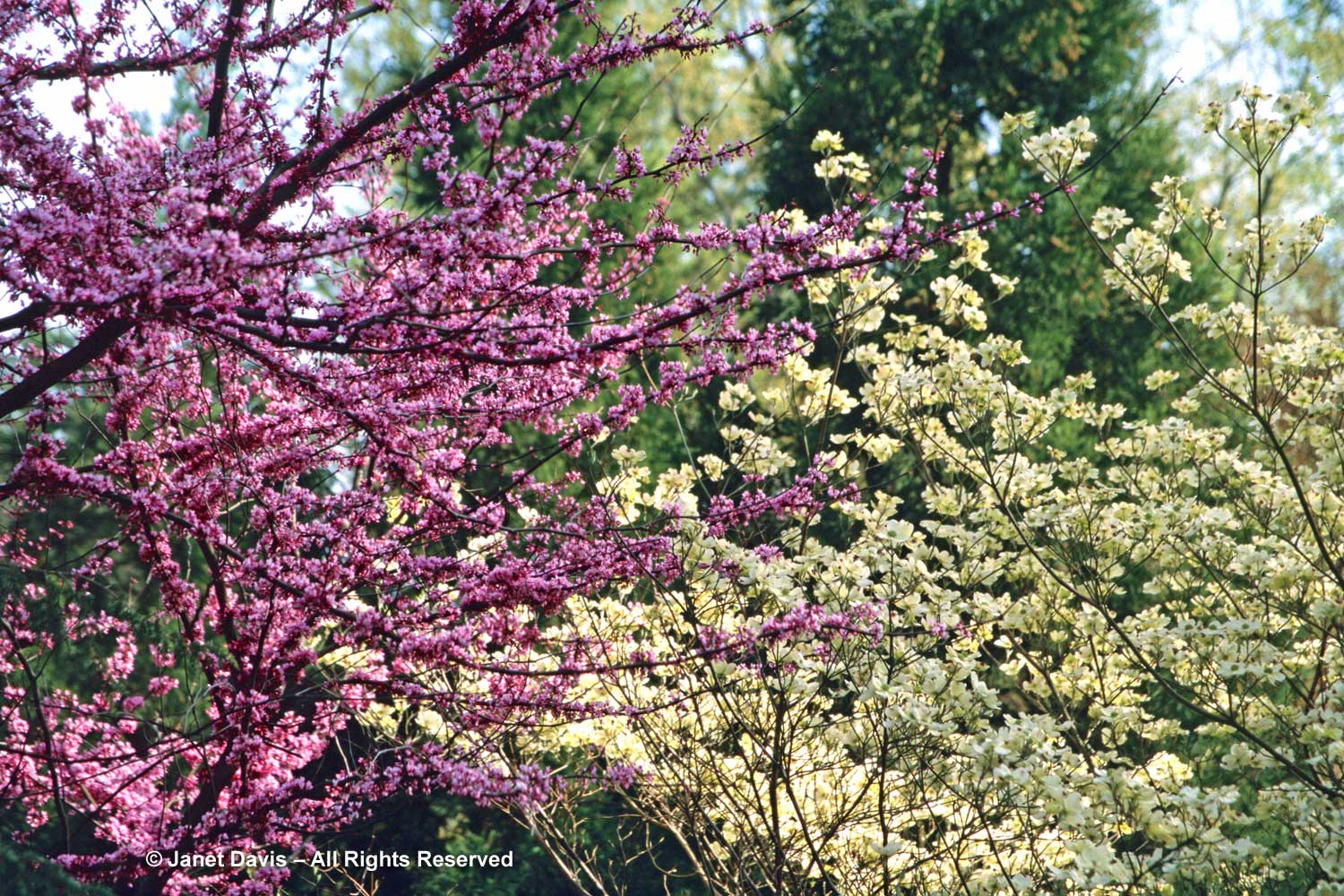
In my second blog looking at trees native to eastern North America, I’m focusing on a crowd favourite: eastern redbud, Cercis canadensis (as well as a few of its overseas cousins). One of my great botanical thrills was driving through North Carolina in early spring 2003 and seeing the spectacular combination of flowering dogwood (Cornus florida) with redbud in the woods along the highway. This photo from my slide film days shows these two native partners at their flowering peak.

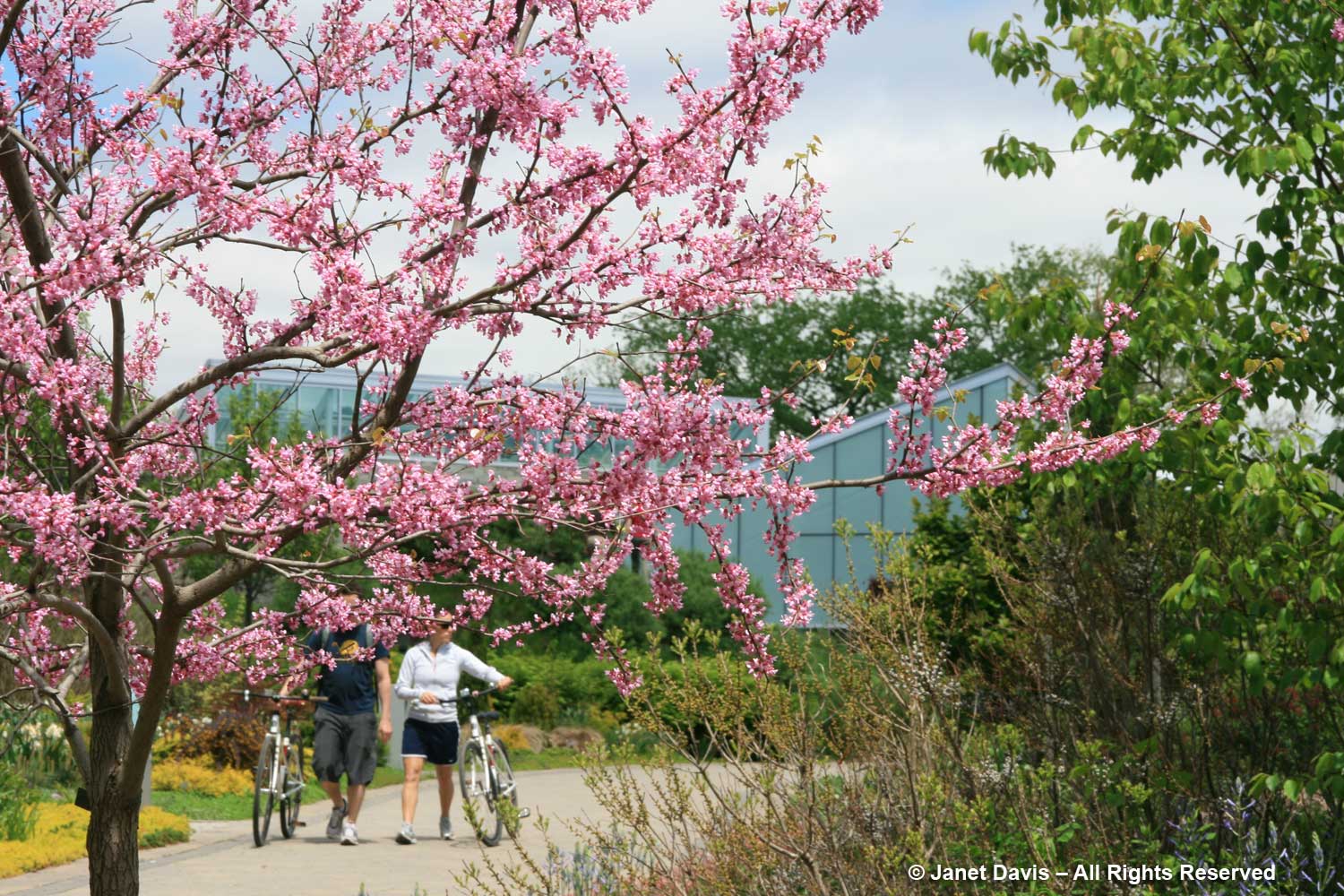
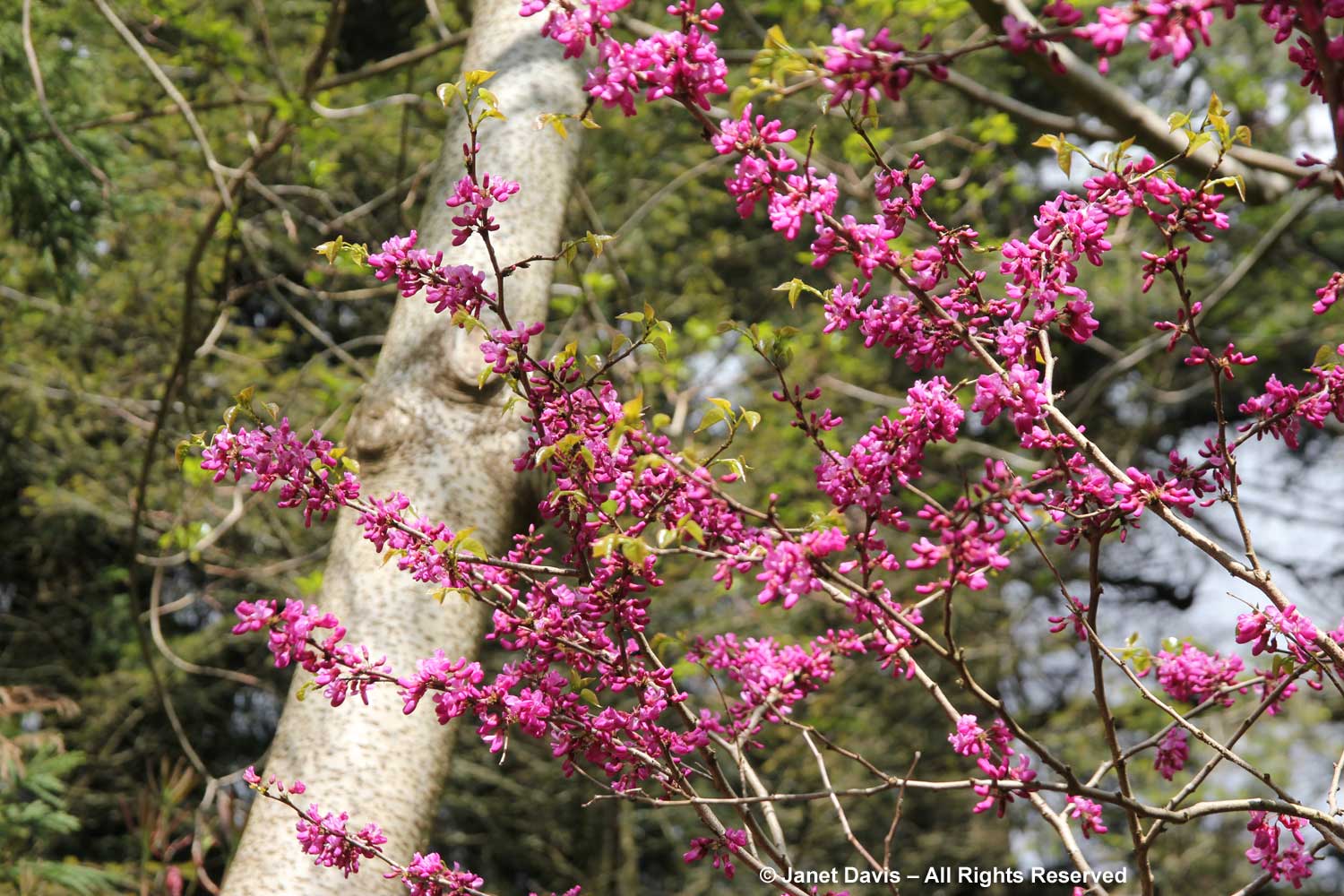
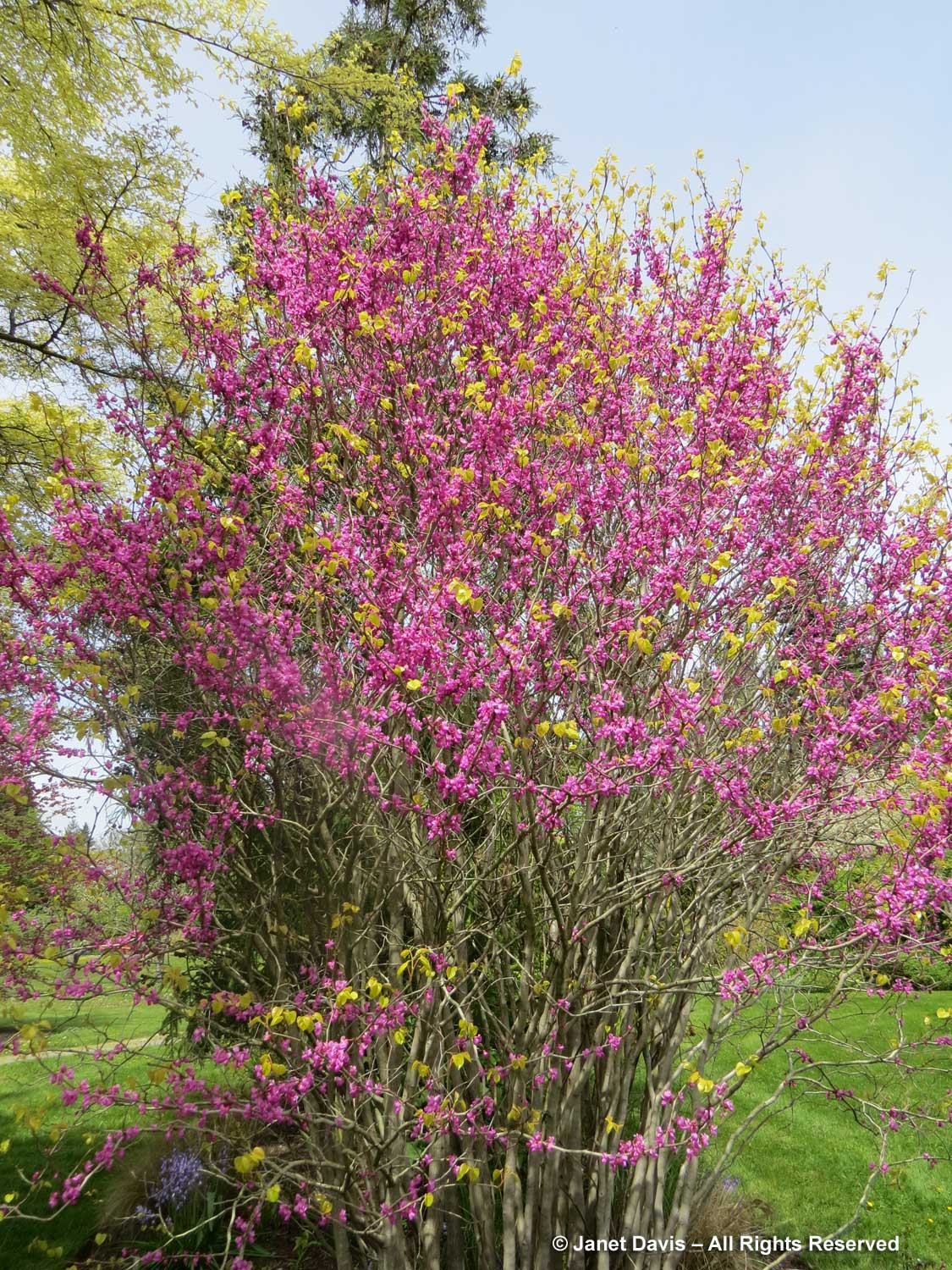
I wish I could say that eastern redbud is native to Ontario, but that is not the case unless you count a reported single sighting in 1892 by botanist John Macoun of a tree on the south shore of Pelee Island (which is itself the most southerly piece of land in Canada). Nevertheless, redbuds grow very well in gardens in southern Ontario, particularly if they’re sourced in Michigan where their hardiness is more assured than those from more southern climes. They reach about 30 ft (9 m) in height and spread. That considerable width, especially, means they’re not always the best choice for a very small garden, though they can be pruned to maintain the desired shape. I love the redbuds that grow at Toronto Botanical Garden, below.

