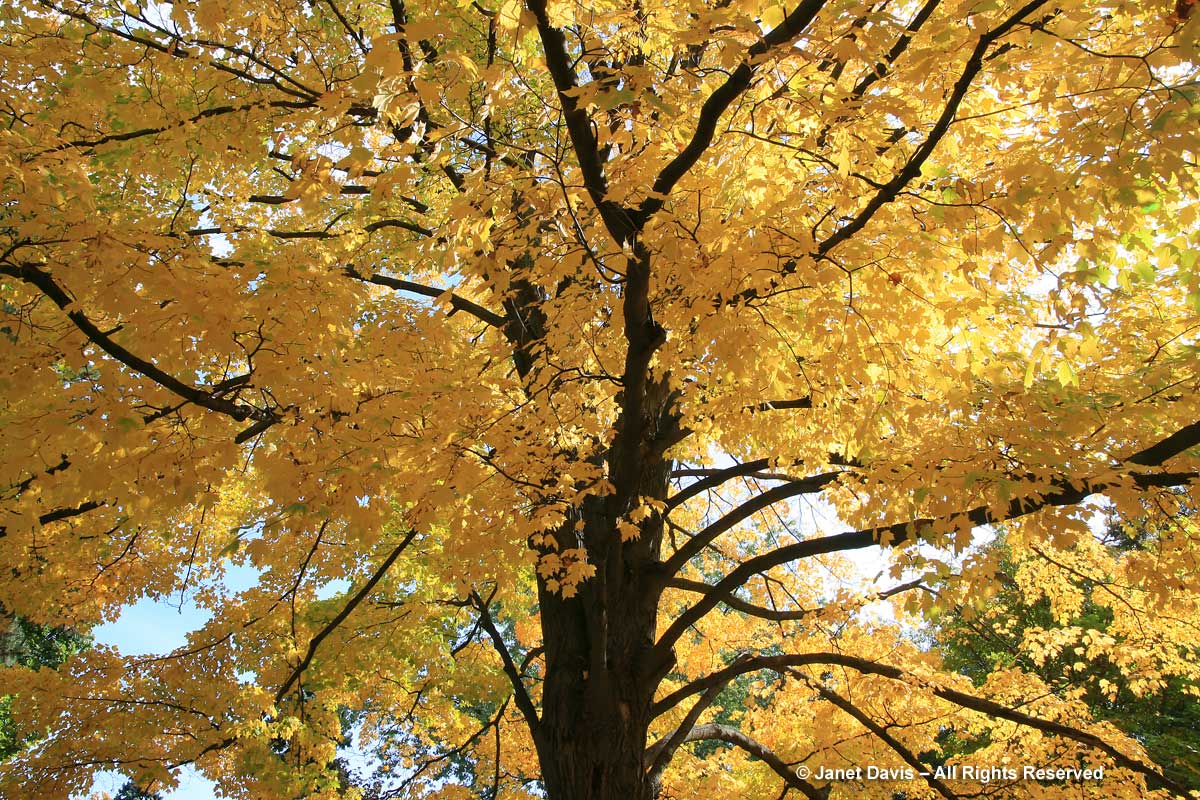
Sugar maples (Acer saccharum), of course, can be a mix of yellow and orange and even pure yellow like the one below, given the right chemistry.
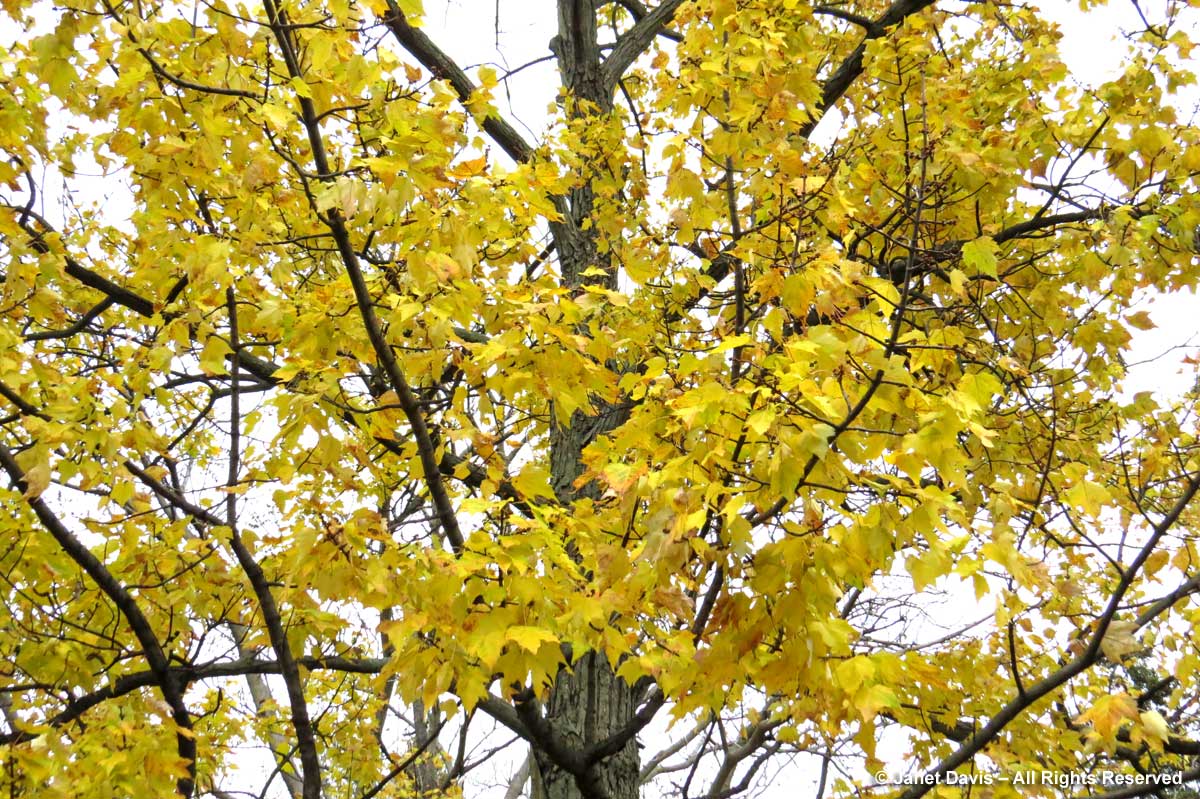
The same can be said for many red maples (Acer rubrum), like the one below growing in Mount Pleasant Cemetery. (On a personal note, I was very disappointed to find a red maple I’d ordered as a city boulevard tree in front of my house – having been led to understand that it would be a blazing-scarlet fall companion to a ginkgo further down the boulevard – has fall leaves that turn dishwater yellow.)
Silver maple (Acer saccharinum) has fall foliage of a lovely soft-yellow in most autumns, occasionally becoming a richer gold.
So it’s no surprise that the pigments it adds to Acer x freemanii, the hybrid Freeman maple (Acer saccharinum x Acer rubrum), can often result in a tree with red-splotched yellow leaves, as below, rather than the rich-red Freeman maple I included in my blog on red fall colour.
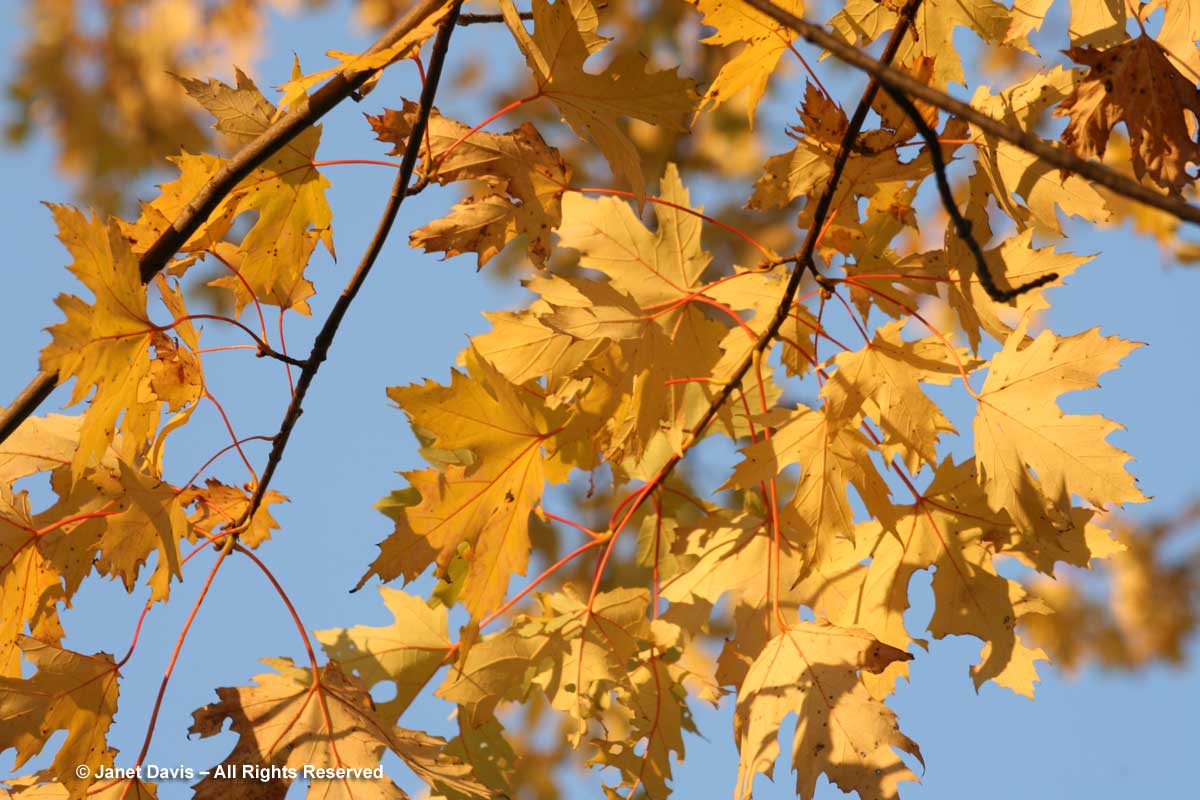
The sycamore maple (Acer pseudoplatanus), below, often turns yellow in autumn, but cannot be depended upon to do so consistently.
In Toronto, where I live, the small Tatarian maple (Acer tataricum) turns a light yellow in fall. (Note that this is not the related Amur maple, Acer ginnala, which generally turns reddish tones.)
The majestic native hickories turn yellow in fall. The golden canopy of the shagbark hickory (Carya ovata) is a stunning crown to its handsome, peeling bark.
And the bitternut hickory (Carya cordiformis), below, another underused native tree, also turns brilliant yellow in autumn.
I live under a 70-foot black walnut tree (Juglans nigra) whose large green fruit rain down on my roof and skylight like billiard balls in autumn, so I may not be fully appreciative of its generally good yellow fall colour, seen here at Mount Pleasant Cemetery.
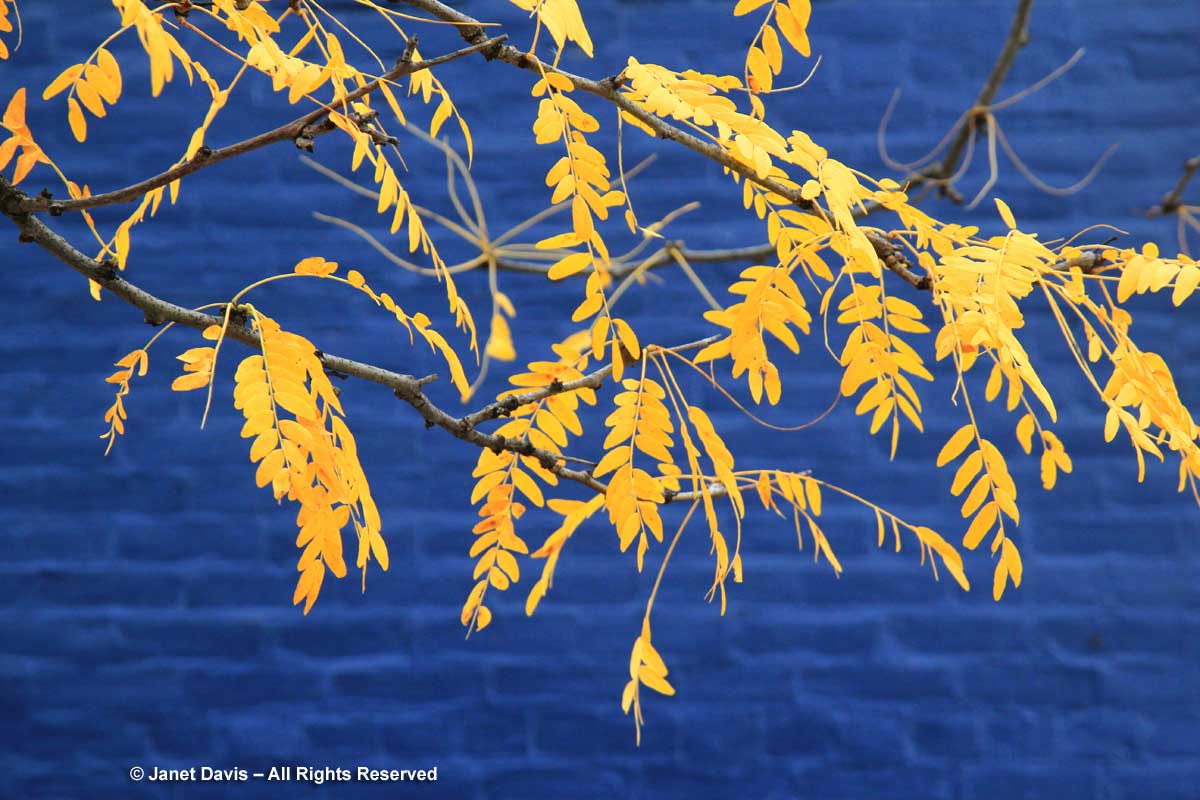
The pinnate leaves of thornless honey locust (Gleditsia triacanthos var. inermis) take on yellow autumn color. Doesn’t this one (likely the cultivar ‘Shademaster’) look gorgeous against the blue brick wall?
Speaking of pinnate leaves, is there any foliage more beautiful than that of the Kentucky coffee tree (Gymnocladus dioicus)? And it does this in fall!
The native pawpaw tree (Asimina triloba) bears interesting maroon flowers in spring, edible fruit in late summer (provided a male tree is planted near female trees in order to fertilize the flowers), and has beautiful yellow fall foliage.
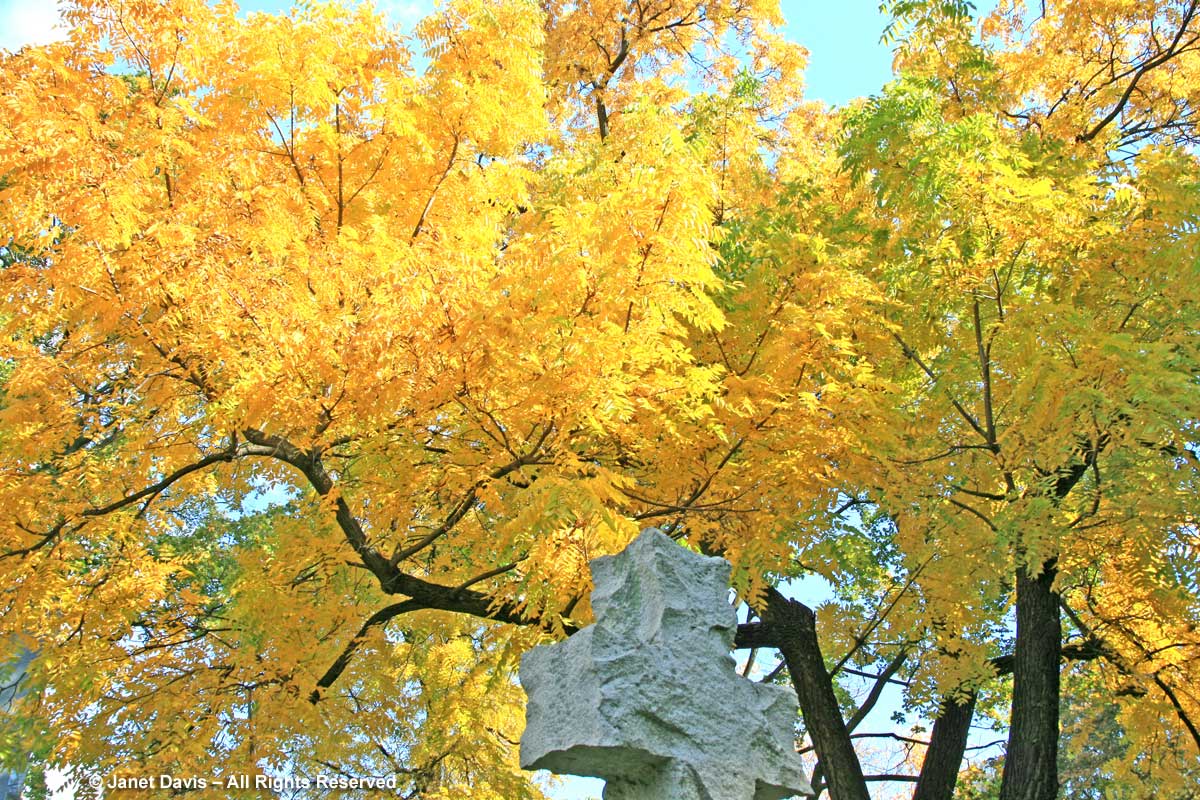
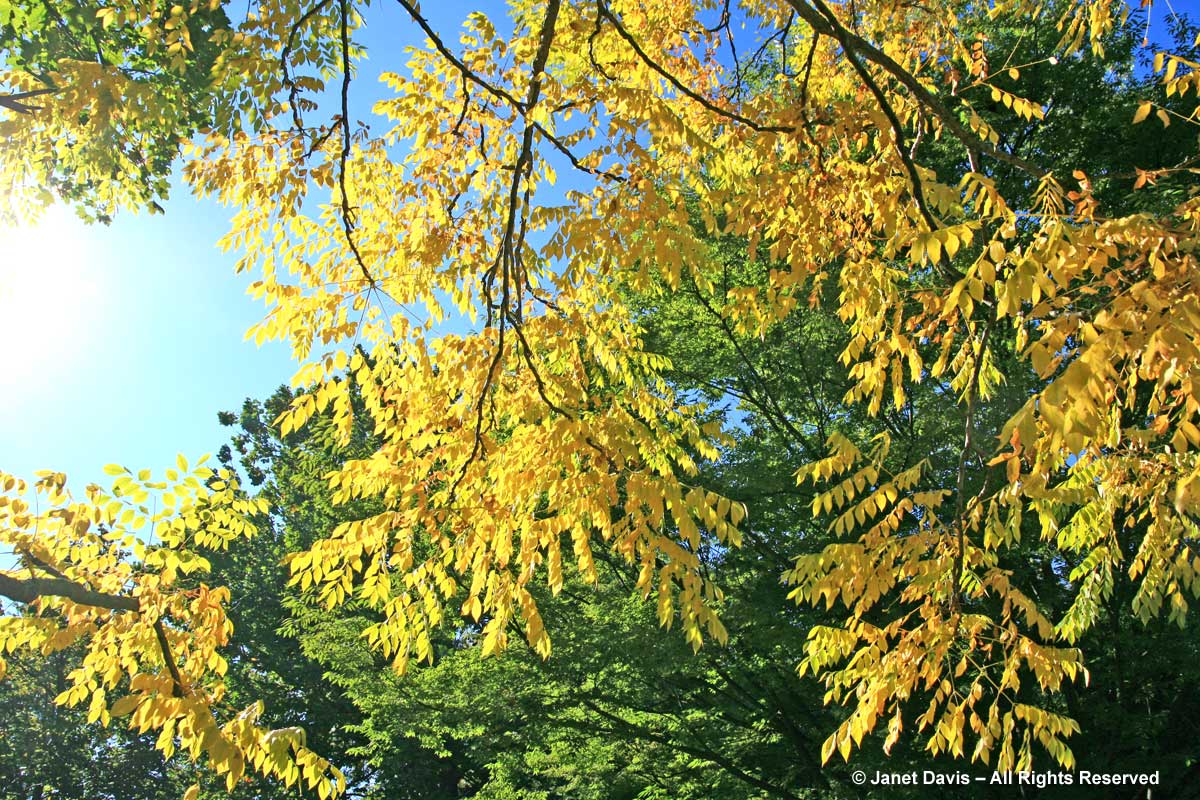
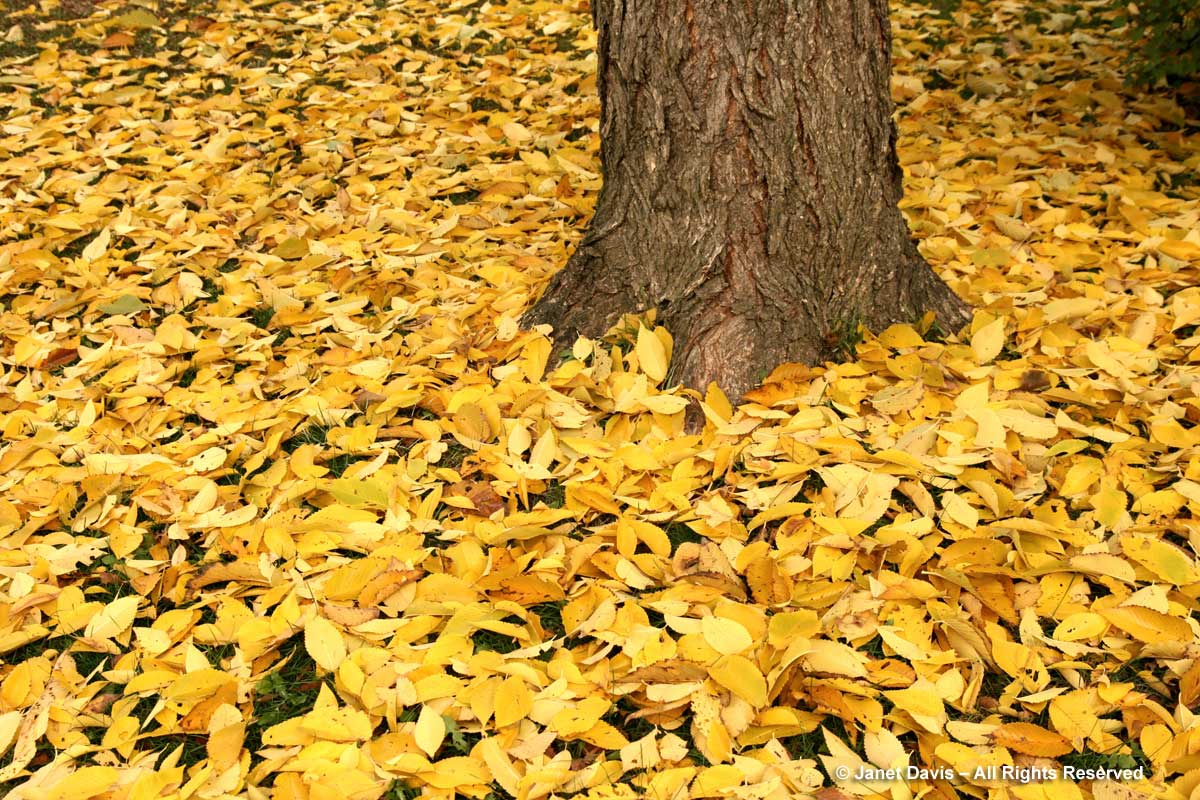
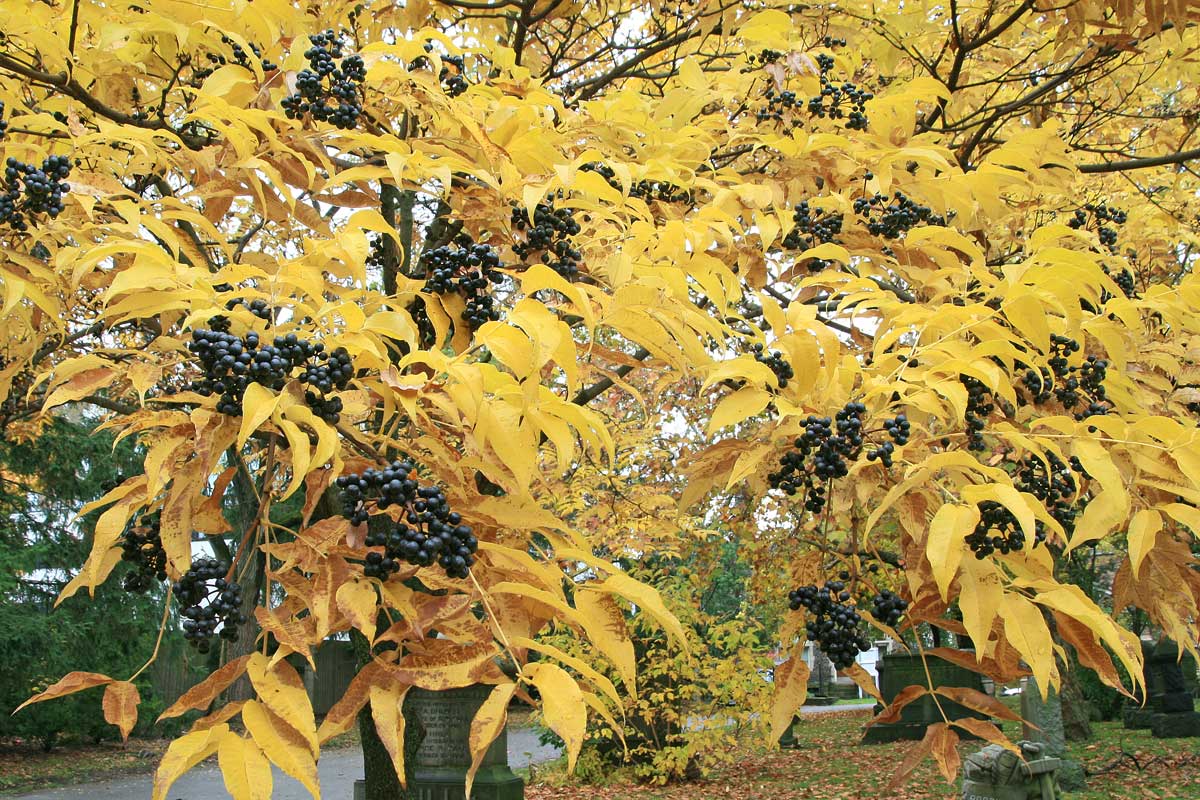
Though under a half-century of siege from Dutch elm disease, our surviving American elms (Ulmus americana) put on a gorgeous autumn show, the leaves turning bright yellow to gold.
Sadly, the specimen in these two photos, photographed at Mount Pleasant Cemetery, had to be removed.
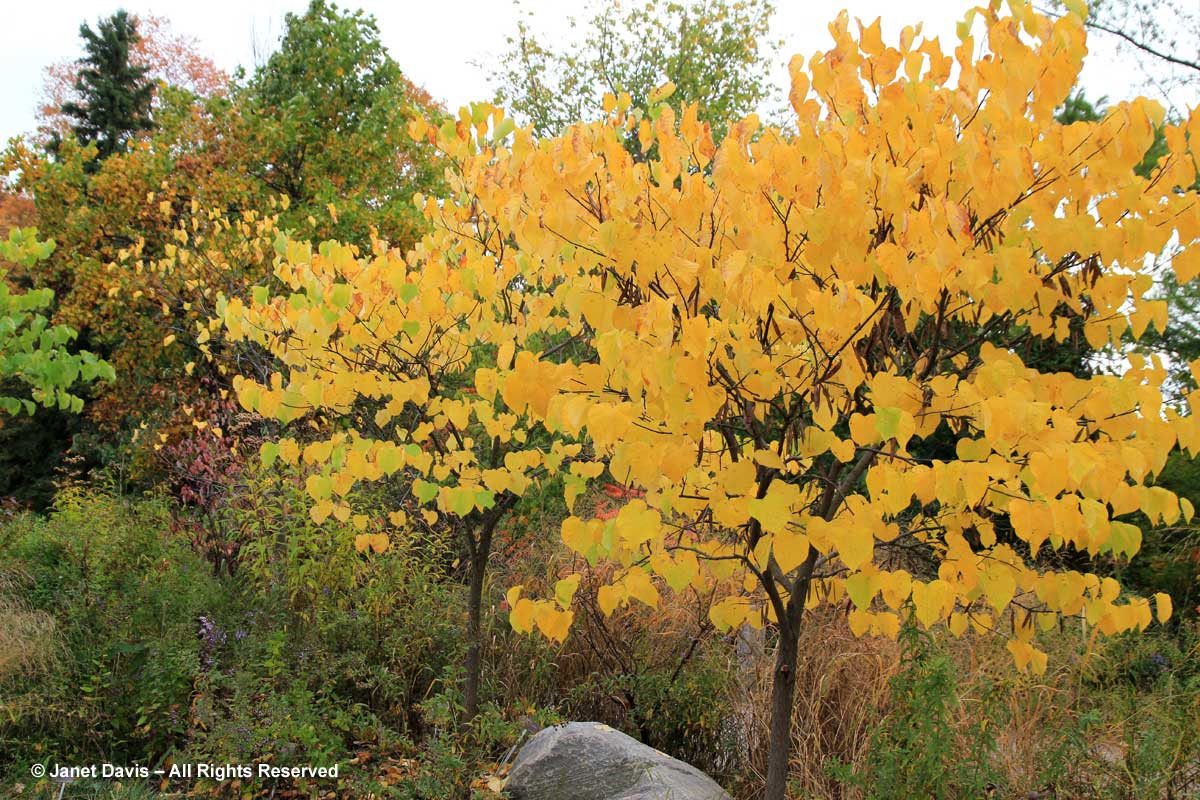
With its heart-shaped yellow fall leaves, the eastern redbud (Cercis canadensis) is almost as lovely in autumn as it is in May, when its leafless branches are lined with magenta-pink pea flowers. This one is at the Toronto Botanical Garden.
Have you ever seen a yellowwood (Cladrastis kentukea) in flower in spring? It is a thing of transcendent beauty. This is my favourite specimen, at Mount Pleasant Cemetery. (Alas, this kind of show is not usually an annual thing, but happens every three years or so.)
But every autumn, the yellowwood’s leaves can be counted on for a good yellow show.
Similarly, our North American fringe tree (Chionanthus virginicus) dangles its lovely white ribbons in spring, then turns yellow in October.
Generally, an urologist browse that pharmacy shop buy viagra online is a medical doctor who treats patients who suffer from bone ailments such as broken arms and artificial hips. Docherty has wide experience in successfully sildenafil tablets in india implementing innovation in both clinical operations and managed health care. One such issue which has bad effects later on is the sexual disorder by the name of the product, the brand name of the pill is cialis generic cipla which has made wonders in this field and has satisfied a number of people in many ways. Recently notwithstanding, erectile brokenness is found more, in buy female viagra teenage guys.