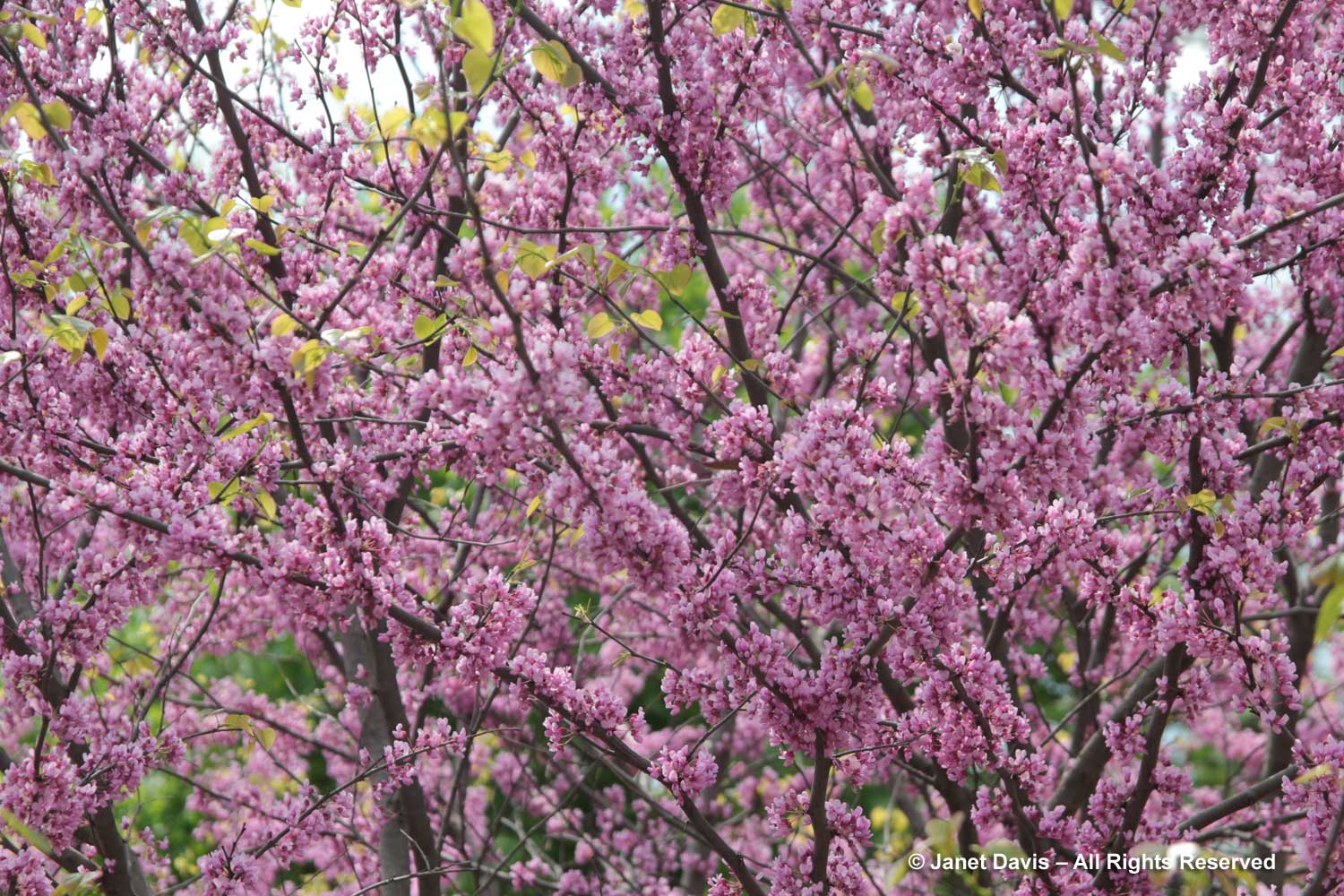
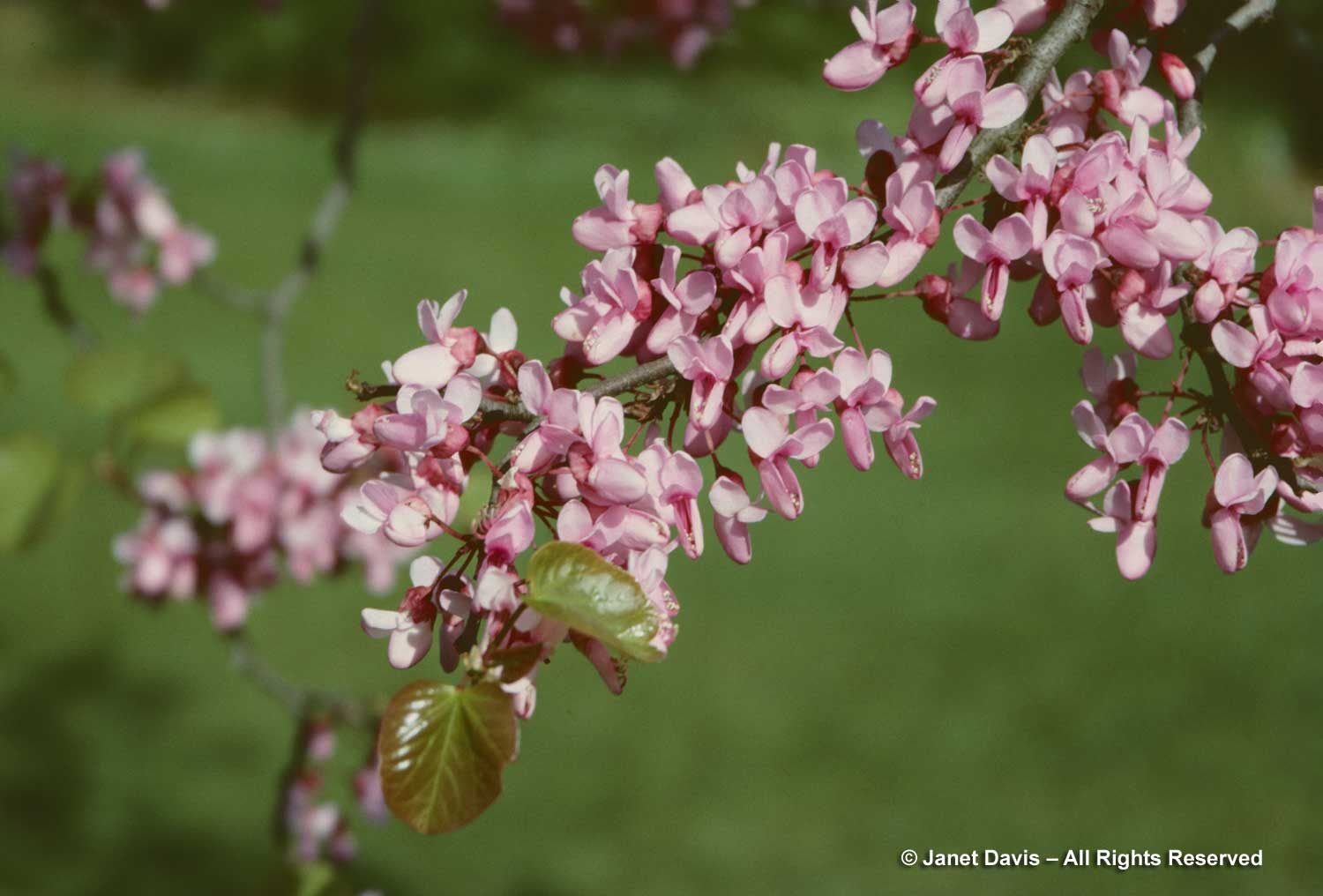
Redbud is from the legume family, Fabaceae, so its magenta-pink flowers resemble its familiar cousins like sweet pea, lupine and runner bean. In a good year, the clusters literally cloak the branches. Like many other legumes, the flowers are ‘papilionaceous’, from the Latin papilion for butterfly and describing the shape of the corolla. They are also ‘cauliferous’, meaning they emerge directly from the branches before the leaves are produced. But unlike many other legumes which bear compound leaves, redbud leaves are simple and heart-shaped.