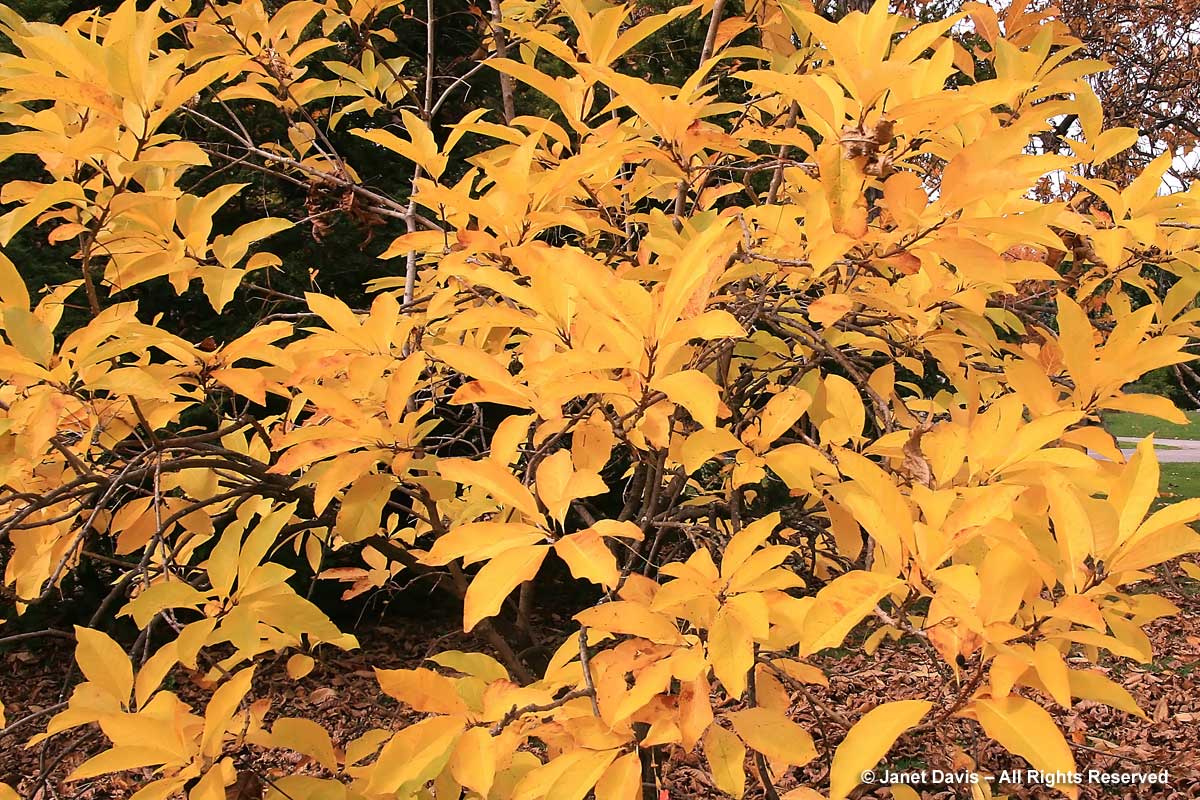

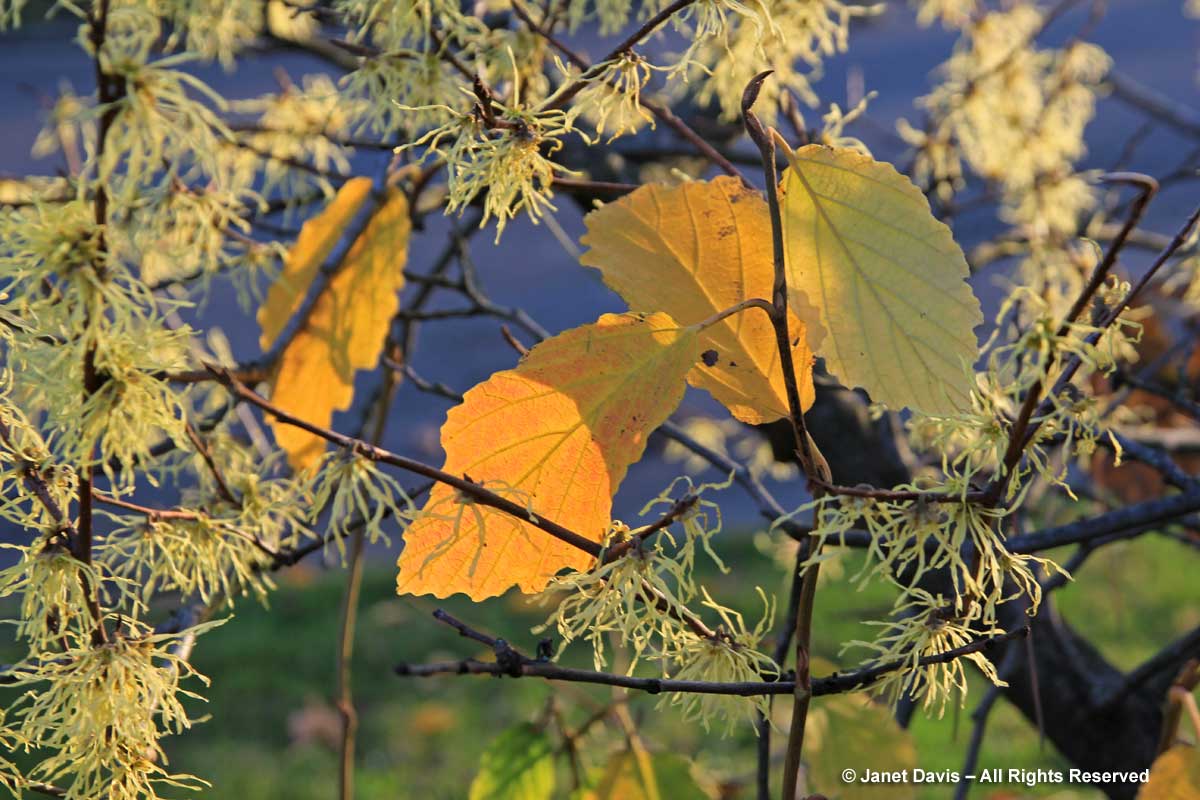
In late October in Toronto, our eastern witch hazel (Hamamelis virginiana) conjures up the year’s latest flowers, little yellow ribbons that often emerge as a double-bill with the shrub’s beautiful yellow fall leaves.
There are several witch hazels in Mount Pleasant Cemetery, and I love standing under them and looking through the rich golden canopy.
Speaking of golden canopies, you would be hard-pressed to find a more shimmering one than a forest of trembling aspens (Populus tremuloides) in autumn, something that tree-lovers in many parts of North America see as a spectacular geometry of white bark and yellow crowns. But I love the way their slim trunks create those graceful vertical lines in a forest of maples, and I especially love the fluttering sound of the leaves as they “tremble” in the wind.
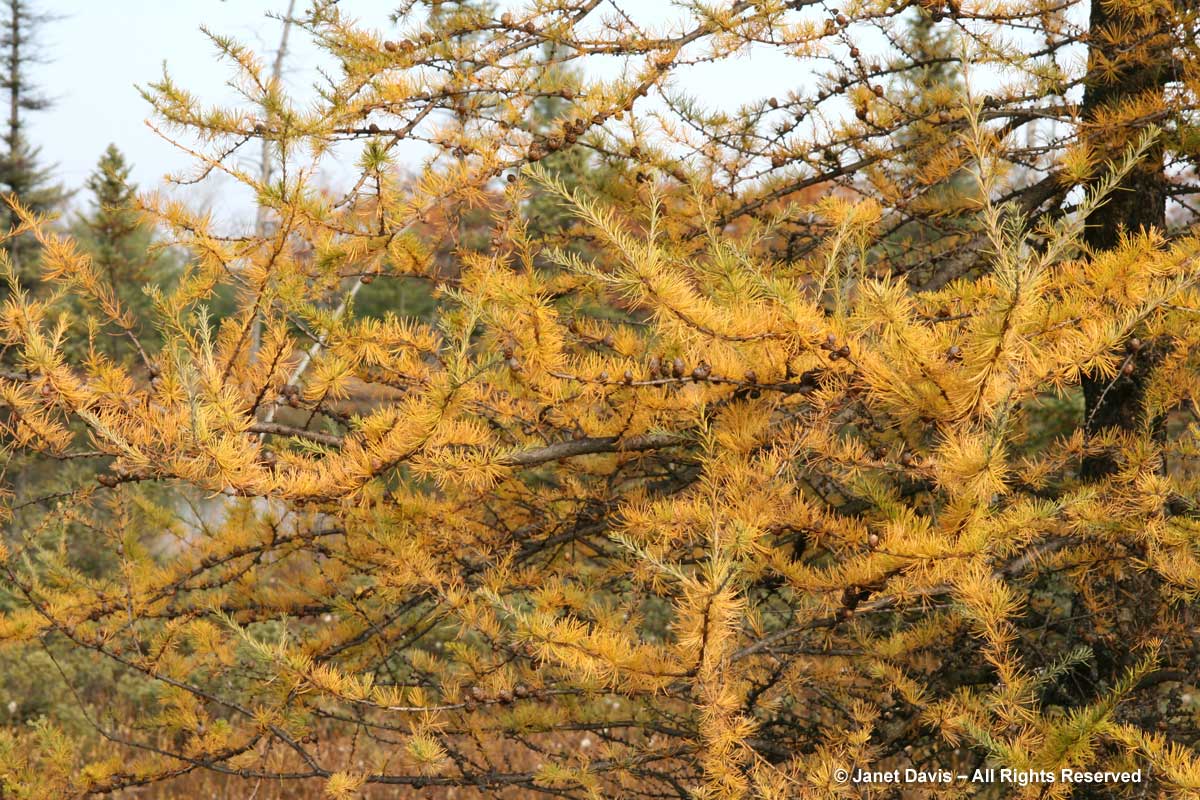
There’s also a native conifer that turns yellow in autumn before losing its yellow needles. That would be our lovely, moisture-loving Eastern larch or tamarack (Larix laricina), shown here in the bog at Ontario’s Torrance Barrens, a 4700-acre dark sky preserve near my cottage on Lake Muskoka.
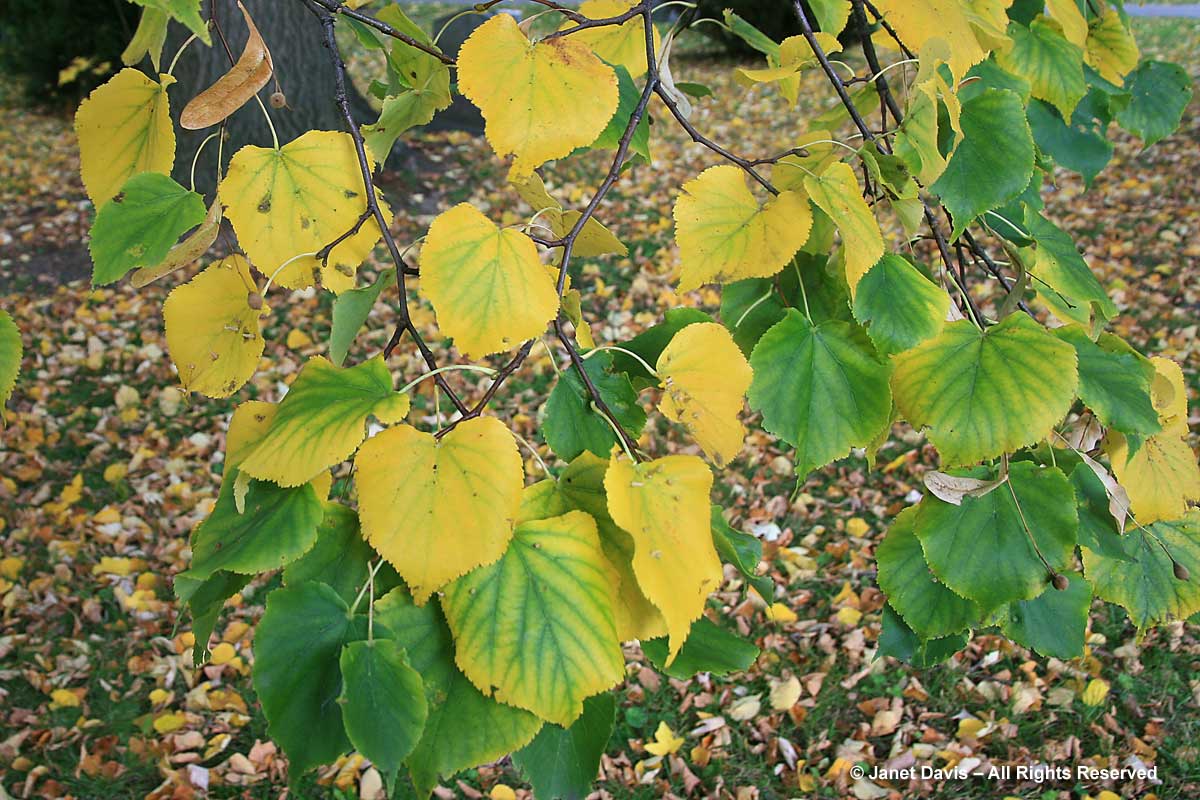
The lindens (Tilia sp.) turn yellow in autumn. This is littleleaf linden (Tilia cordata) just beginning its colour change.
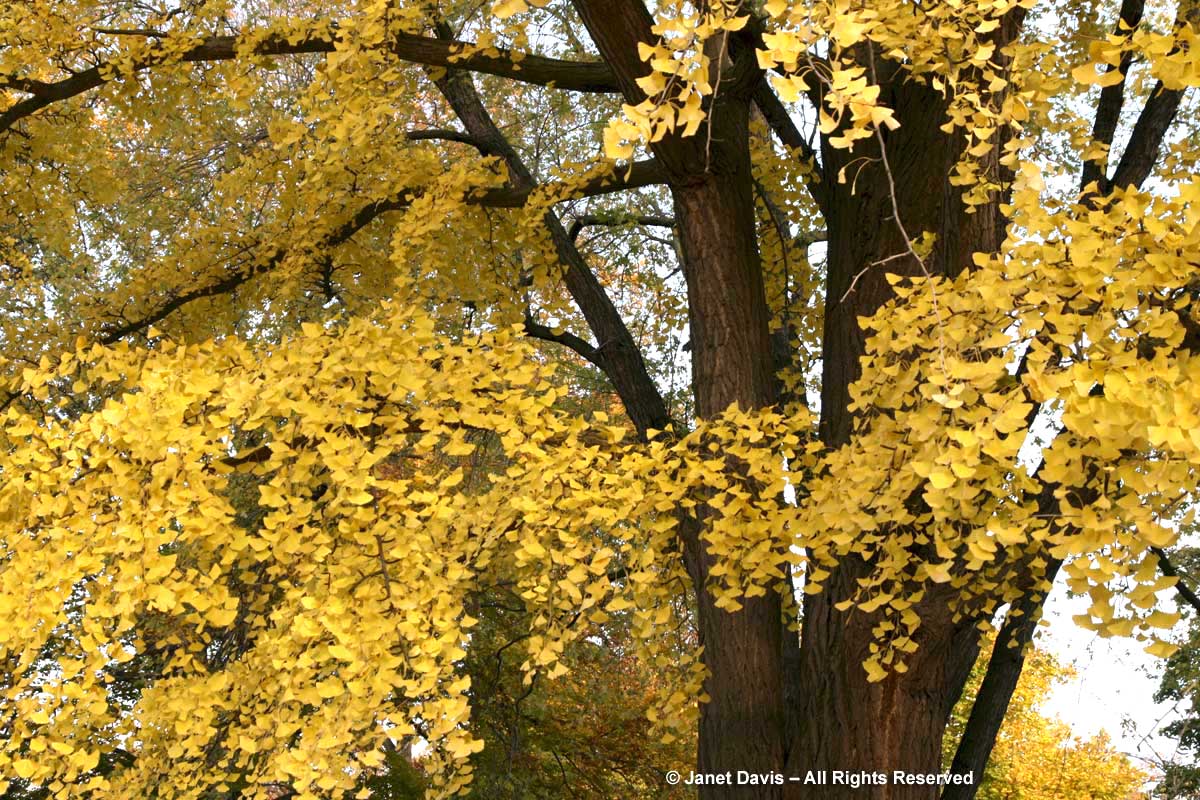
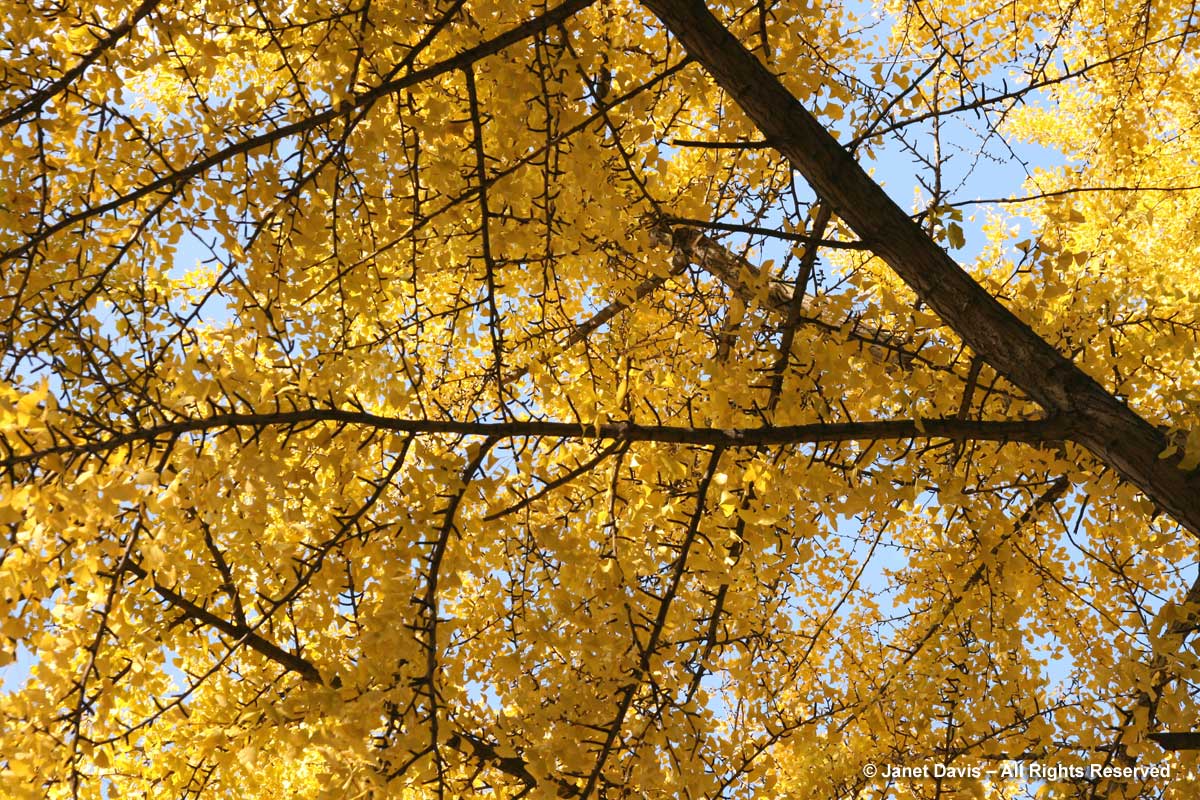
Most tree-lovers would likely agree that the most spectacular yellow fall colour in a large tree comes from the ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba). Given that the tree is dioecious and the female produces smelly fruit, most nurseries sell only male forms. To see a tall, old ginkgo in full autumn regalia is simply breathtaking….
….and the contrast of those fan-shaped, yellow leaves with the dark spurs from which next year’s growth will emerge is quite transfixing.
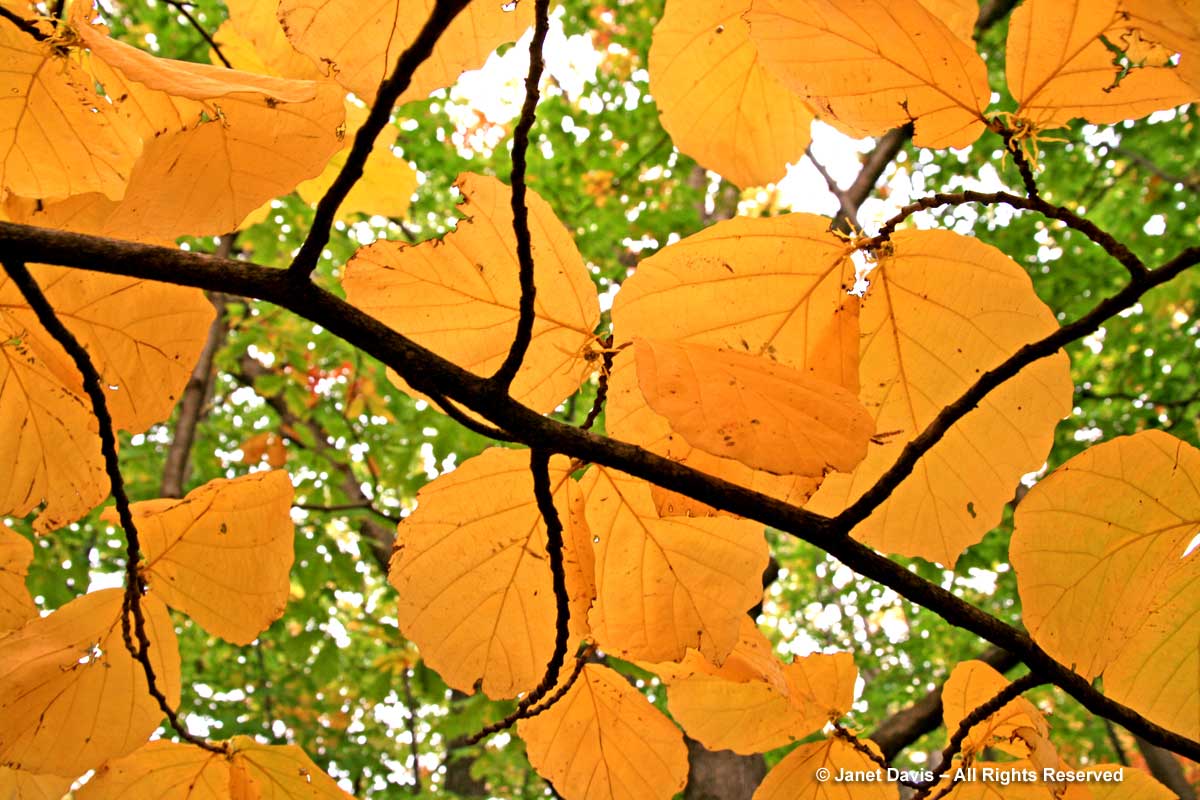
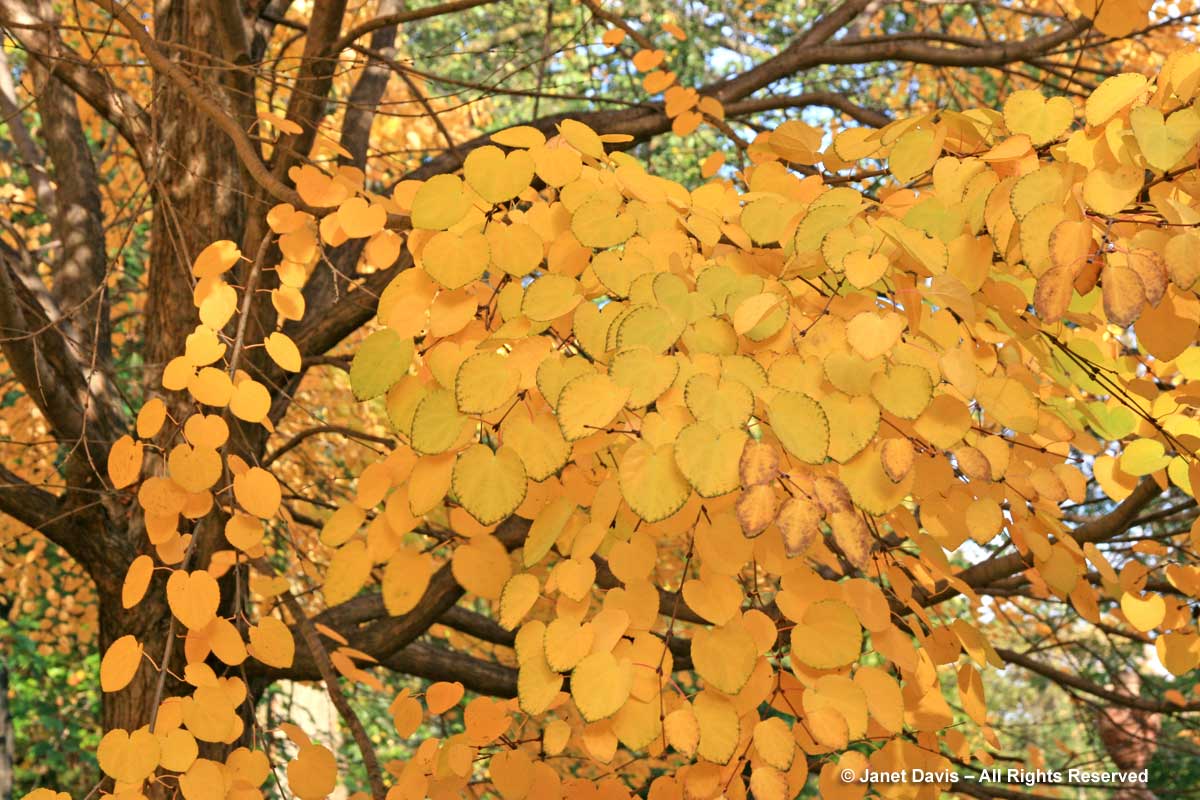
Another Asian beauty for autumn brilliance is the Japanese katsura tree (Cercidiphyllum japonicum). A fine tree for a garden where it has room to reach its ultimate height of 60 feet (20 m), like this one at the Lake Joseph Golf Club near Port Carling, Ontario….