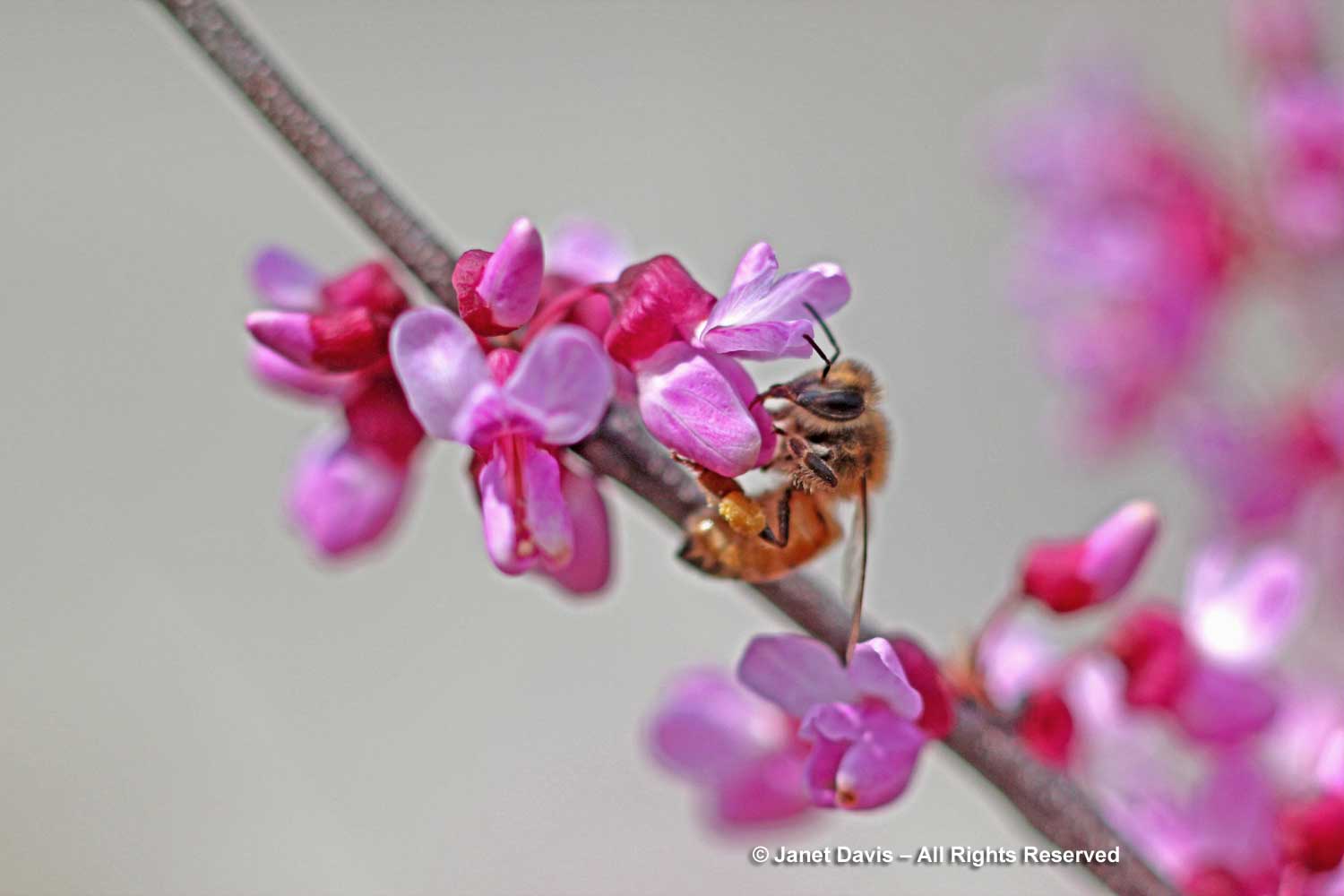
Redbud flowers are edible, rich in Vitamin C and especially good in salads. According to Mother Earth News, they “have a delicious flavor that is like a green bean with a lemony aftertaste”. They are also excellent sources of nectar and pollen for early bees, and used by native bees like this cellophane bee (Colletes inaequalis) in Toronto…..
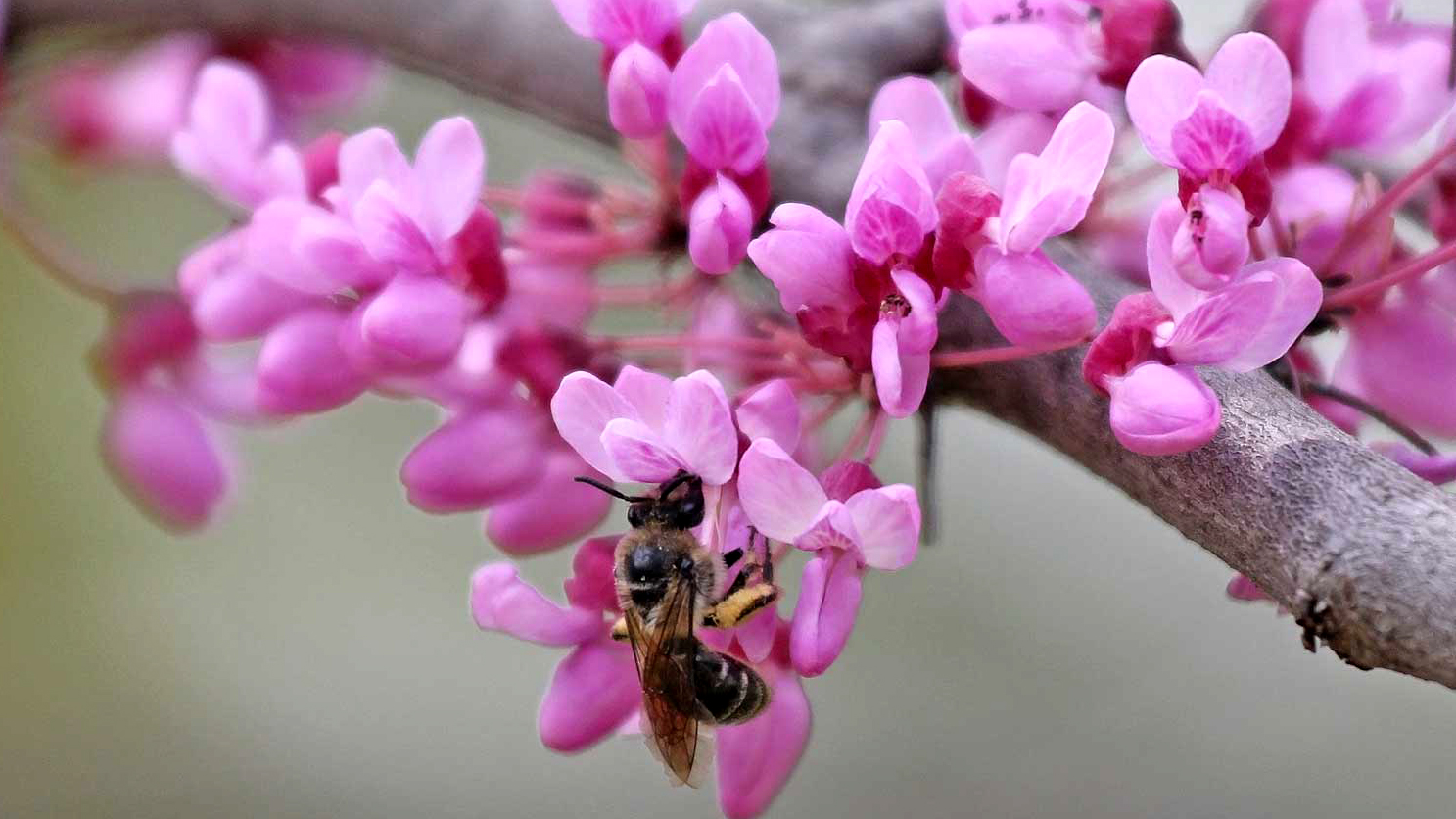

…. and also honey bees (Apis mellifera), provided temperatures are warm enough for them to fly. This one was near the hives at the Toronto Botanical Garden.

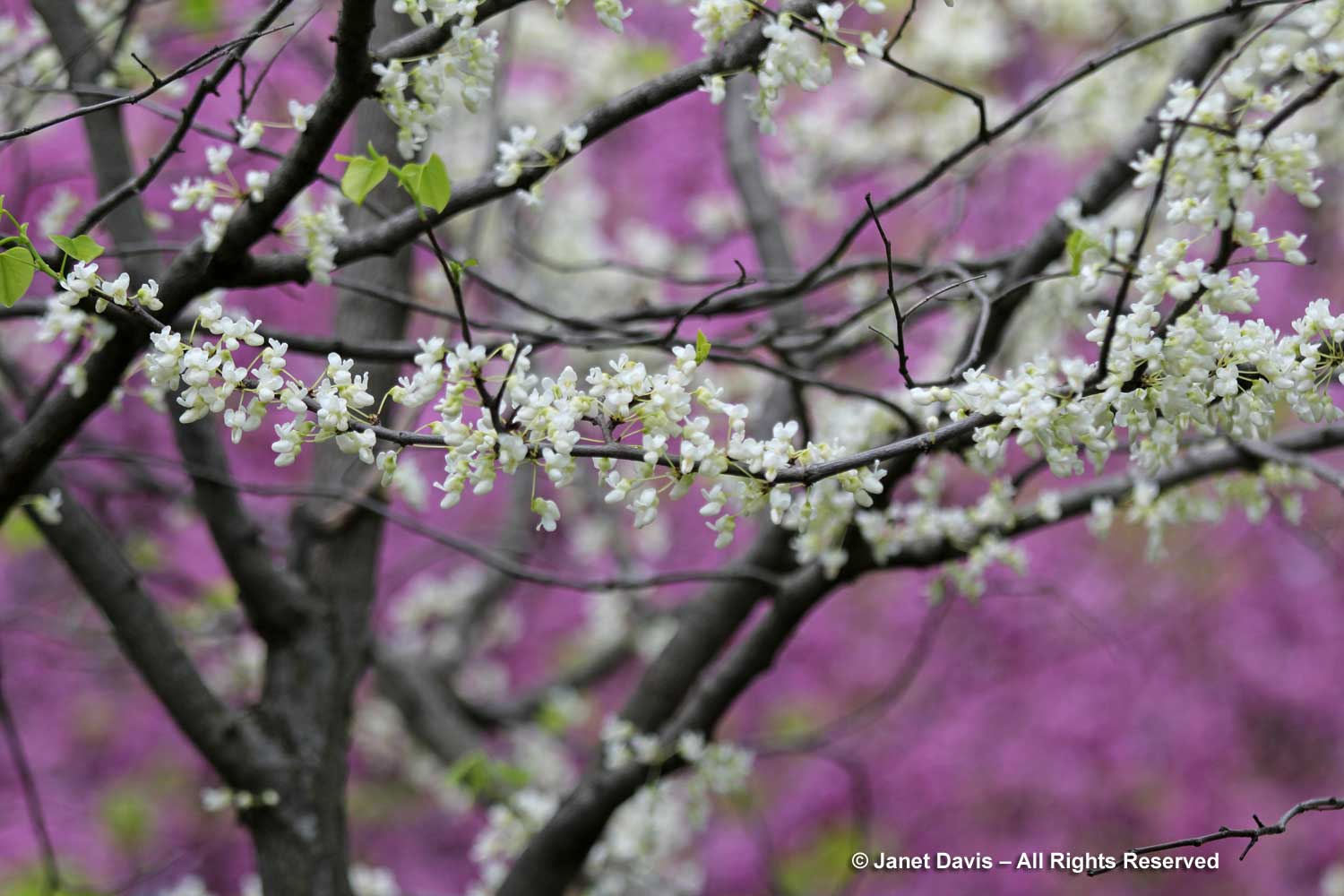
There is a white-flowered form (C. canadensis f. alba) which looks especially beautiful when planted amidst pink-flowered redbuds.

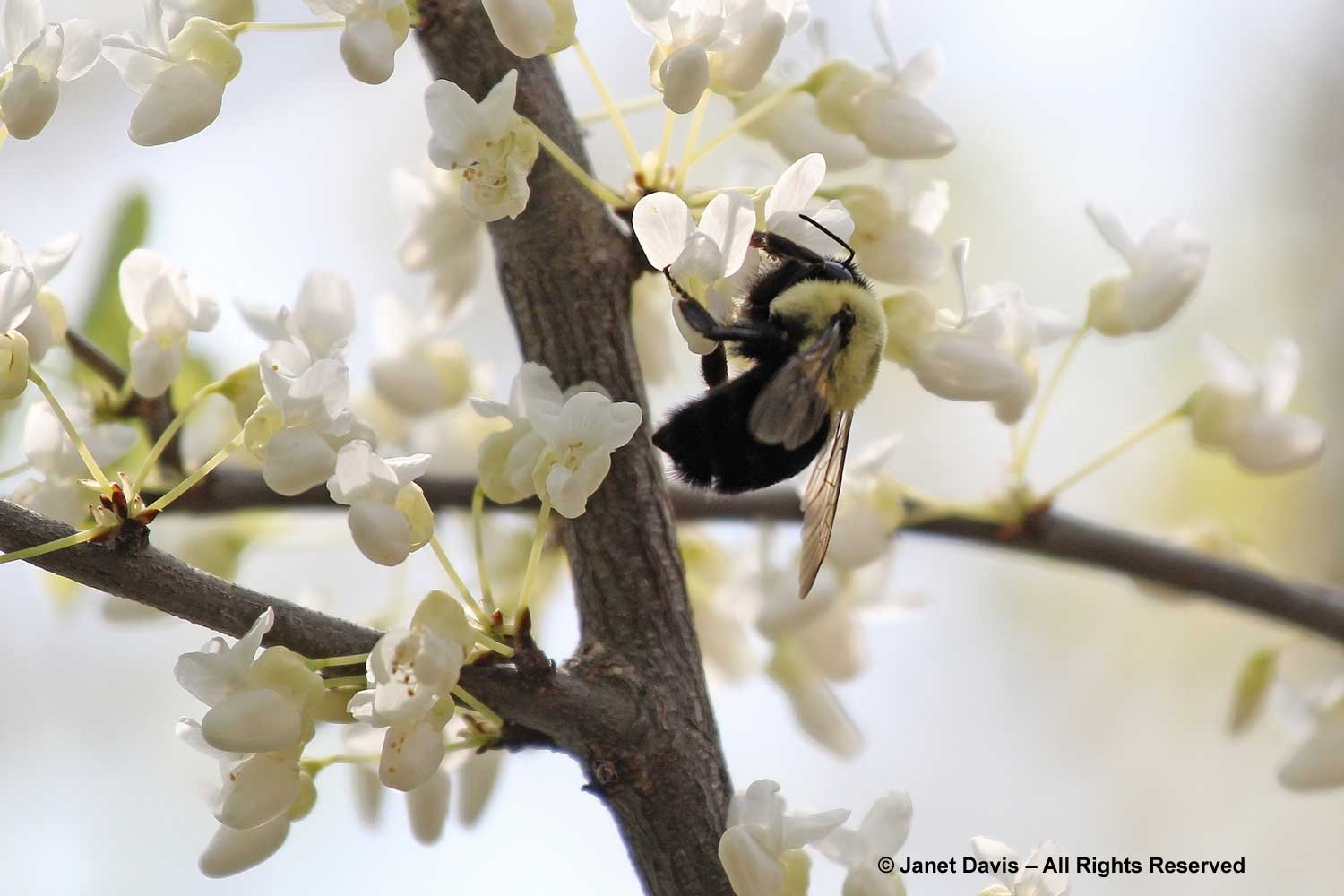
It is also popular with bees, like this bumble bee queen.