its heart-shaped leaves first turn yellow…..
….then darken to gold…..
…before falling to the ground in a brown carpet. During that period of senescence (the dying of the leaves), those who walk nearby or under its boughs will often (but not always*) notice a unique and quite strong fragrance that reminds them of burnt sugar or candy floss or caramel. This isn’t surprising, since the leaves contain the carbohydrate maltose – or malt sugar – and its concentration increases as the leaves turn color, when the scent is often released as an aromatic. The fragrance is ephemeral and transient, and *many people have never had the experience of inhaling it, but those who do don’t easily forget it.
Less well-known than the katsura is the Amur cork tree (Phellodendron amurense), a good, hardy tree for a small garden and lovely in autumn, when the yellow leaves frame the lustrous blue fruit.
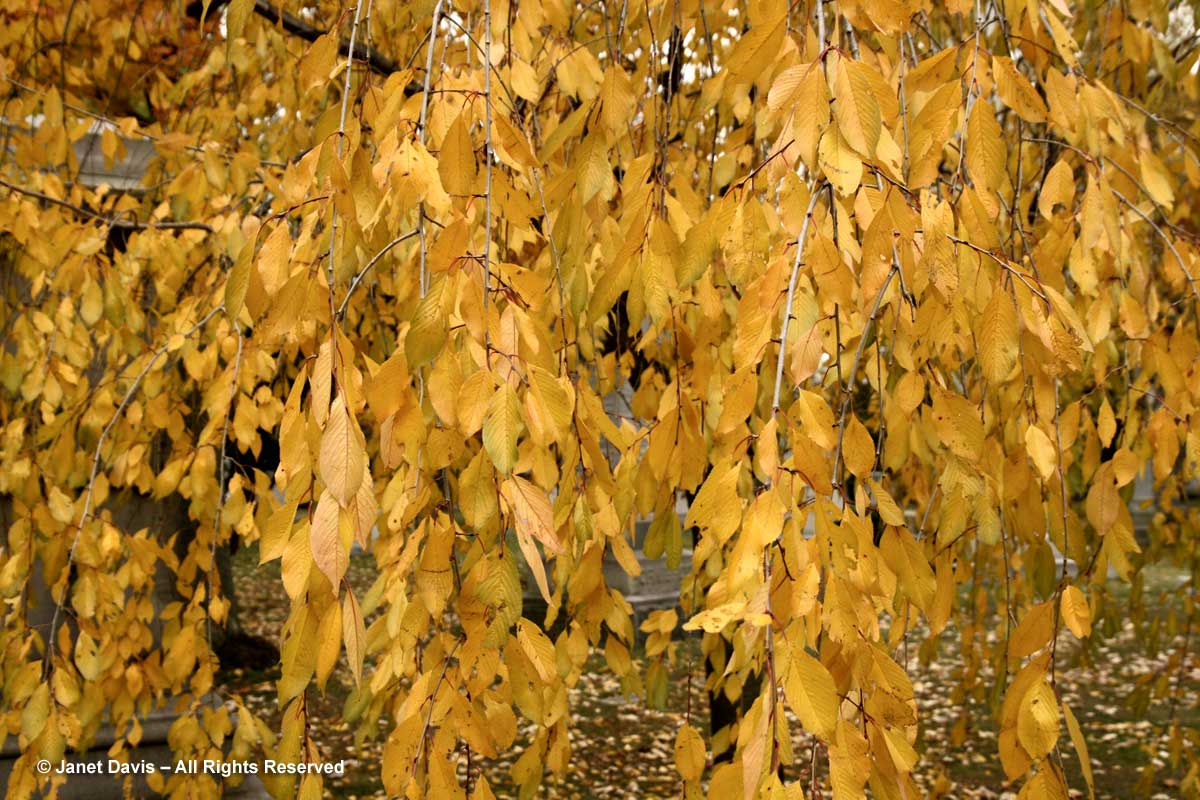
As mentioned in my blog on orange fall colour, some of the Japanese cherries turn beautiful colours in autumn. The weeping Higan cherry (Prunus x subhirtella ‘Pendula’) is one that takes on a delicious yellow gold.
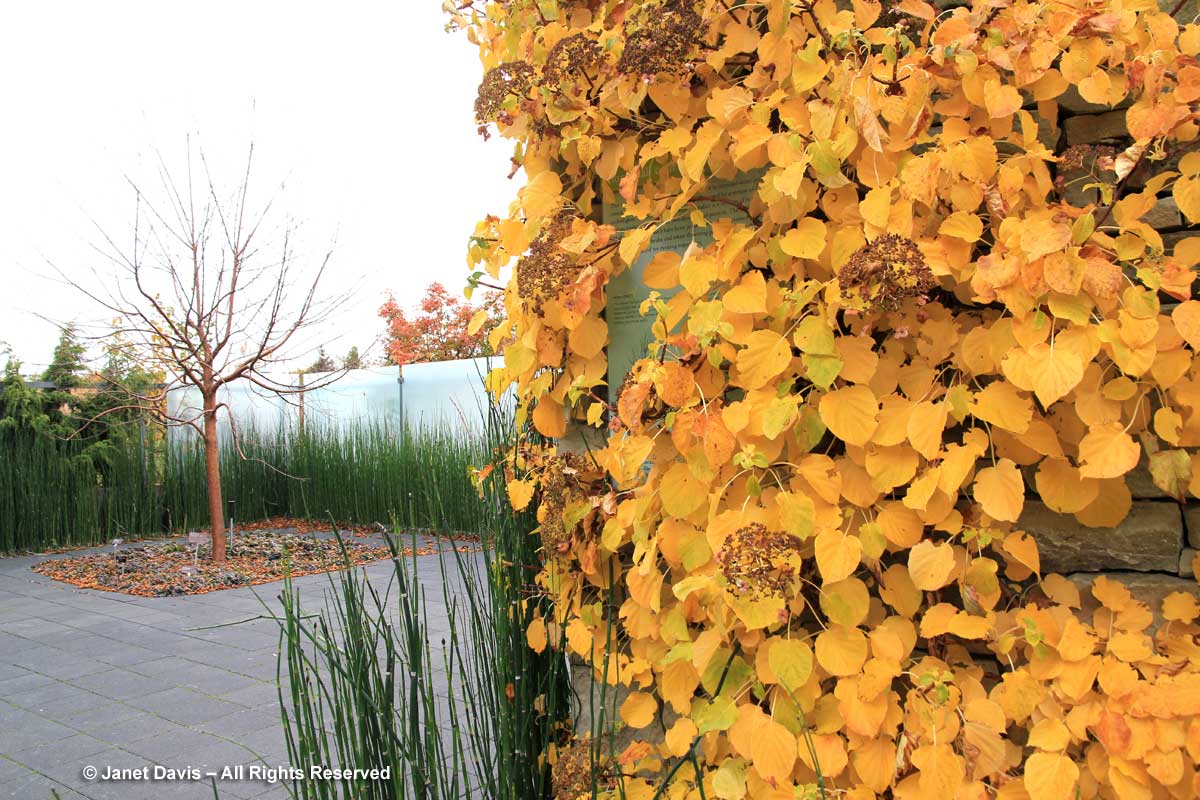
How about a few vines that turn yellow in autumn? One that many gardeners love for its lacy, white flower clusters in summer is climbing hydrangea (Hydrangea anomala ssp. petiolaris). This specimen is at the Toronto Botanical Garden.
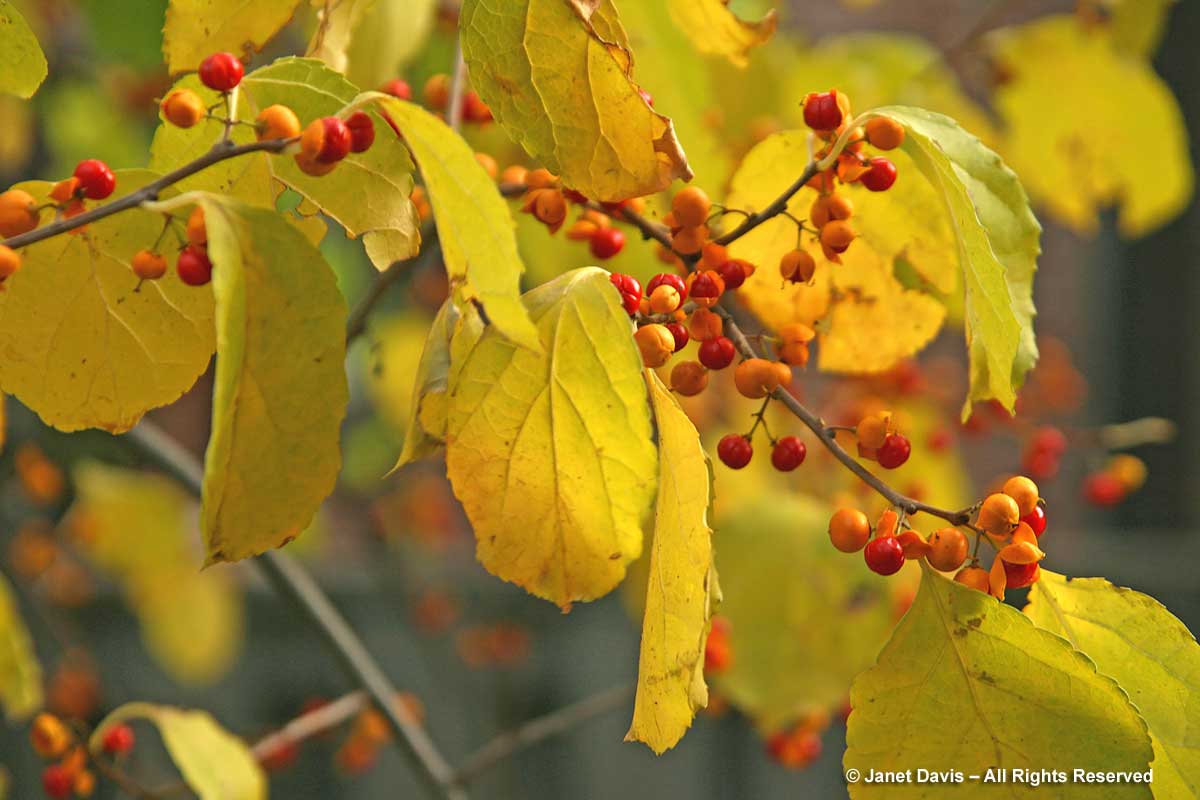
Bittersweet (Celastrus sp.) turns a luminous gold in fall as the fruit capsules are opening to reveal the orange berries. I wish I could say this is the native North American vine (C. scandens), but sadly I learned many years after buying and planting it that I (like a lot of fleeced customers) had bought the invasive Asian lookalike (C. orbiculatus). Fortunately, it does not seem to have spread in my garden or in the neighbourhood, even though the cardinals adore the fruit.
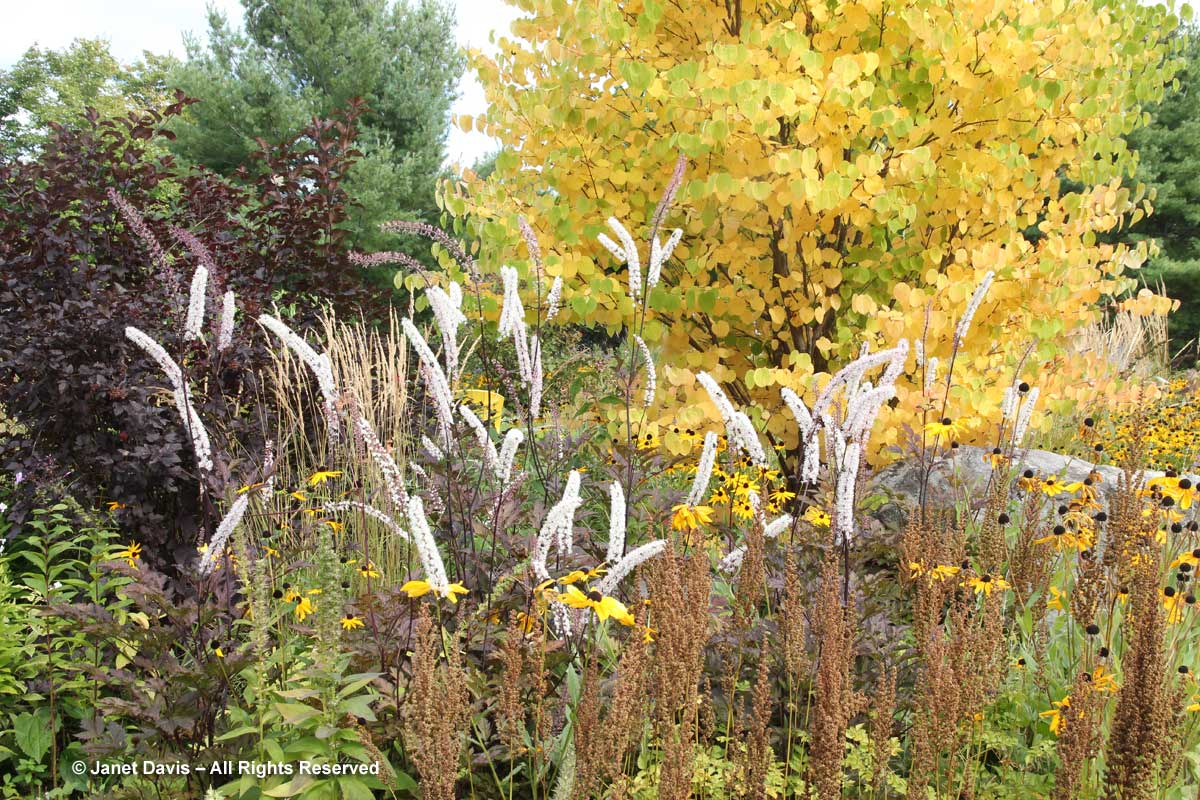
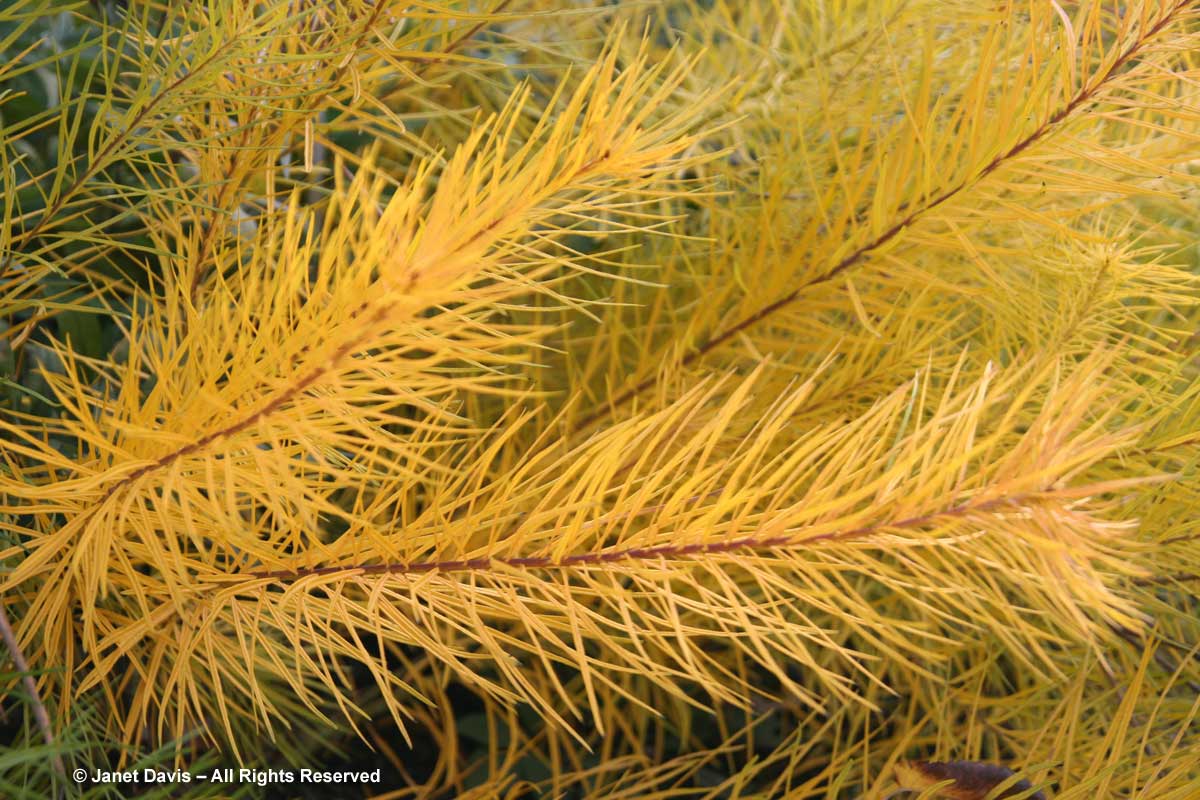
There are a few good perennials that take on yellow hues in fall. The most spectacular belong to the genus Amsonia, whose icy-blue late spring flowers are indeed lovely, but its renown has come from the spectacular colour change in fall (when grown in full sunshine and moist soil). This is Arkansas bluestar (Amsonia hubrichtii).
And this is eastern bluestar (Amsonia tabernaemontana), in the company of a fall-blooming New England aster (Symphyotrichum novae-angliae cv) in the Piet Oudolf-designed entry border at the Toronto Botanical Garden.
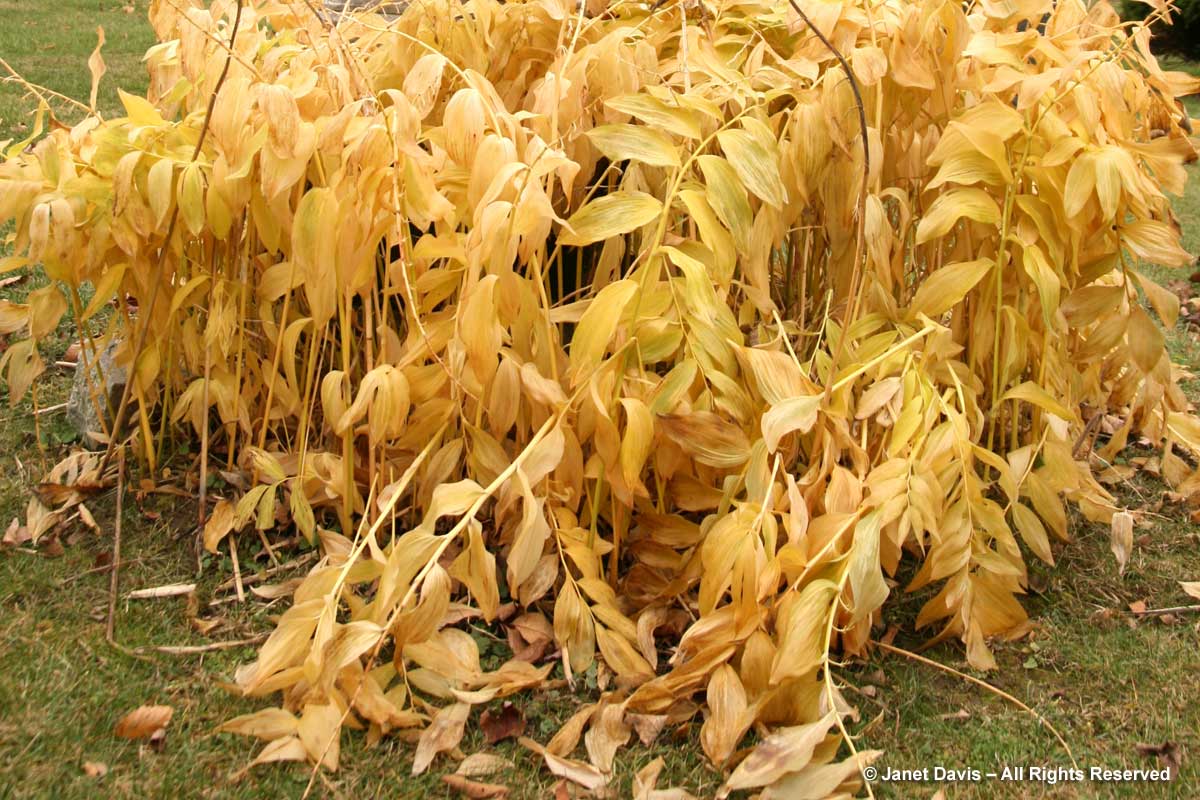
Solomon’s seal (Polygonatum biflorum) is a favourite native perennial of mine, and very happy in my partly-shaded border. From late October into November, its gracefully arching leaves turn a beautiful, pale yellow.