At the Toronto Botanical Garden, there is a lovely raised copse of assorted redbuds underplanted with spring bulbs.
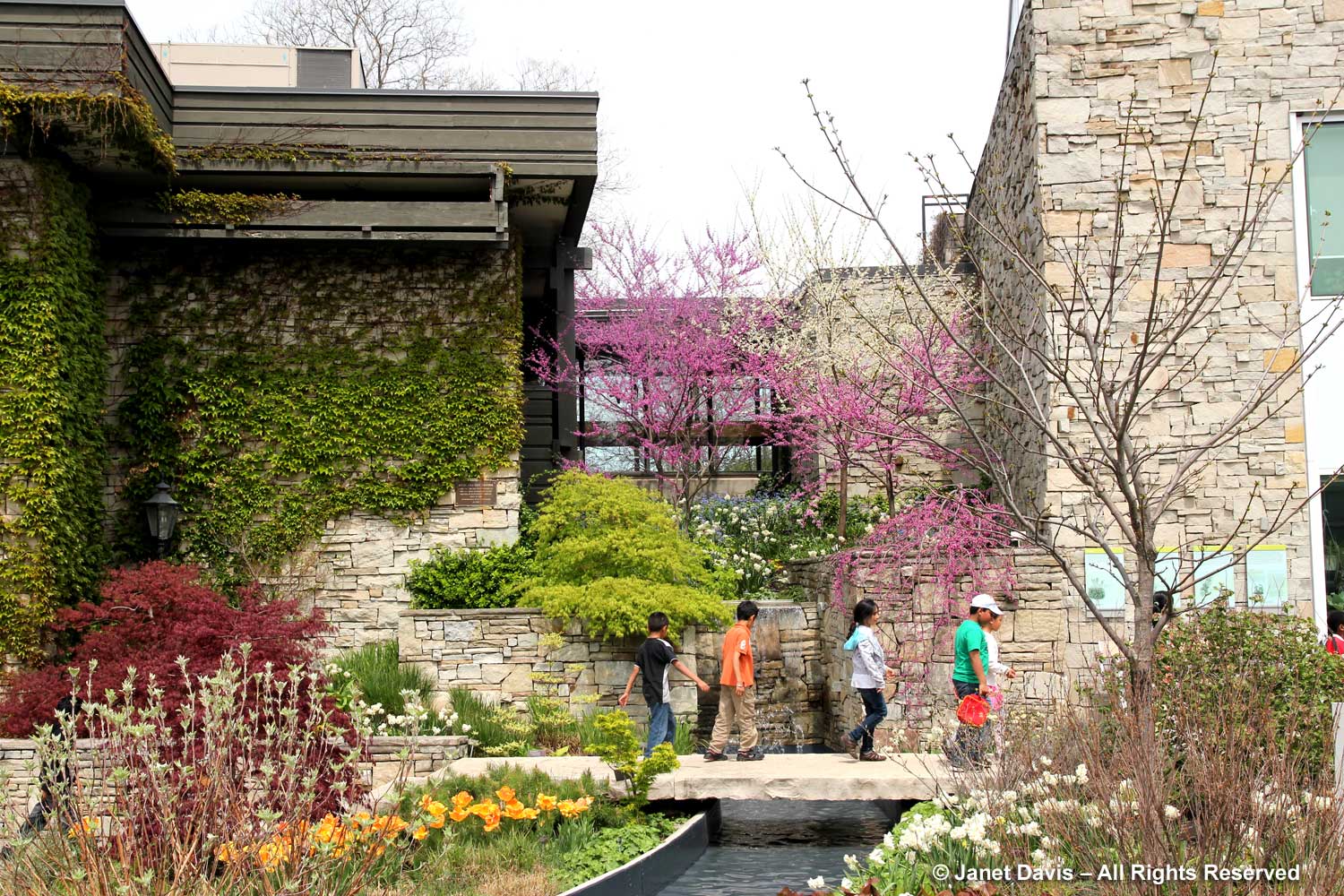

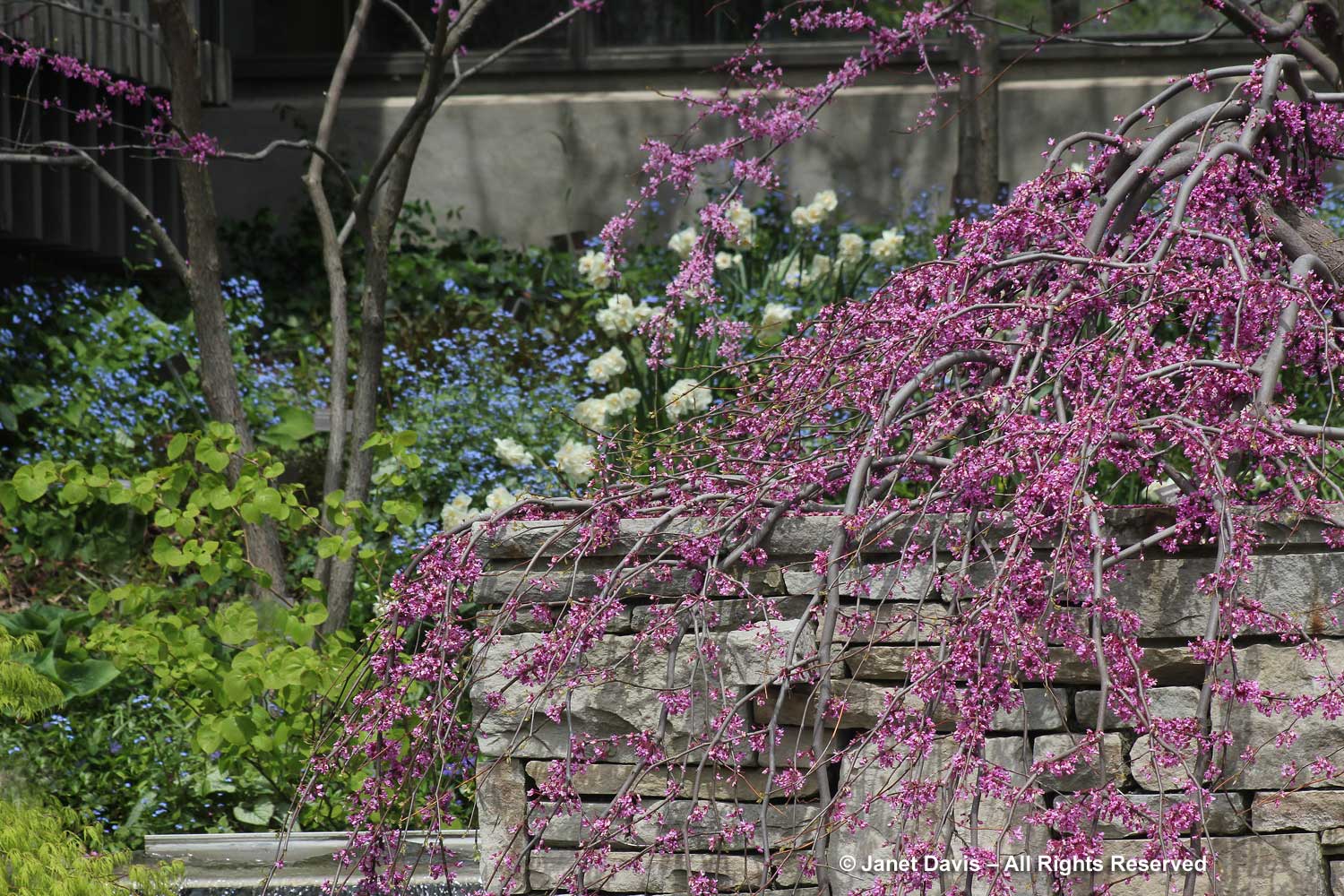
Cascading over the stone wall in the photo above is C. canadensis ‘Covey’ or Lavender Twist™, a small, weeping eastern redbud found in Cornelia Covey’s garden in Westfield, NY in the 1960s and propagated and patented by Tim Brotzman. It is perfectly placed in this garden, below.

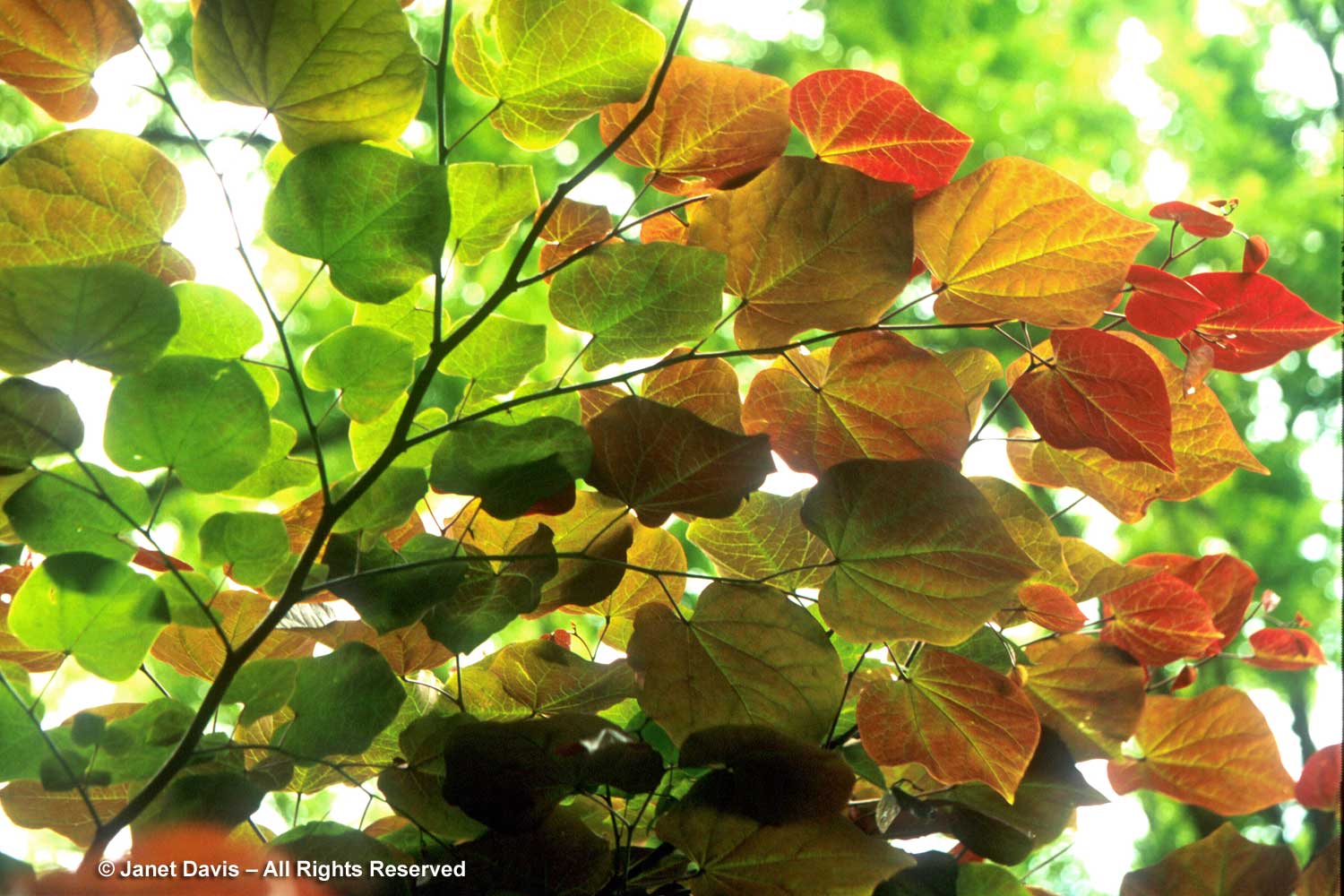
There are several good cultivars of eastern redbud, if your taste runs to coloured foliage. ‘Forest Pansy’ is one of the oldest. Found originally in 1947 at Forest Nursery in McMinnville, Tennessee, it was patented in 1965. In spring and early summer it is a rich, wine-red, but I love standing under it later in the season when it has lost some of its red anthocyanins pigments and takes on this mottled look.

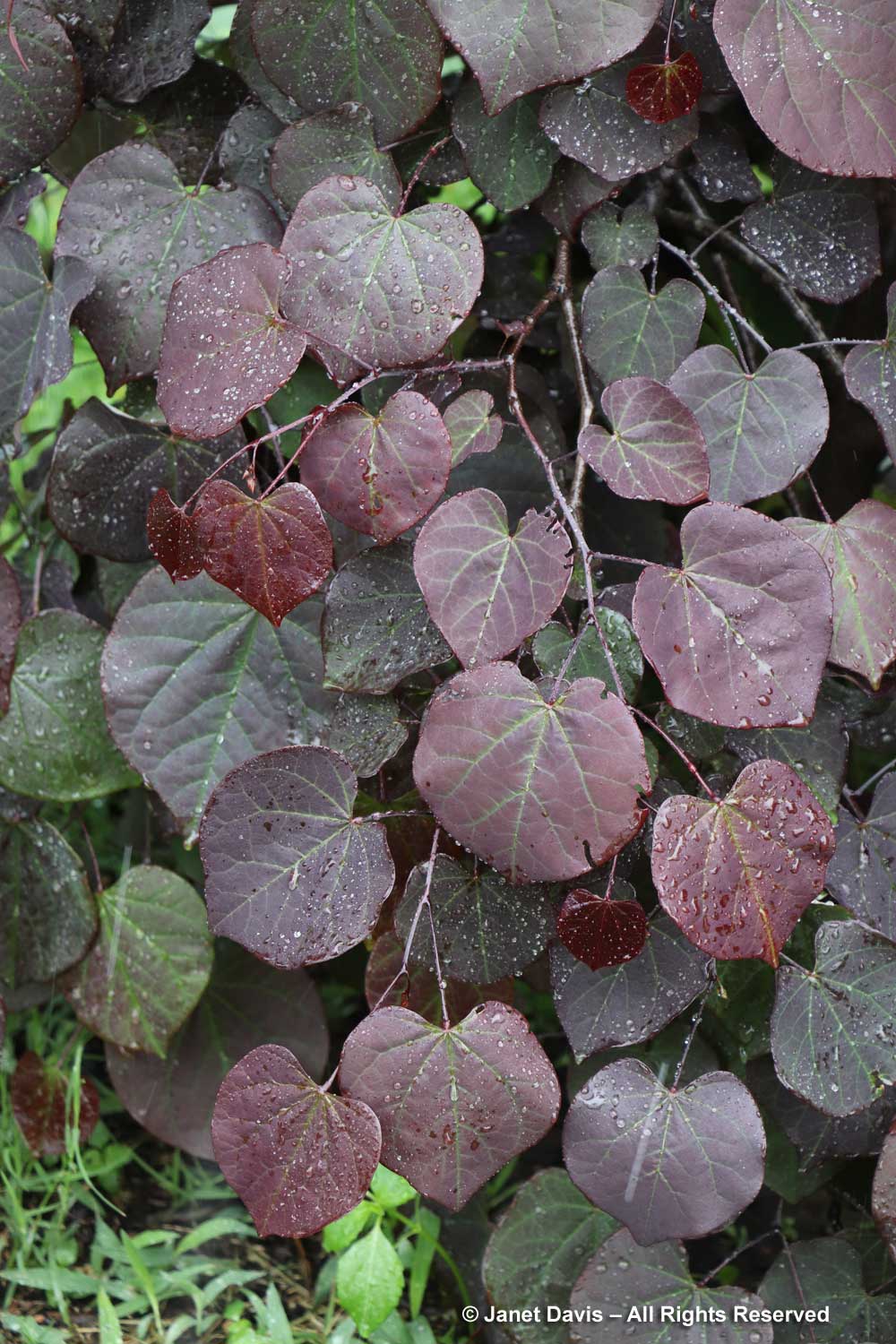
‘Ruby Falls’, below, is a cross between ‘Covey’ and ‘Forest Pansy’. It’s a small tree, 6 ft (2 m) tall and 4 ft (1.3 m) wide.

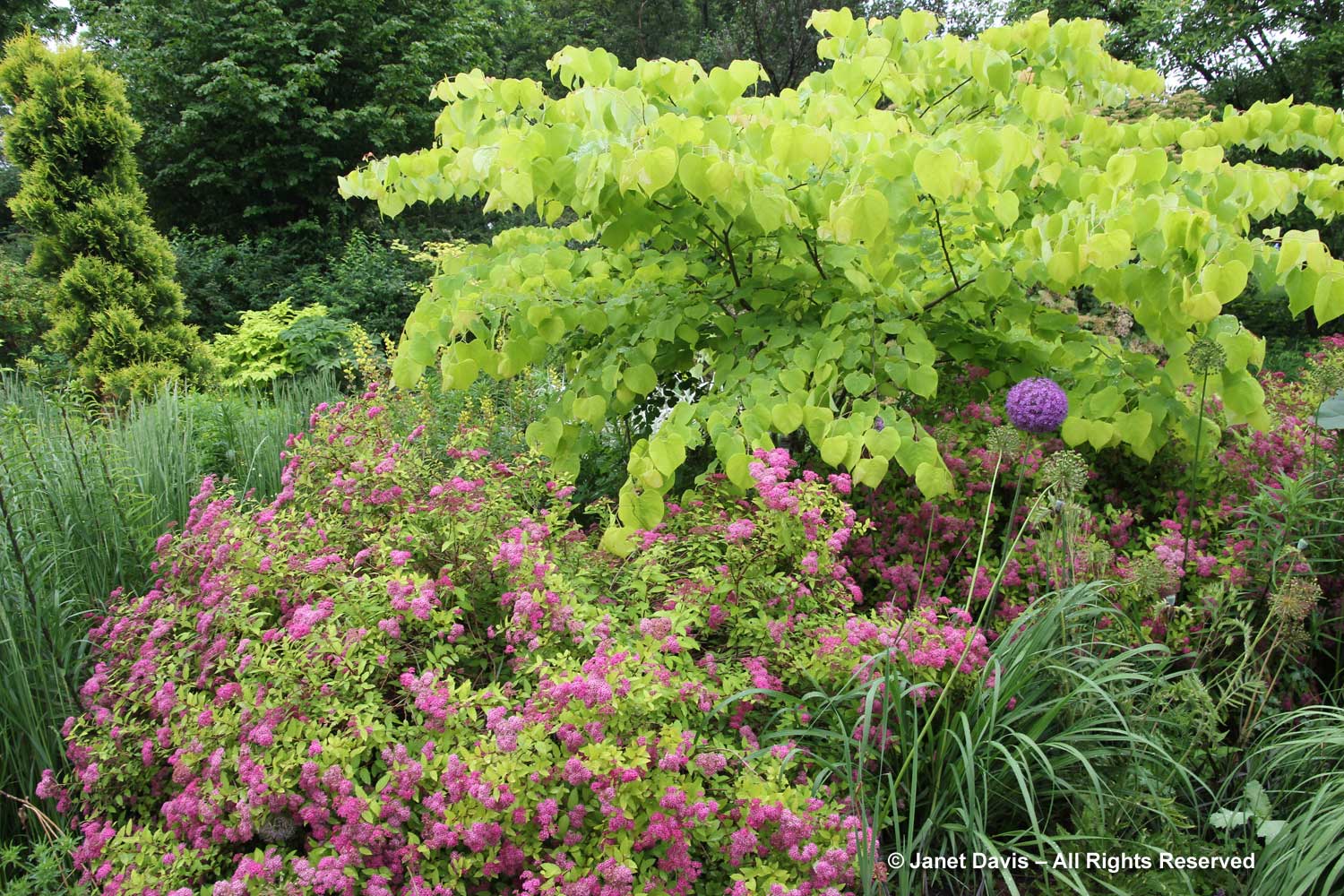
I photographed luminous C. canadensis ‘Hearts of Gold’ at wonderful Chanticleer Garden near Philadelphia, my very favourite garden in the U.S. (If you haven’t been to Chanticleer, have a read of my 2-part blog starting here.) ‘Hearts of Gold’ with its large, chartreuse-yellow leaves was discovered in spring 2002 in Greensboro, N. Carolina by Jon Roethling (now director of Reynolda Gardens in Winston-Salem).

When I was visiting the United States Botanic Garden in Washington DC in June 2017, I was entranced by the beautiful foliage of Cercis canadensis ‘JN2’ or Rising Sun™, below. Long past flowering, I was treated to the sight of apricot-orange emerging leaves, changing to yellow, then chartreuse, then dark green. With a 12-ft (3.6m) height and 8-ft (2.4m) spread, this redbud was found in 2006 and introduced by Ray and Cindy Jackson of Jackson Nursery in Belvedere, TN.
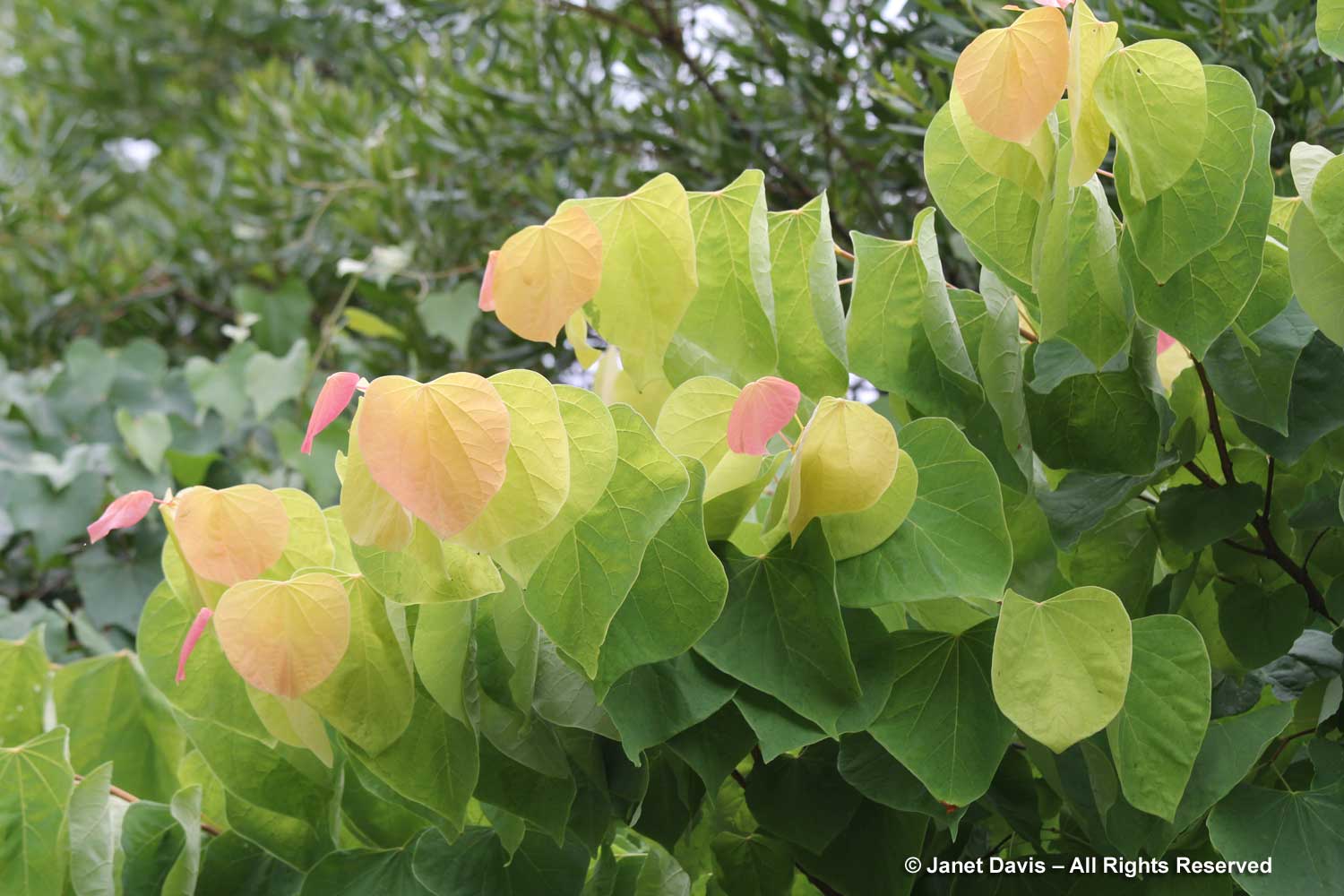