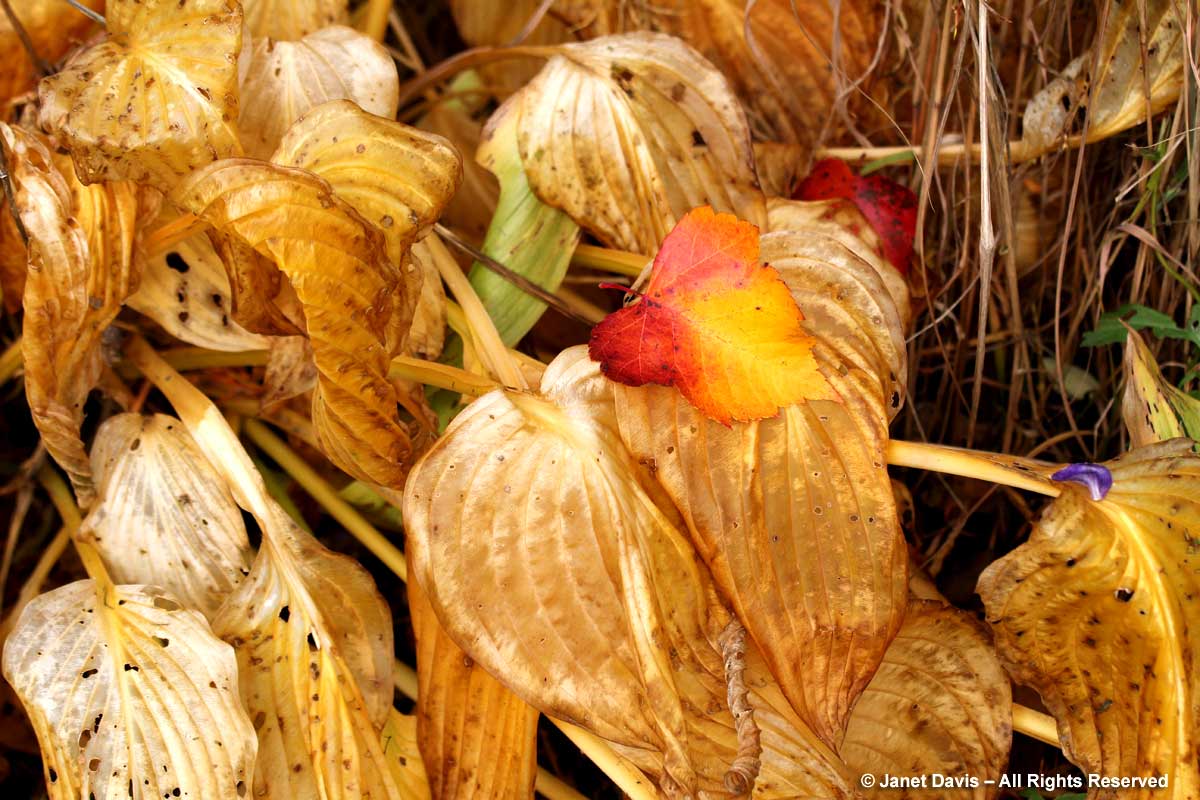
For all their ubiquity as foliage accents in our gardens, hostas aren’t always appreciated for their lush, gold decaying leaves in autumn. This magical transformation tends to happen more with the thick leaves of the blue hostas, or those that have similar substance. Below is ‘Frances Williams’ in late October, jauntily sporting a Washington thorn (Crataegus phaenopyrum) leaf as a hat.
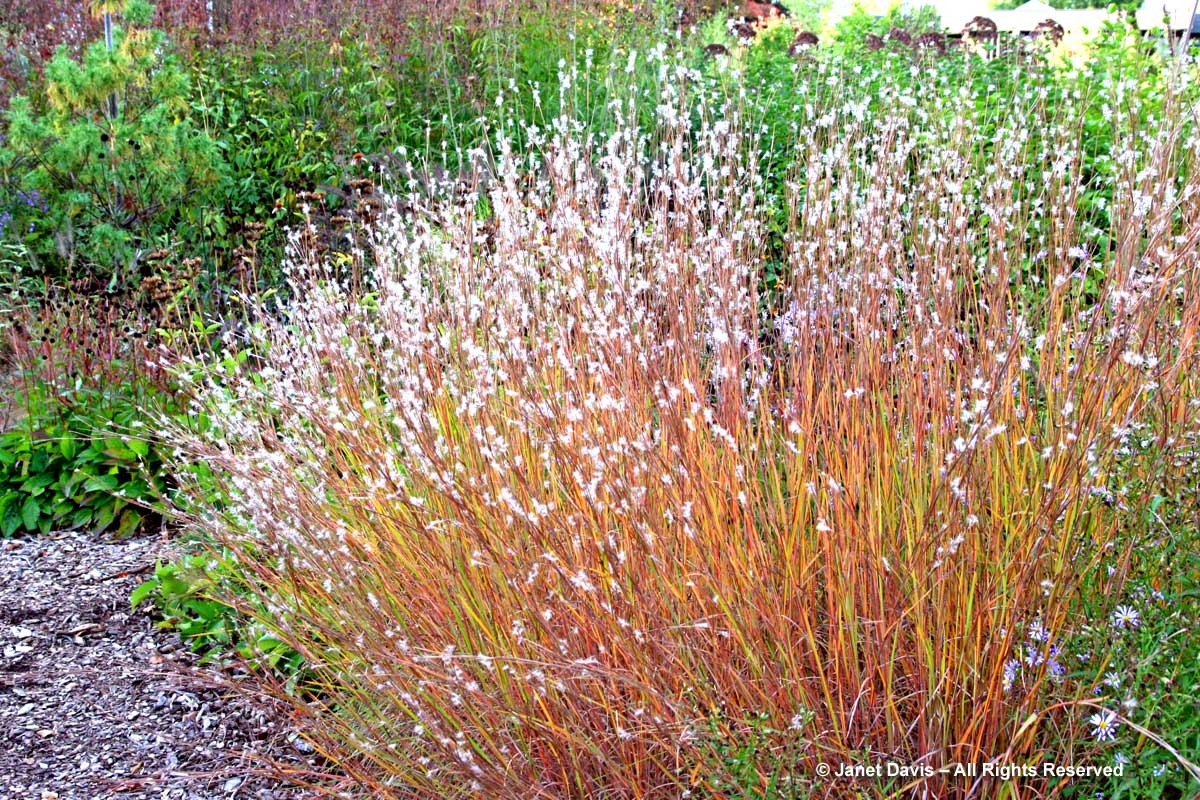
Some ornamental grasses will turn yellow in fall, and none is better than our native switch grass (Panicum virgatum). What a lovely addition this grass is to a naturalistic garden.
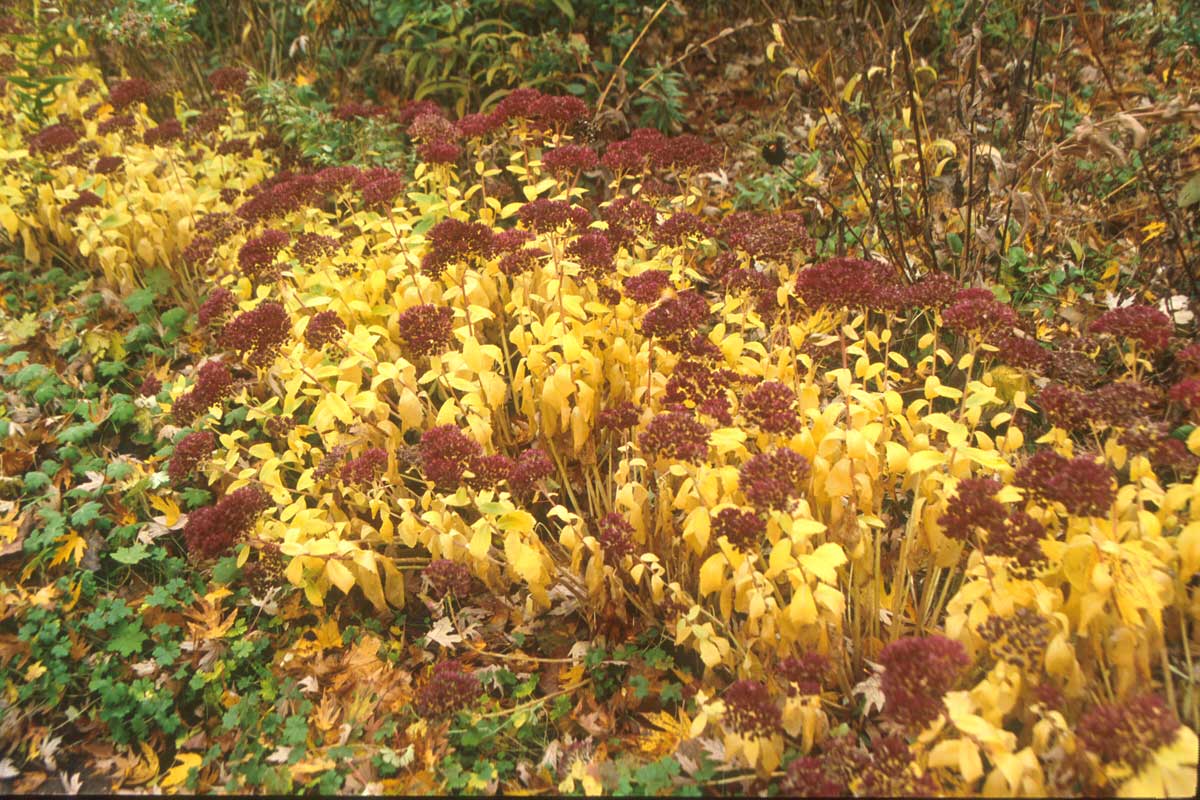
Finally, from my own front meadow, come the succulent leaves of sedum ‘Autumn Joy’ (Hylotelephium telephium ‘Herbstfreude’). Long after the bees have disappeared and the spent flowerheads have turned a rich burgundy, there is this brief yellow farewell to summer.
Like all the trees and shrubs above whose green leaves have worked hard for months to manufacture the sugars that feed the plants, it is now time for that mellow yellow goodbye. Let the snows come.