The abundant fruit pods of redbuds are called ‘siliques’, from the Latin word siliqua, meaning a pod or husk. It is defined as a long dry, fruit (seed capsule) with its length measuring more than twice the width, consisting of two fused carpels that separate when ripe. I found the eastern redbud, below, loaded with seedpods in Toronto’s Mount Pleasant Cemetery one August.
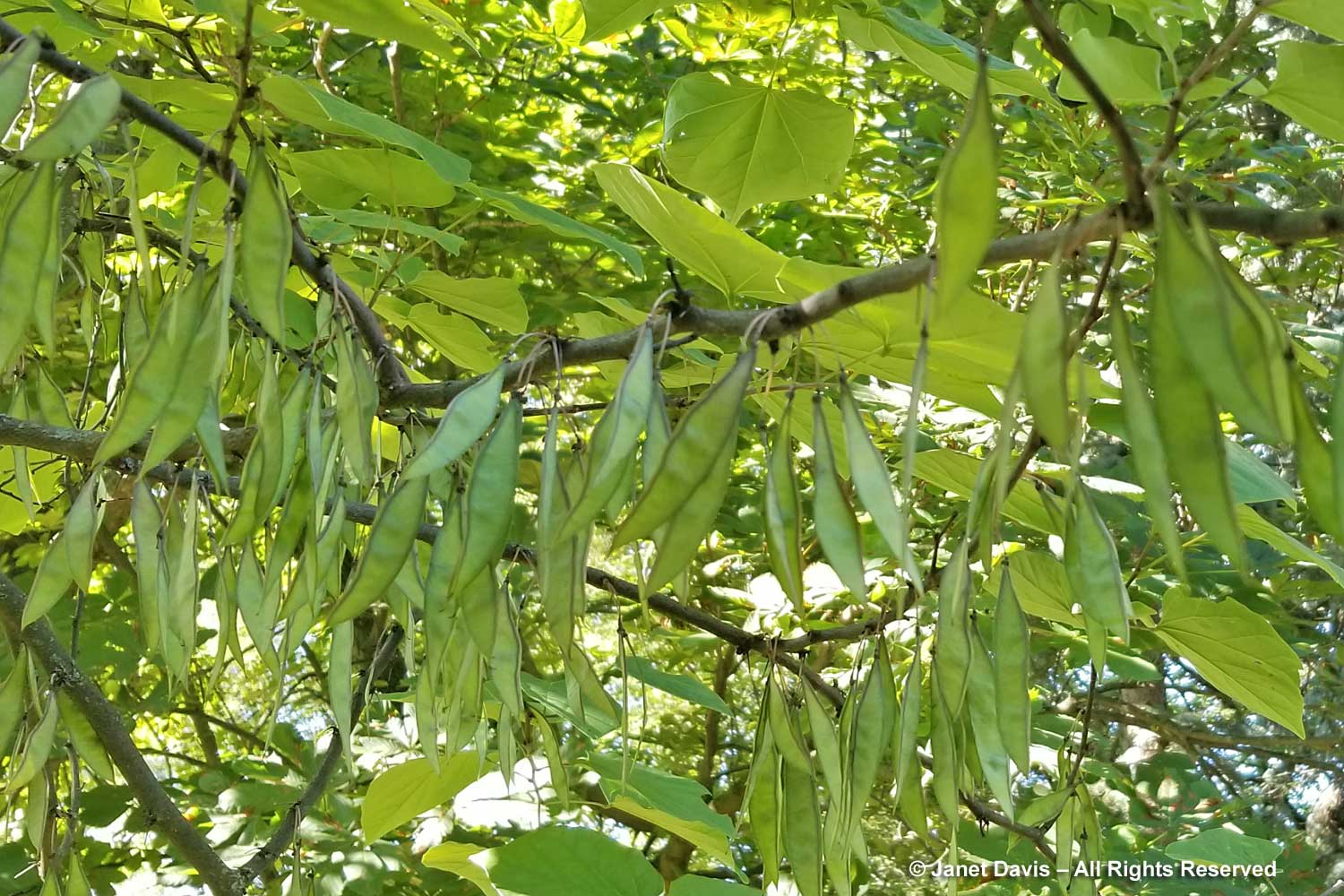

This is that same tree in the cemetery in autumn, showing off its bright yellow fall colour.
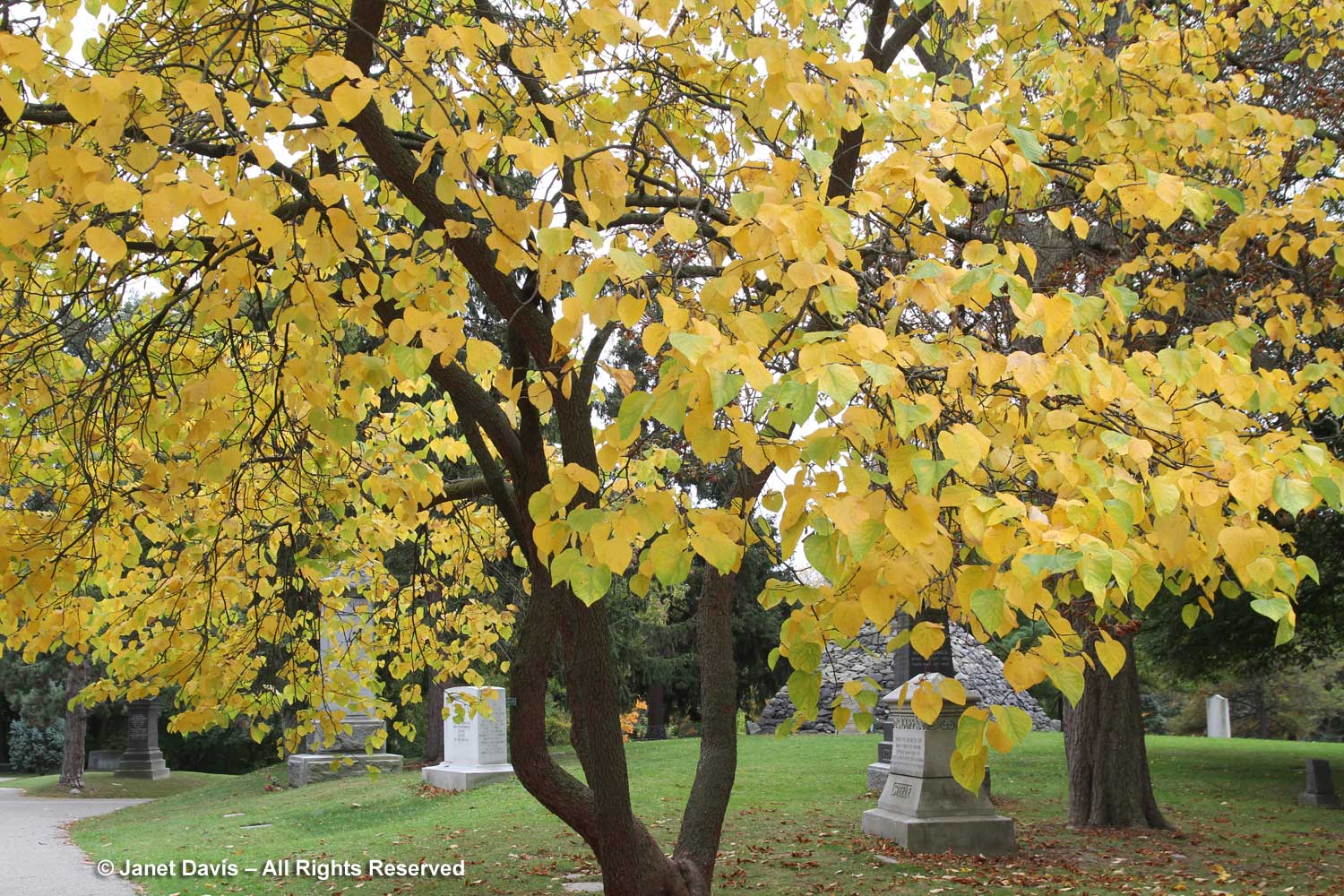
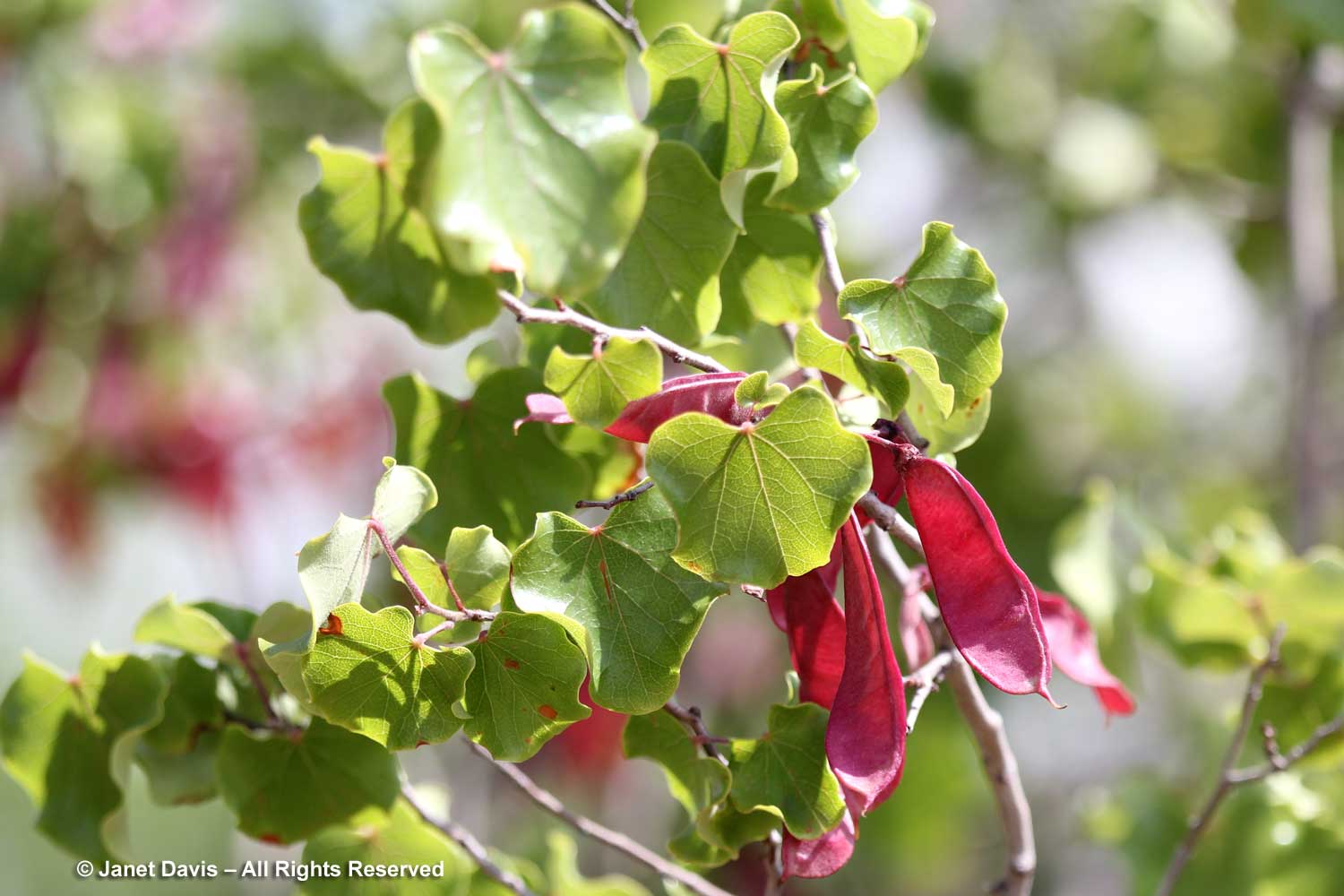
There are two other varieties of North American redbud: Texas redbud, C. canadensis var. texensis and Mexican redbud, C. canadensis var. mexicana. I found the latter with its frilly, circular leaves and deep-pink ‘siliques’ at the University of California Berkeley Botanical Garden.

The native European redbud is Cercis siliquastrum from the Mediterranean, its Latin specific epithet chosen by Linnaeus to denote those siliqua. When I was on my wonderful botanical tour of Greece in autumn 2019, I found redbuds putting out a second flowering in Thermopylae, scene of the historic 480 BC battle between the Persians and Spartans.
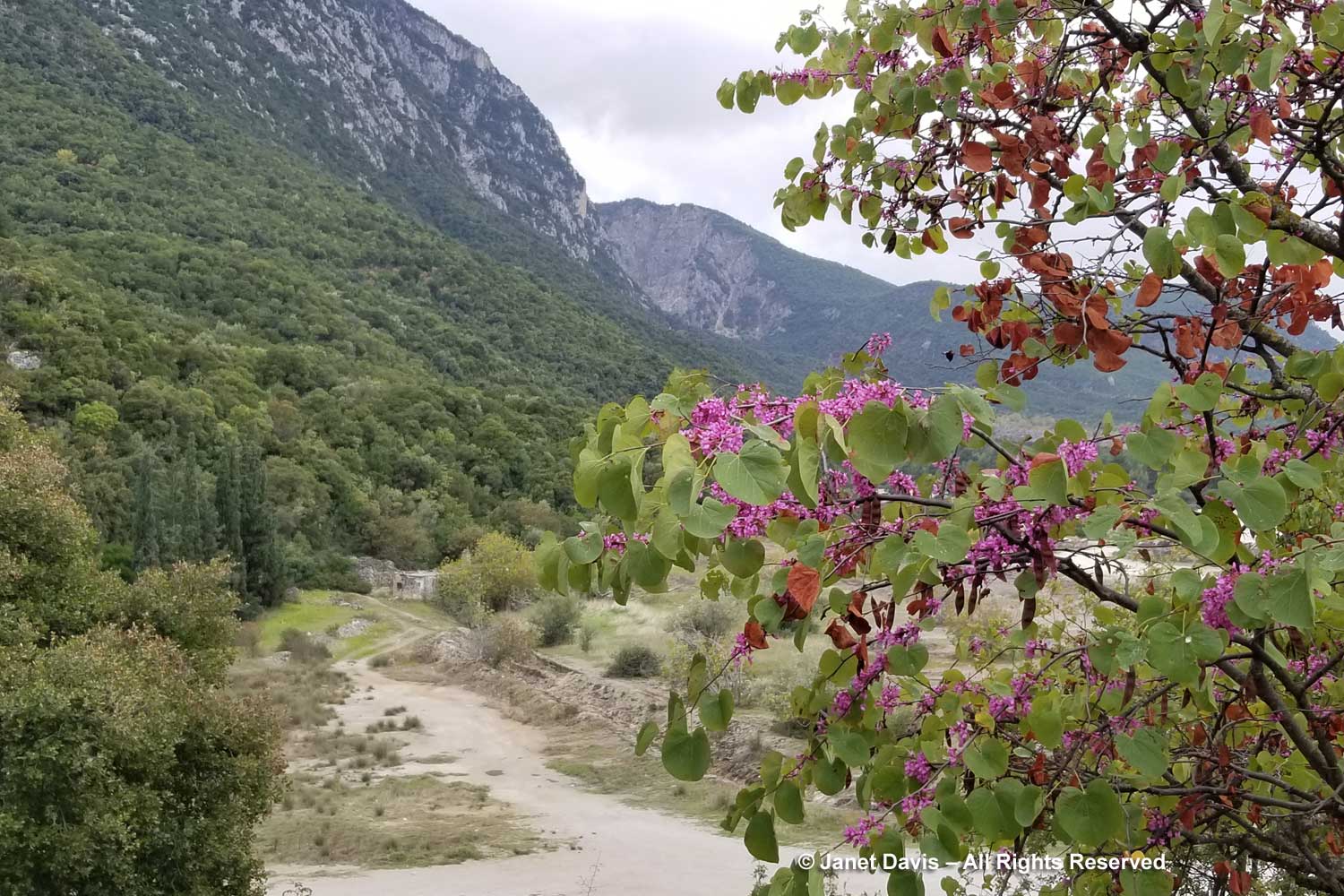

And I found it flowering in the pouring rain in the countryside in Attica.
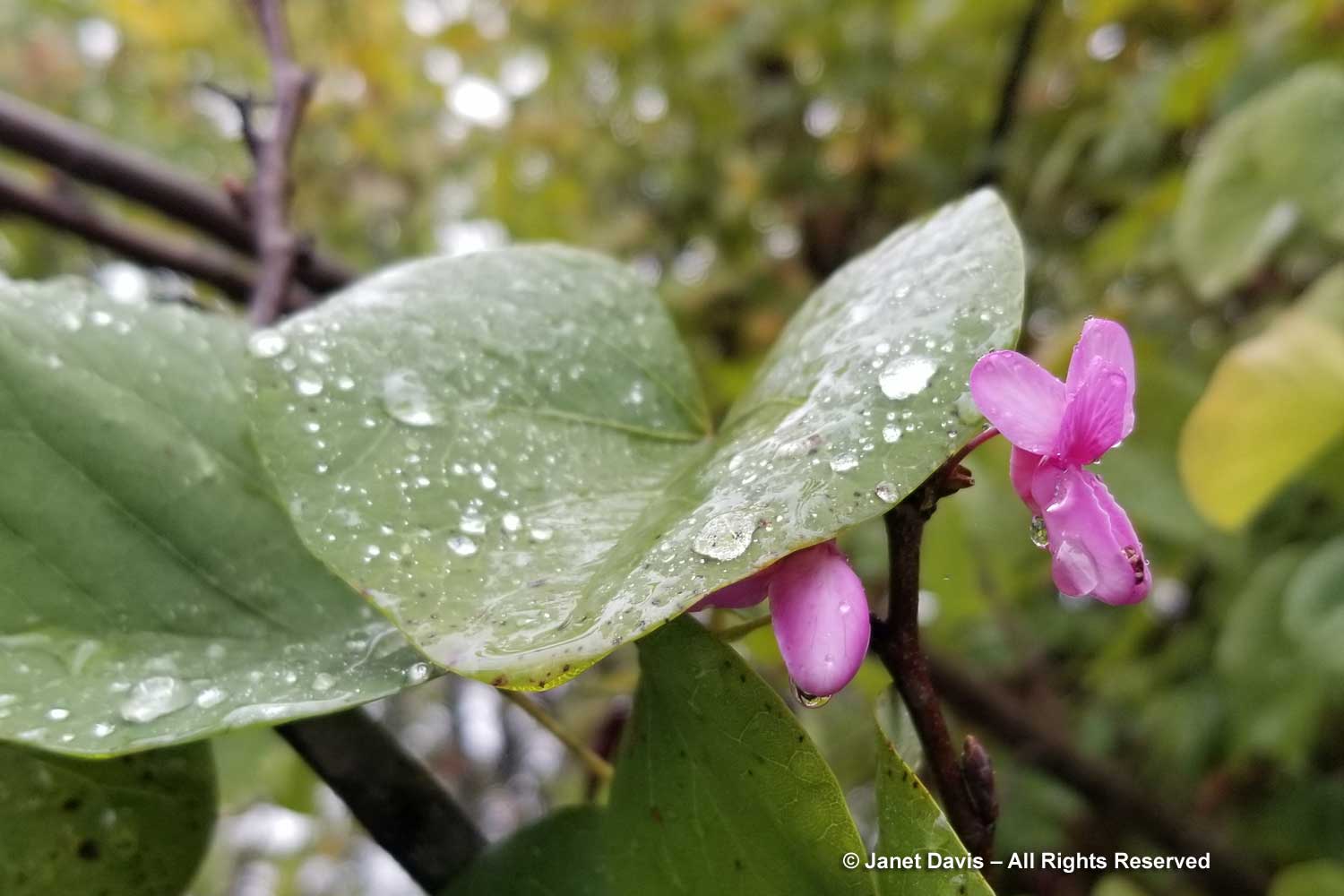

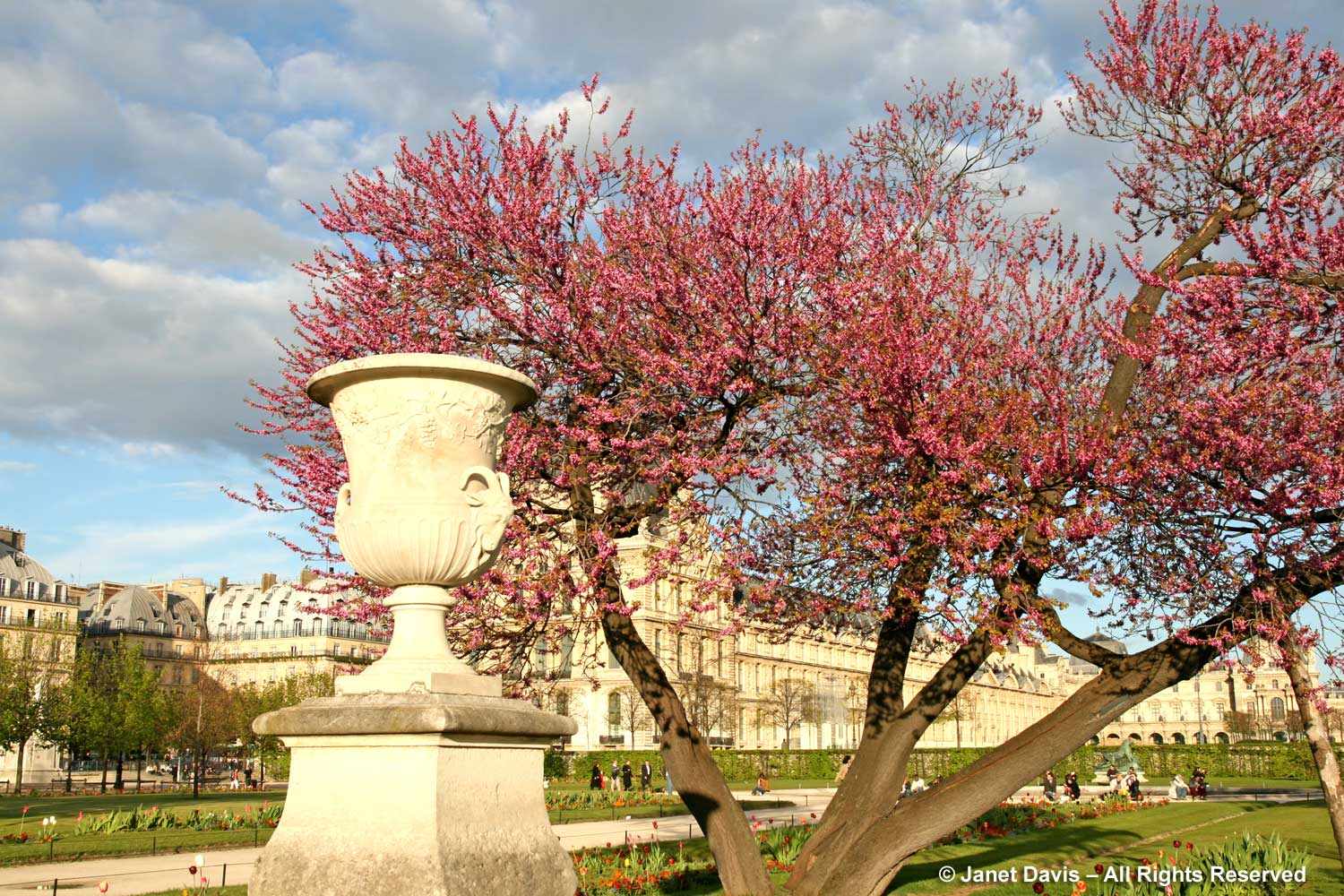
On a long-ago trip to Paris, there it was in the garden of the Tuileries, below.

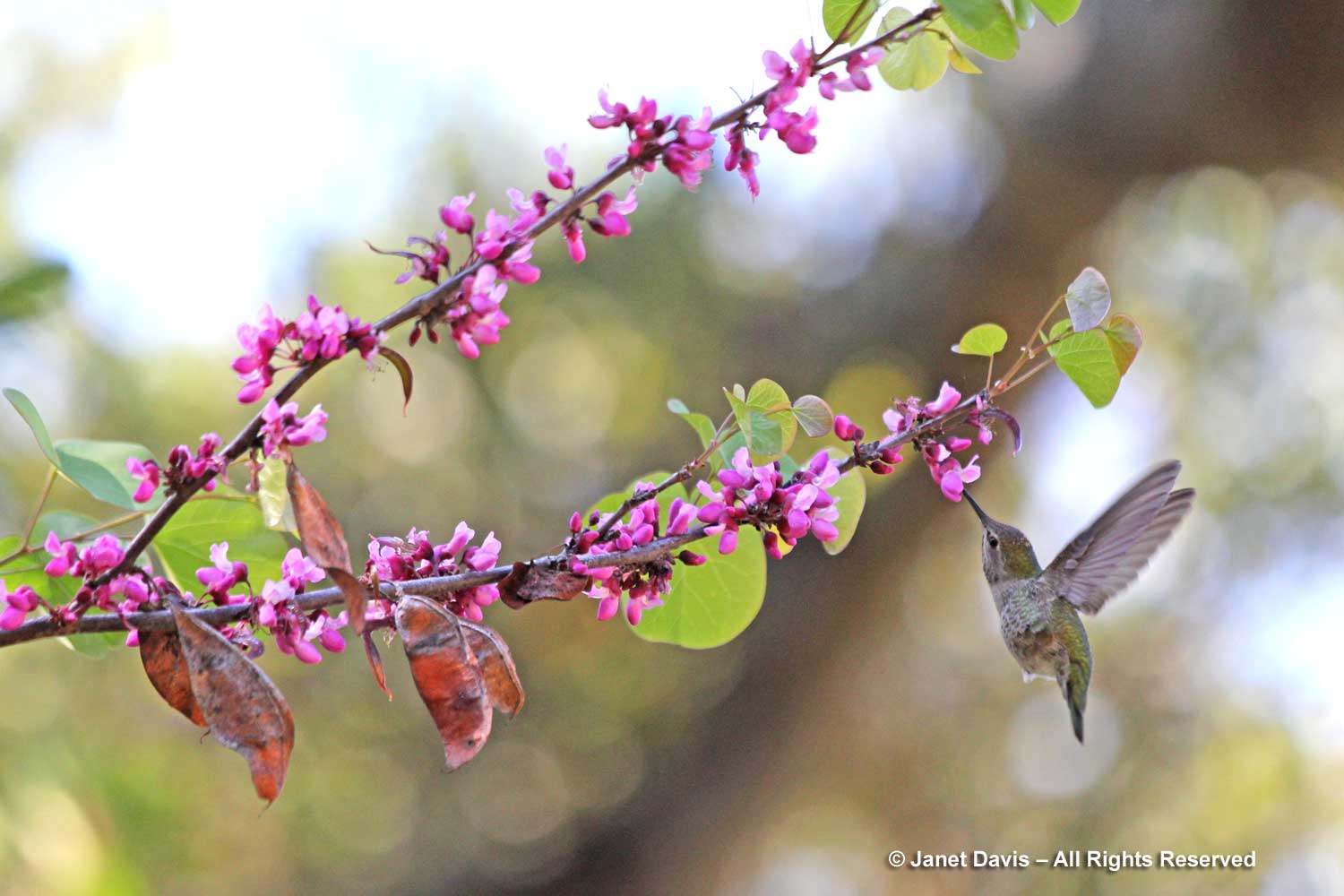
Back to North America, I was visiting the Santa Barbara Botanical Garden in March 2014 and was delighted to capture an Anna’s hummingbird (Calypte anna) nectaring in the flowers of the western redbud (Cercis occidentalis). This is usually a multi-stemmed shrub and about half the size of eastern redbud and the leaves are more round.

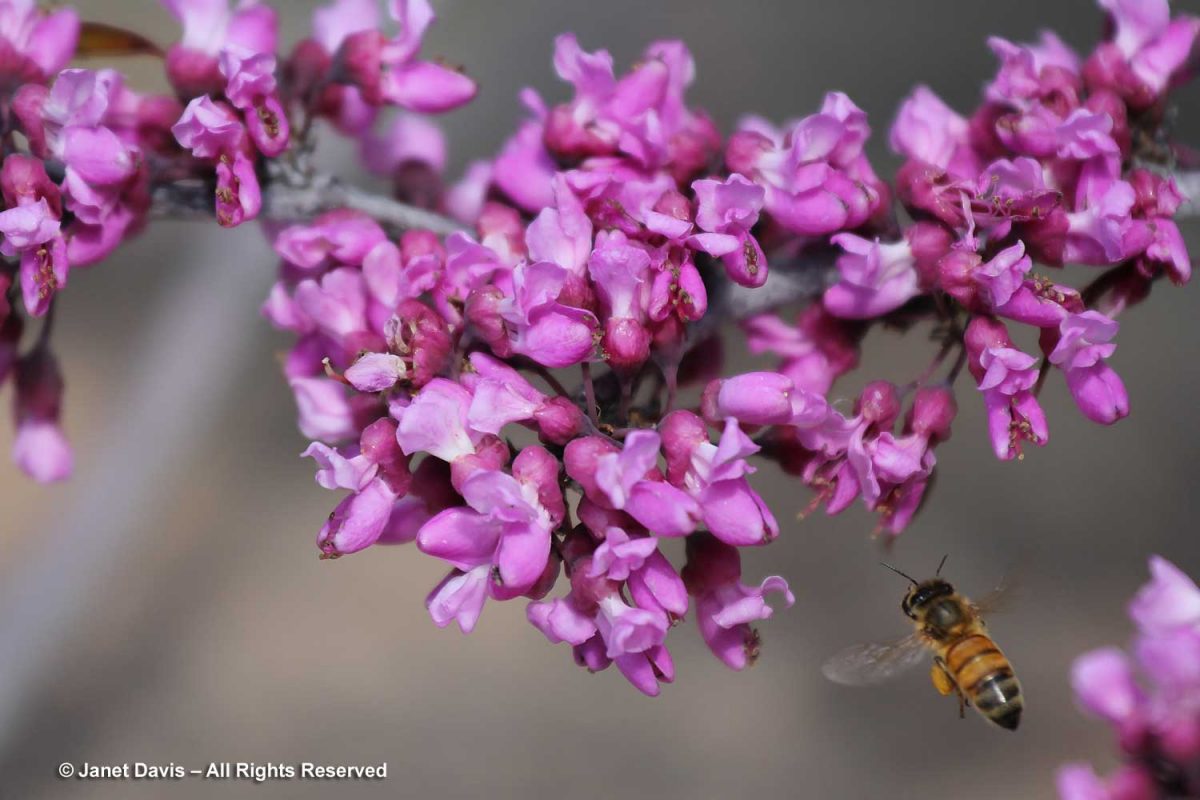
Honey bees were enjoying the western redbud flowers as well.

I found Chinese redbud (Cercis chinensis), below, at RHS Wisley in England way back in 1992. Although it is listed as much taller (49 ft or 15m) than eastern redbud, it evidently usually grows in the wild as a multi-stemmed shrub.

While visiting Van Dusen Botanical Garden in Vancouver in May 2014, I found C. chinensis ‘Avondale’ in flower in their Asian collection. A fairly small tree introduced by Duncan and Davies Nursery in Avondale, New Zealand, it grows about 10 ft (3m) tall x 6 ft (2m) wide.

On May 4, 2019, I photographed a dense, multi-stemmed shrub labelled Cercis gigantea at the late plantswoman Francisca Darts’s garden, Darts Hill Garden Park in Surrey, B.C. (below). In ‘Trees and Shrubs Online’, authors Ross Bayton and John Grimshaw write: “This species is enigmatic. There is no record of the publication of the name in either the International Plant Names Index (www.ipni.org) or the International Legume Database & Information Service (www.ildis.org), and it is not described in the (currently draft) Flora of China treatment, and yet it appears in the catalogues of several nurseries and botanic gardens…. The limited information available via the internet suggests that C. gigantea is similar to C. chinensis but has much larger leaves and a more vigorous growth rate. Plants originating from seed collected as C. chinensis during the 1980 Sino-American Botanical Expedition ( western Hubei) were later identified as C. gigantea by Dr Ted Dudley at the US National Arboretum…. supporting this supposition of similarity between the two taxa.”

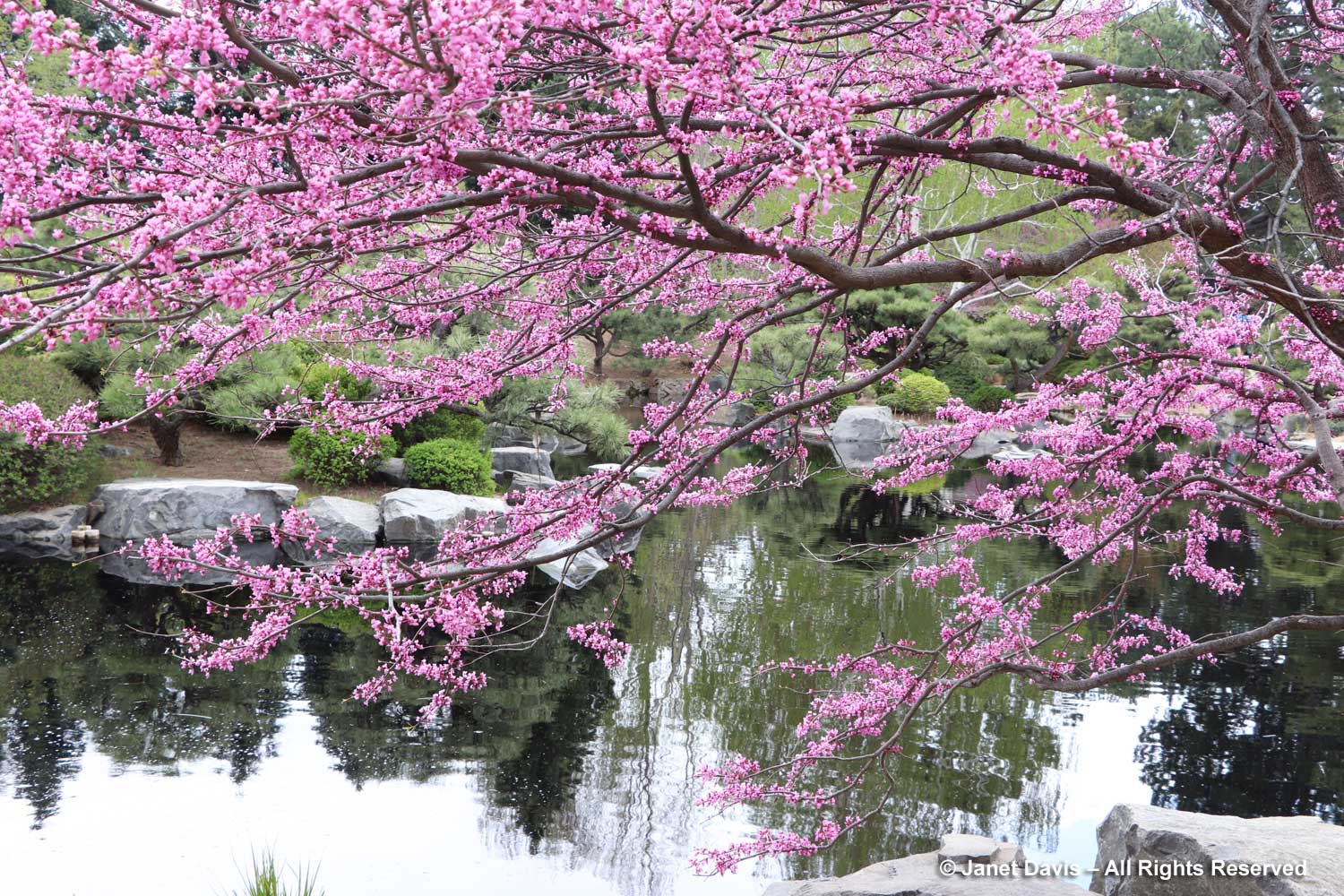
I will leave you with my photo of eastern redbud in the Japanese Garden at Denver Botanic Gardens from April 28, 2018, and the words of naturalist Donald Culross Peattie — always the romantic — from his ‘A Natural History of Trees of Eastern and Central North America’. “When the redbud flowers, the still leafless deciduous woods display its charms down every vista; it shines in the somber little groves of Scrub Pine; it troops up the foothills of the Appalachians; it steps delicately down towards swampy ground in the coastal plain, flaunts its charms beside the red clay wood roads and along the old rail fences of the piedmont. Inconspicuous in summer and winter, Redbud shows us in spring how common it is.”


Beautiful pictures!
Do you think it is one of the plants that mutates easily, ie sports are readily found if you look for them?
Martine – I don’t know what’s involved in finding sports, or how long it takes to develop a fully gold-leaved form, or one with dark foliage. And since they aren’t native here, I don’t know how I would. I just appreciate the species when it flowers!
Janet,
Lovely overview of a favorite of mine such a graceful and alluring Beauty in all its seasonal manifestations. Also appreciate your several references to where we lie
with Putin the crumbling man knows nothing of Beauty
Thank you Maggie. I must say it feels surreal to be trying to do normal things while the world bleeds.
Keep the trees coming, I loved this and the last on Liriodendron tulipifera, great work.
Thanks, Andrew. A short series to tide me over until spring warms the air (here!)
I am also enjoying your tree series. I have a fairly young tulip tree in my city Blvd and I covet having a redbud. I had no idea of the varieties and that the flowers are edible! Thank you!
You’re welcome, Jessica. I wish I’d planted a tulip tree many years ago!
Thank you for this! I’ve always loved these trees, but I didn’t know there were so many species (and varieties) — or that the flowers are edible. I’m about to plant a couple in my back yard. I’m in Zone 10b (San Diego) and they do well here, though you have to water them (supplemental irrigation). Interestingly, I think most of the ones I see around town are the eastern form.
That is interesting, Amy. The leaves would be the distinguishing characteristic. Good luck!
As always, Janet, your photographs are stunning and your information deep. I bask in your glory! No, really.
Helen, that is very kind of you. But I wish we could both bask in spring sunshine! (I know.. don’t complain… we’re lucky, etc. etc.)